Separation of Vitamin K Isomers with Enhanced Selectivity
Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamins that are needed for the post-translational modification of certain proteins, mostly required for blood coagulation but also involved in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue.
Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamins that are needed for the post-translational modification of certain proteins, mostly required for blood coagulation but also involved in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue. The primary members of the group are Vitamins K1 and K2 (Figure 1). Plants synthesize Vitamin K1 while bacteria can produce a range of Vitamin K2 forms, including the conversion of K1 to K2 by bacteria in the small intestines. Exposure to light is known to isomerize vitamin K in the isoprenoid chain.
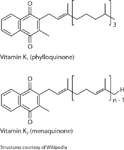
Figure 1: Chemical structure of Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2.
Strongly hydrophobic molecules, such as triglycerides, carotenoids, and fat-soluble vitamins may be analyzed using reversed-phase LC with low-aqueous or even non-aqueous mobile phases. While standard C18 silica columns fail to provide adequate shape selectivity to resolve structural isomers of these long chain hydrophobic compounds, the C30 phase is ideal for this application due to its excellent shape selectivity.
By choice of surface area and pore size in the silica substrate, the Thermo Scientific Acclaim™ C30 stationary phase has been designed to offer enhanced selectivity without excessive retention times. In many ways, it can be used as a general-purpose RP column same as the Acclaim C18 column, but with improved performance. For example, the Acclaim C30 column can separate highly hydrophilic analytes with high-aqueous mobile phases, or strongly hydrophobic analytes with low-aqueous mobile phases.
Results and Discussion
Figure 2a shows the resolution of the photo-isomers of Vitamins K1 and K2 using the Acclaim C30 column with a 98% methanol mobile phase at 20 °C. Under the same conditions, the Acclaim C18 column fails to resolve these structural isomers (Figure 2b). We also evaluated the effect of temperature and found that as temperature decreased, selectivity improved but the peak width also increased. The temperature of 20 °C was determined to be optimal for the separation. Acetonitrile can also be used instead of methanol, with slightly different selectivity, and somewhat longer retention times.
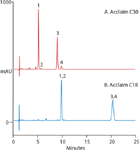
Figure 2: Columns: (a) Acclaim C30 and (b) Acclaim C18, 3 μm, 3.0 Ã150 mm. Mobile phase: 98% methanol, 2% D.I. water; temperature: 20 °C; flow rate: 0.65 mL/min. Injection volume: 2.5 μL. Detection: Diode Array (UV at 250 nm shown). Sample: 500 μg/mL Vitamins K1 and K2 in acetonitrile, (exposed to UV light for 20 min). Peaks: (1) Vitamin K2; (2) Isomer of Vitamin K2; (3) Vitamin K1; (4) Isomer of Vitamin K1.
All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries.
Dionex, now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088
tel. (408) 737-0700, fax (408) 730-9403
Website: www.thermoscientific.com/dionex

Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.
Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














