Analysis of Pesticides in Baby Food Using Triple-Quadrupole GC–MS-MS
Contamination of food products with pesticides is a growing concern because of recognized damaging health effects. This concern is particularly acute for baby foods because of the vulnerability of young children to harmful effects of synthetic chemicals, particularly pesticides. This application note presents results for analysis of trace levels of 24 organophosphorus (OP) pesticides in baby foods using the Shimadzu GCMS-TQ8030 triple quadrupole GC–MS-MS.
Contamination of food products with pesticides is a growing concern because of recognized damaging health effects. This concern is particularly acute for baby foods because of the vulnerability of young children to harmful effects of synthetic chemicals, particularly pesticides. This application note presents results for analysis of trace levels of 24 organophosphorus (OP) pesticides in baby foods using the Shimadzu GCMS-TQ8030 triple quadrupole GC–MS-MS.
GC–MS has historically been used extensively to quantify trace-level pesticides in food matrices. The most significant challenges have been matrix interference and achievement of meaningful health-based detection limits for the compounds of interest. The QuEChERS sample preparation method has helped to overcome some of the problems of matrix interference, and commercialization of QuEChERS "kits" has promoted widespread screening of foodstuffs for trace pesticides. But significant interferences still present a formidable problem for analysis of trace-level pesticides in foods.
Triple quadrupole GC–MS-MS has emerged as the technique of choice for analysis of trace-level contaminants in complex matrices. Operation of the GCMS-TQ8030 in the simultaneous Scan/MRM mode provides trace level analysis of the targeted pesticides, with confirmation of compound identity and detection of unknowns using the simultaneous Scan mode. A Shimadzu GCMS-TQ8030 system with highly sensitive advanced Scan/MRM scanning capabilities was used to analyze for pesticide residues in baby foods.
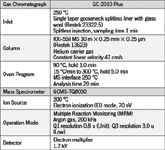
Experimental Conditions
The MRM method was developed and optimized using the Shimadzu Pesticide Database, which includes quantitative and qualifier transitions with optimized collision energies for approximately 500 pesticides. QuEChERS extracts were prepared in four sample matrices. Calibration standards of 24 organophosphorus pesticides were prepared in one sample matrix (peas extract) at 0.5–200 ng/mL (ppb), and replicate analyses of spiked sample extracts were analyzed to assess precision and accuracy.

Figure 1: Simultaneous Scan (black trace) and MRM (pink trace) chromatograms of the blended baby food peas, spiked with OP pesticides and analyzed in the simultaneous scan/MRM mode.
Results
Three MRM transitions were monitored for each analyte, and all pesticides eluted in less than 15 min. In addition, using a unique simultaneous Scan/MRM mode, in which full-scan mass spectra and MRM data are simultaneously acquired in the same run, most co-extracted matrix interferences were virtually eliminated.
Conclusion
Detection of the organophosphorus pesticides was demonstrated at low ng/mL (parts-per-billion, ppb) levels in the sample matrix, and linear calibration was demonstrated from 0.5–200 ng/mL. Precision and accuracy were demonstrated by ten replicate analyses of matrix spiked aliquots at 1 and 10 ng/mL.
Additional Information
For a complete description of instrument operating conditions, and analytical results for all four baby food matrices tested, please go to the Shimadzu web site, www.ssi.shimadzu.com and search for Application News No. GCMS-1304.
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, Inc.,
7102 Riverwood Drive, Columbia, MD 21046
Tel. (800) 477-1227
Website: www.ssi.shimadzu.com

New Study Reviews Chromatography Methods for Flavonoid Analysis
April 21st 2025Flavonoids are widely used metabolites that carry out various functions in different industries, such as food and cosmetics. Detecting, separating, and quantifying them in fruit species can be a complicated process.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)
















