Analysis of Mycotoxins in Cannabis Plant and Cannabis-Containing Products
The Application Notebook
As medical and recreational cannabis use gains broader acceptance, regulations are being put in place to mandate the testing of consumer products containing cannabis. Legally available cannabis plant and cannabis-containing edible products are tested for the presence of pesticides, heavy metals, residual solvents, and other harmful substances. Mycotoxins is another group of contaminants that state regulations have established maximum allowed levels for. In cannabis products sold to consumers the maximum allowed levels for total aflatoxins G1, G2, B1, and B2 are set at <20 ppb and for ochratoxin A at <20 ppb.
Pickering developed an easy and sensitive method to analyze aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2 and ochratoxin A in cannabis plant and edible products. Mycotoxins are isolated using immunoaffinity clean-up columns and analyzed with fluorescence detection. To increase sensitivity of aflatoxins B1 and G1, an in-line photochemical reactor is installed before the detector. This method utilizes standard HPLC equipment and allows laboratories to easily determine mycotoxins at levels below the limits established by state regulations.
Method
Isolation of Aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2 and Ochratoxin A
Blend 1 g of finely ground sample with extraction solution (10 mL of methanol/water 80:20, 5 mL of hexane, 0.1 g of NaCl) using a handheld homogenizer. Centrifuge for 10 min. Mix 2 mL of the aqueous layer with 12 mL of PBS buffer (pH 7.2) containing 4% of Tween 20. Apply the solution to AflaOTAClean™ Immunoaffinity column at a flow rate of 1–2 drops/sec.
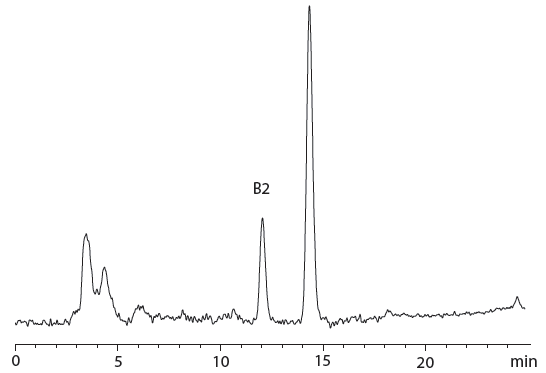
Figure 1: Chromatogram of cannabis-containing peanut butter cookie sample naturally contaminated with 1.58 ng/g of aflatoxins B1 and 0.26 ng/g of B2.
Wash the column with 10 mL of water at a flow rate of 1–2 drops/s. Elute the toxins with two 1-mL portions of methanol at a flow rate of 1 drop/s. Allow 5 min before applying the second portion of the methanol to ensure complete breaking of the antibody-toxin bond.
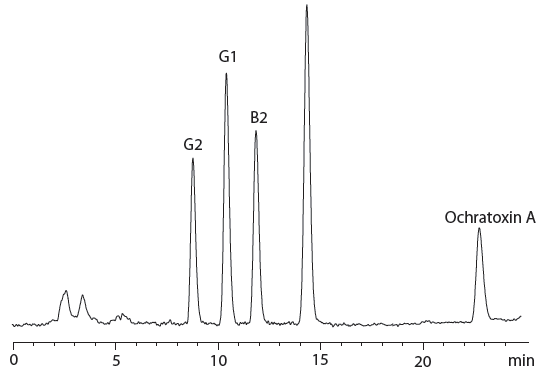
Figure 2: Chromatogram of cannabis pre-roll sample spiked with 6 ng/g of aflatoxin B1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxin B2; 5.94 ng/g of aflatoxin G1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxins G2 and 20 ng/g of ochratoxin A.
Evaporate to dryness at 55 °C. Reconstitute in 1 mL of methanol/water 50:50. Other immunoaffinity columns, such as Vicam's AflaOchra HPLC, could be used for sample clean up as well.
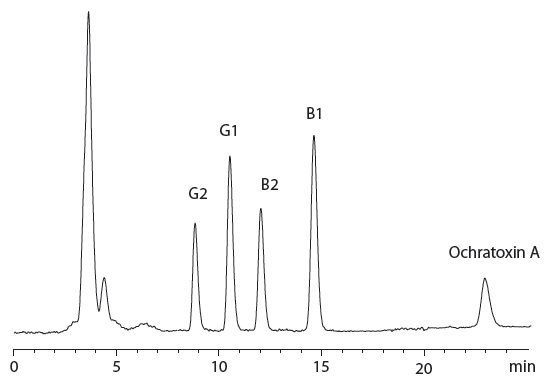
Figure 3: Chromatogram of cannabis inflorescence sample spiked with 6 ng/g of aflatoxin B1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxin B2; 5.94 ng/g of aflatoxin G1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxins G2, and 20 ng/g of ochratoxin A.
Analytical Conditions

Click here to view full-size graphic
Calibration
The 5-point calibration curves were built in the ranges of 0.25–5 ppb for B1, 0.075–1.5 ppb for B2, 0.248–4.95 ppb for G1, 0.075–1.5 ppb for G2, and 1–10 ppb for ochratoxin A. Correlation coefficient R2 > 0.999 for all toxins. All calibration standards were prepared in methanol/water 50:50
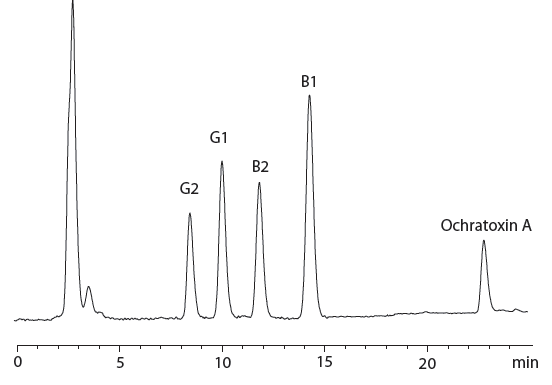
Figure 4: Chromatogram of cannabis-containing chocolate chip cookie sample spiked with 6 ng/g of aflatoxin B1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxin B2; 5.94 ng/g of aflatoxin G1; 1.8 ng/g of aflatoxins G2 and 20 ng/g of ochratoxin A.
Flow diagram for UVE™ photochemical reactor
Click here to view full-size graphic

Pickering Laboratories, Inc.
1280 Space Park Way, Mountain View, CA 94043
tel. (800) 654-3330, (650) 694-6700
Website: www.pickeringlabs.com


.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)

















