Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) Analysis with SEC–MALS
The Application Notebook
There has been a significant resurgence in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) as target-directed therapeutic agents for cancer treatment. Among the factors critical to effective ADC design is the Drug Antibody Ratio (DAR). The DAR describes the degree of drug addition that directly impacts both potency and potential toxicity of the therapeutic, and can have significant effects on properties such as stability and aggregation. Determination of DAR is, therefore, of critical importance in the development of novel ADC therapeutics.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
There has been a significant resurgence in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) as target-directed therapeutic agents for cancer treatment. Among the factors critical to effective ADC design is the Drug Antibody Ratio (DAR). The DAR describes the degree of drug addition that directly impacts both potency and potential toxicity of the therapeutic, and can have significant effects on properties such as stability and aggregation. Determination of DAR is, therefore, of critical importance in the development of novel ADC therapeutics.
DAR is typically assessed by mass spectrometry (MALDI–TOF or ESI–MS) or UV spectroscopy. Calculations based on UV absorption are often complicated by similarities in extinction coefficients of the antibody and small molecule. Mass spectrometry, though a powerful tool for Mw determination, depends on uniform ionization and recovery between compounds - which is not always the case for ADCs.
Here we present a method for DAR determination based on size-exclusion chromatography combined with multi-angle light scattering (SEC–MALS) in conjunction with UV absorption and differential refractive index detection. Figure 1 shows UV traces for two model ADCs; molecular weights of the entire ADC complexes are determined directly from light scattering data.
Figure 1: Molar masses for two distinct ADC formulations are determined using SEC-MALS analysis.
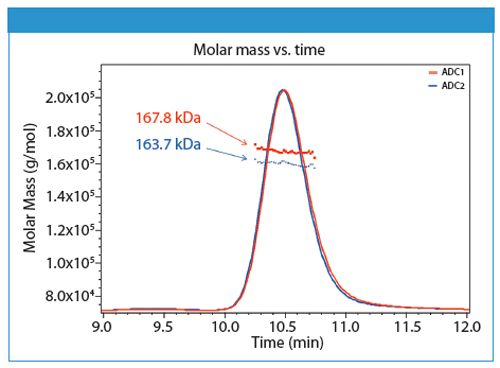
Component analysis is automated within the ASTRA 6 software package by using the differential refractive index increments (dn/dc) and extinction coefficients, which are empirically determined for each species or mined from the literature, to calculate the molar mass of the entire complex as well as for each component of the complex.
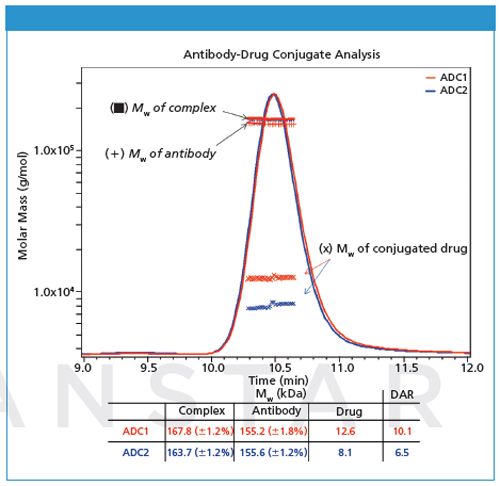
In this example an antibody has been alkylated with a compound having a nominal molecular weight of 1250 Da (Figure 2). Molar masses of the antibody fractions are similar, which indicates that the overall differences between the two formulations reflect distinct average DARs that are consistent with values obtained by orthogonal techniques. Note that the molar mass traces for the conjugated moiety represent the total amount of attached pendant groups; the horizontal trends indicate that modification is uniform throughout the population eluting in that peak.
Figure 2: Molar masses for the antibody and total appended drug are calculated in the ASTRA software package based on prior knowledge of each components extinction coefficent and dn/dc, allowing determination of DAR based on a nominal Mw of 1250 Da for an individual drug.

Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
Tel: +1 (805) 681 9009 Fax: +1 (805) 681 0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

Regulatory Deadlines and Supply Chain Challenges Take Center Stage in Nitrosamine Discussion
April 10th 2025During an LCGC International peer exchange, Aloka Srinivasan, Mayank Bhanti, and Amber Burch discussed the regulatory deadlines and supply chain challenges that come with nitrosamine analysis.













