Fast Cap IC Determinations of Inorganic Anions and Cations in Drinking Water
The Application Notebook
Thermo Scientific Application Note
Fei Pang, Terri Christison and Khalil Divan, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Sunnyvale, California, USA.
The determination of common inorganic anions and cations in drinking water is important due to the toxicity of anions (e.g., fluoride, nitrite and nitrate) and secondary contaminants (e.g., chloride and sulfate) which can affect the water's aesthetics. Therefore, these secondary contaminants are monitored and primary contaminants regulated for compliance by the U.S. EPA and other agencies around the world.
Ion-exchange chromatographic determination of dissolved alkali and alkaline earth metals and ammonia in drinking water is another important application. Sodium is monitored under the U.S. EPA Safe Drinking Water Act, whereas ammonium is a required target analyte for wastewater discharge permits and is monitored in process wastewaters.
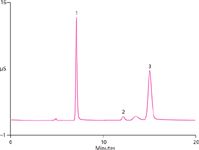
Figure 1
Capillary IC requires µL/min flow rates. Due to its low consumption of eluent, the system can remain on continuously, thereby eliminating the need for calibration prior to each use to provide a true walk-up system. The low flow rate leads to longer lifetime of consumables and smaller amount of waste, thereby reducing the overall cost of ownership.
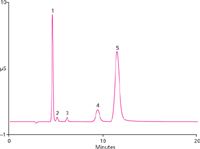
Figure 2
Conditions and Sample Preparation
The experimental setup and the sample preparation procedures are described in Application Brief 133, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (formerly Dionex Corp.).
Conclusion
All anions were separated and eluted within 13 min. The peak area relative standard deviations for each analyte was 0.6% when 60 injections were evaluated within 24 h. Capillary Reagent-Free IC redefines the workflow for IC analysis of inorganic anions and cations, providing enhanced mass sensitivity and ease of use. It is a fast and accurate solution for routine characterization of different water samples.
Scan to receive complete application note.
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (formerly Dionex Corp.)
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088, USA
tel. (408) 737-0700, fax (408) 730-9403
Website: www.thermoscientific.com/dionex

Determining Enhanced Sensitivity to Odors due to Anxiety-Associated Chemosignals with GC
May 8th 2025Based on their hypothesis that smelling anxiety chemosignals can, like visual anxiety induction, lead to an increase in odor sensitivity, a joint study between the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (Erlangen, Germany) and the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging (Freising, Germany) combined behavioral experiments, odor profile analysis by a trained panel, and instrumental analysis of odorants (gas chromatography-olfactometry) and volatiles (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry).
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.
Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















