Determination of Trace Concentrations of Bromate and Bromide in Natural Mineral Waters by Reagent-Free Ion Chromatography
LCGC Asia Pacific
Brian De Borba and Jeffrey S. Rohrer, Dionex Corporation
Bottled water has emerged as one of the fastest growing and most dynamic beverage categories over the last five to ten years. In 2004, the US and global community consumed nearly 7 billion gallons and 41 billion gallons, respectively, according to the Beverage Marketing Association.1 Many bottled water companies prefer ozone as a disinfectant because it is one of the most effective disinfectants available. It does not alter the taste, and bottlers do not need to be concerned about leaving a residual disinfectant in water that is sealed in a container.2 Unfortunately, ozone can react with naturally occurring bromide in the source water to produce bromate, a potential human carcinogen. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) established a maximum permissible limit of 10 mg/L of bromate in bottled drinking water.3 However, the European Commission set a maximum permissible limit of 3 mg/L of bromate for natural mineral waters and spring waters treated by ozonation.4 In this paper, we describe the use of the hydroxide-selective IonPac AS19 column to determine trace concentrations of chlorite, bromate, chlorate, and bromide in natural mineral waters obtained from three European countries.
Experimental
An integrated Dionex ICS-2000 Reagent-Free Ion Chromatography (RFIC) system equipped with an EluGen EGC-KOH cartridge was used in this work. An IonPac AS19 (4 × 250 mm) with its respective guard column AG19 (4 × 50 mm) was used for all separations with a flow-rate of 1 mL/min. Analytes were detected by suppressed conductivity with an ASRS ULTRA II (4 mm) operating at 130 mA in the recycle mode. A 250 µL injection volume was used throughout. Chromeleon Chromatography Management Software was used for system control and data processing.
Results and Discussion
In the US, mineral water is defined as "water not containing less than 250 ppm total dissolved solids (TDS)".5 However, mineral water that originates from Europe can contain less than 50 ppm TDS.6 We evaluated three European mineral waters with TDS that varied from 136 to 2359 ppm using a hydroxide-selective IonPac AS19 column. Hydroxide eluents provide considerable advantage over carbonate eluents by producing significantly lower background conductivity and thereby lower baseline noise and lower detection limits. The AS19 column combined with an electrolytically generated hydroxide eluent enabled a method detection limit of 0.31 µg/L bromate and is therefore ideally suited to meet the current European regulatory requirement for bromate in mineral water. Figure 1(a) shows an example chromatogram of a European mineral water (TDS = 136 ppm) with no chlorite or bromate detected and < 5 µg/L chlorate. This bottled water manufacturer did not indicate that ozonation was used for disinfection and, therefore, bromate was not expected. However, this mineral water contained approximately 16 µg/L bromide indicating a potential for bromate production, if treated with ozone. Figure 1(b) shows the same sample spiked with 10 µg/L each of chlorite and chlorate and 5 µg/L bromate, resulting in recoveries in the range of 88–91%. An RFIC system equipped with an AS19 column easily, accurately and simultaneously determines bromate and bromide in mineral water at concentrations below the regulatory limits.
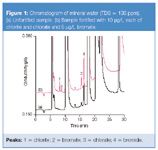
Figure 1
References
1. Rodwan, J.G. Reprint from The Bottled Water Reporter, Aug/May (2005). http://www.beveragemarketing.com/news3e.htm (accessed Nov 30, 2006).
2. Water Health Series: Bottled Water Basics; US Environmental Protection Agency, US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, Sept (2005).
3. Fed. Reg., 66(60), 16858 (2001).
4. Establishing the list, concentration limits and labelling requirements for the constituents of natural mineral waters and the conditions for using ozone-enriched air for the treatment of natural mineral waters and spring waters; European Parliament and Council Directive No. 2003/40/EC (2003).
5. L.M. Posnick and K. Henry, Food Safety Magazine, Aug/Sept (2002).
6. The Approximation of the Laws of the Member States Relating to the Exploitation and Marketing of Natural Mineral Waters; European Parliament and Council Directive No. 80/777/EEC (1980).
Brian De Borba and Jeffrey S. Rohrer, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, California, USA.
Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale,
California 94088-3603, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.
New Guide: Characterising Impurity Standards – What Defines “Good Enough?”
April 25th 2025Impurity reference standards (IRSs) are essential for accurately identifying and quantifying impurities in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Yet, with limited regulatory guidance on how much characterisation is truly required for different applications, selecting the right standard can be challenging. To help, LGC has developed a new interactive multimedia guide, packed with expert insights to support your decision-making and give you greater confidence when choosing the right IRS for your specific needs.
Using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorisation Approach (CPCA) to Classify N-nitrosamine Impurities
April 25th 2025Learn how to manage nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals with our free infographic. Discover how the CPCA approach establishes acceptable intake limits and guides the selection of NDSRI reference samples. Stay compliant and ensure safety with our ISO-accredited standards.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)
















