The Retention Behavior of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7, a Novel Adamantyl Stationary Phase in the Reversed-Phase Chromatography of Polar Compounds
The Application Notebook
Shiseido succeeded in development of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7, a novel stationary phase with an adamantyl group having a cage structure. This is characterized as alkyl group; therefore, the packed column is still easy to use just as a reversed-phase column.
CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 (ADME) is a column packed with a novel stationary phase of superficially porous silica (core–shell particle) modified by adamantyl functional groups. ADME has separation characteristics with a balance between moderate hydrophobicity and extra-high surface polarity which is completely different from the conventional C18. Therefore, The ADME is found to exhibit retention behavior different from the conventional C18 phase, because ADME has a higher surface polarity and a tendency to maintain a hydrophobicity. In addition, it is suggested simply use as a significant alternative to the C18 phase for the improved separation of highly polar substances such as metabolites, and biological samples.
The C18 column is the most popular one used in reversed-phase chromatography, but this phase has difficulty in retaining the highly polar compounds. Therefore, in order to increase the retention, separation modes such as HILIC (1) and ion exchange are some of the choices. However, these are in separation mechanism different from the reversed phase mode, the column selection and the mobile phase condition becomes complicated.
In general, in order to increase the retention of highly polar compounds in the reversed phase mode, packing material with enhanced surface polarity by decreasing the density of alkyl groups or embedding polar functional group is conventionally used, but has slight effect on changing the retention of them.
Shiseido succeeded in development of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7, a novel stationary phase with an adamantyl group having a cage structure. This is characterized as alkyl group; therefore, the packed column is still easy to use just as a reversed-phase column.
In this study, the characteristics of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 and the retention behavior of highly polar compounds on the same mobile phase were evaluated.
Experimental
1. Basic Feature of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7
(1) Determination of Separation Parameters
CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 (ADME) is a column packed with a novel particle with 1.7-µm solid core and 0.5-µm porous layer modified with adamantly functional group (Figure 1). The parameter of Hydrophobicity and Surface polarity was determined with ADME by the resolution factor of toluene with benzoate, and toluene with methyl benzoate (2).
(2) Comparison of Separation Characteristics
The effect of separation parameters on retention and separation were determined by comparison of the analysis of catechines with CAPCELL CORE C18 S2.7 and CAPCELL CORE AQ S2.7, and CAPCELL CORE PFP S2.7, respectively.
2. Application of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7
Acetaminophen and its conjugated metabolites were analyzed under acidic and neutral conditions with CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 and CAPCELL CORE C18 S2.7, respectively.
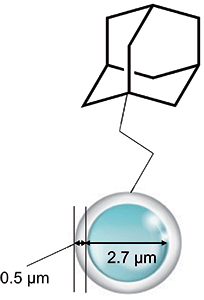
Figure 1: Superficially porous silica (core-shell particle) modified by adamantyl functional groups.
Results and Discussion
1. Basic Feature of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7
(1) Determination of Separation Parameters
In Figure 2, the parameters of hydrophobicity and surface polarity of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 (ADME) derived from the resolution factors of toluene with benzoate, and toluene with methyl benzoate, were plotted on the parameter graph including CAPCELL CORE C18 S2.7, CAPCELL CORE AQ S2.7, CAPCELL CORE PFP S2.7, and other reverse-phase columns. In the parameter map, ADME is positioned with moderate hydrophobicity and extra-high surface polarity.
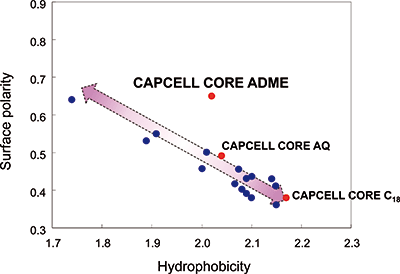
Figure 2: Parameter map of separation.
(2) Comparison of Separation Characteristics
As shown in the chromatograms in Figure 3, CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 (ADME) showed a large retention and a highly resolution of catechines compared with more hydrophobic CAPCELL CORE C18 S2.7, similarly hydrophilic CAPCELL CORE AQ S2.7 and CAPCELL CORE PFP S2.7. Therefore, it is suggested that not only the hydrophobicity but also the high surface polarity of ADME provided effect on the separation of catechines.
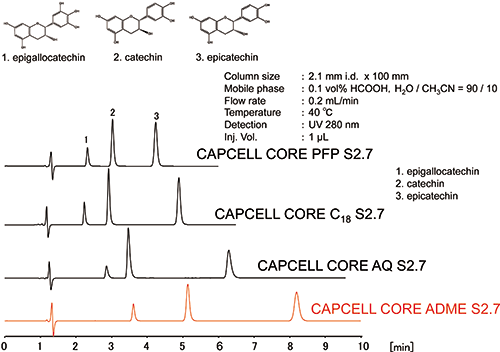
Figure 3: Chromatograms of catechines.
2. Application of CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7
Acetaminophen and its conjugated metabolites containing glycoside were analyzed under acidic and neutral conditions with CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 and CAPCELL CORE C18 S2.7, respectively (Figure 4). It is clear that the metabolites of acetaminophen, conjugate of sulfuric acid, and glucuronic acid were certainly separated under acidic and neutral conditions. In particular, a good separation and large retention was obtained with CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 under acidic conditions.
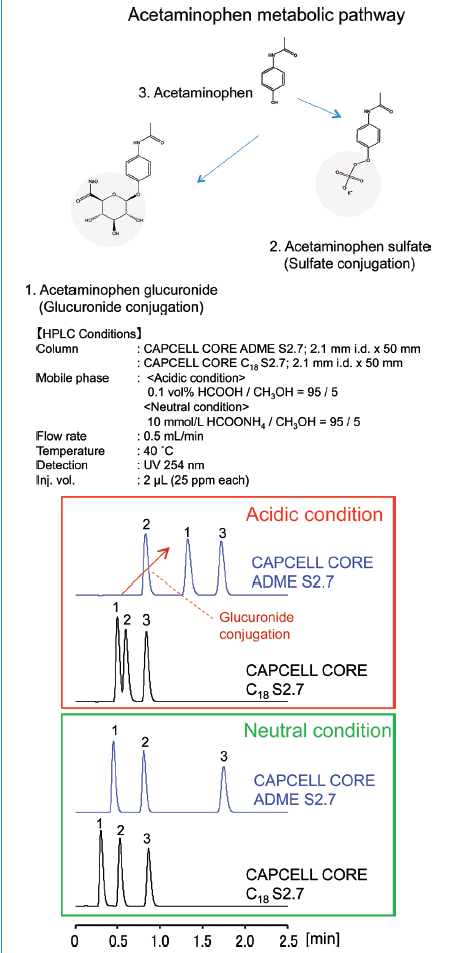
Figure 4: Chromatograms of acetaminophen and its metabolites.
Conclusion
CAPCELL CORE ADME S2.7 is a novel core–shell type column with adamantly-functional group modified stationary phase and provides improved separation to highly polar metabolites which was previously unavailable by the conventional C18 and PFP columns. It is suggested particularly useful in retaining and separation of highly polar compounds. It is also an easy-to-use reverse-phase column and is expected to work as an alternative to the C18 column in the improved separation of highly polar compounds and matrix components in biological samples.
References
(1) A.J. Alpert, J. Chromatogr. A499, 177–196 (1990).
(2) S. Kobayashi, I. Tanaka, O. Shirota, T. Kanda, and Y. Ohtsu. J. Chromatogr. A828, 75–81 (1998).

Shiseido Co., Ltd.
4F Shiodome Bl., 1-6-2, Higashi-shin-bashi, Minato-ku,
Tokyo, Japan, tel. +81-3-6253-1412
Email: hplc@shiseido.co.jp, Website: http://hplc.shiseido.co.jp/e/

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.














