Light Scattering for the Masses Green Polymer Chemistry: Efficient Synthesis of Disulphide Polymers and Networks
Wyatt Application Note
The objective of this experiment was to develop a greener synthesis of disulphide polymers, which are reducible under specific biological conditions.
Synthesis of poly(DODT)
The monomer, 3,6-dioxa-1,8-octanedithiol, and triethylamine (1:1.25 equivalent ratio) were reacted under bulk conditions for 10 min. To the bulk mixture, 2.0 equivalents of hydrogen peroxide (3% aqueous solution by weight) were added. The polymer was allowed to react with oxidative solution for a given amount of time. It was then removed from the solution, purified in acetone and dried.
Instrumentation
Molecular weights of soluble products were determined by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) on a system equipped with six Waters Styragel columns, a Waters 2487 dual absorbance UV detector, an Optilab DSP interferomatic refractometer (Wyatt Technology), a DAWN EOS multi-angle laser light-scattering detector (Wyatt Technology) and a ViscoStar viscometer (Wyatt Technology). The data from the SEC was processed using Wyatt's ASTRA software.

Figure 1: Light scattering and rms radius plots for sample EQR-3-7B.
Results and Conclusions
The dn/dc value for the polymer was calculated by two methods: 100% mass recovery (0.116 mL/g) and by RI analysis of a series of polymer dilutions (0.132 mL/g). It was found that the molecular weight of the polymer depends heavily on the reaction time of the oxidative step and on the reaction temperature. Data from two example polymerizations demonstrates the time dependence. Only 9 min after the addition of hydrogen peroxide, the reaction reached 73% conversion, and Mn = 14000 g/mol (sample EQR-3-7B). Additional reaction time in the oxidative solution increased the conversion to 90% and Mn to 230000 g/mol (EQR-2-13-062910D).
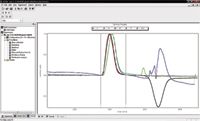
Figure 2: All detector traces for sample EQR-2-13-062910D.
DAWN, miniDAWN, ASTRA, Optilab and the Wyatt Technology logo are registered trademarks of Wyatt Technology Corporation.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
tel: +1 805 681 9009 fax: +1 805 681 0123
E-mail: info@wyatt.com Website: www.wyatt.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















