Rapid Determination of DNPH Derivatized Carbonyl Compounds by UHPLC
LCGC Asia Pacific
Knauer Application Note
Silvia Marten and Mareike Naguschewski, KNAUER, Berlin, Germany.
Introduction
Carbonyl compounds, in particular aldehydes, are reactive volatile substances. They are of concern to the public, because they are emitted as air pollutants by a large range of industrial processes and other combustion sources. In addition, they can also be found indoors when emitted from sources such as insulation, furniture or tobacco smoke.1,2 Because of their adverse health effects, monitoring of these substances is important. Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are known for their irritating effects on animals and humans whereby formaldehyde is also carcinogenic.3
Low molecular weight aldehydes are highly volatile and polar substances resulting in a hindered analysis by RP-UHPLC methods. In addition, many known carbonyl compounds have no chromophores and are for this reason not detected by UV. Due to their functional carbonyl group, low molecular weight aldehydes and ketones can, however, be derivatized with 2,4 dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH). In acidic media, DNPH reacts with the carbonyl group to form stable hydrazones (DNPH-carbonyls) with a lower vapour pressure that can be separated by UHPLC on a C18 column and detected easily by UV.2
In this work, six DNPH derivatized low molecular weight carbonyls are separated by UHPLC in less than 3 minutes. Optimizing the speed and resolution of routine analyses by applying a UHPLC method can not only save time but also dramatically decrease eluent costs, particularly important for analyses using acetonitrile.
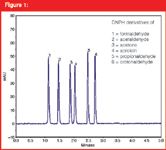
Figure 1
Experimental
A very fast method for identifying six DNPH-derivatized carbonyls in a mixture was possible using the Knauer PLATINblue UHPLC system. Employing the BlueOrchid C18 A phase with a 1.8 μm particle size allowed for the reduction of analysis time from about 20 to less than 3 minutes compared to a conventional HPLC method. A binary high pressure gradient configuration at a flow rate of 0.8 mL/min in combination with a 2 mm column i.d. and UV detection was applied. After measuring a sample containing 2 ng/μL DNPH derivatized carbonyls, calibration in the range of 2 up to 40 ng/μL was performed.

Results and Conclusion
By means of derivatization with DNPH, six carbonyl compounds could be easily determined in less than 3 minutes by employing a Knauer PLATINblue UHPLC system, a BlueOrchid C18 A stationary phase and an acetonitrile elution gradient. The 2 mm inner diameter of the chosen column resulted in a comparable small amount of required eluent. All carbonyls are baseline separated with resolution values in the range of 2.5 up to 7.3. The analysis time could be reduced more than six times compared to the method using a conventional HPLC system. The limits of detection (LOD) lie in the range of 0.1 ng for all six carbonyls. Calibration is realized for all analysed compounds and the linearity (r2) was in the range of 0.999131–0.999916. By using UHPLC and its advantages, long equilibration and analysis times can be avoided, and a UV detection of DNPH-derivatized carbonyl concentrations in the range of 4 ng can be realized.
References
1. M. Possanzin et al., Chromatographia, 23(11), 829–834 (1987).
2. Y. Feng and J. Zhu, Anal. Sci., 20, 1691–1695 (2004).
3. J. Zhang, Environ. Sci., Technol., 28(1), 146–152 (1994).
Knauer GmbH
Hegauer Weg 38, 14163 Berlin, Germany
tel. +49 30 809727 0 fax +49 30 801501 0
E-mail: info@knauer.net Website: www.knauer.net

Determining Enhanced Sensitivity to Odors due to Anxiety-Associated Chemosignals with GC
May 8th 2025Based on their hypothesis that smelling anxiety chemosignals can, like visual anxiety induction, lead to an increase in odor sensitivity, a joint study between the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (Erlangen, Germany) and the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging (Freising, Germany) combined behavioral experiments, odor profile analysis by a trained panel, and instrumental analysis of odorants (gas chromatography-olfactometry) and volatiles (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry).
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.
Detecting Hyper-Fast Chromatographic Peaks Using Ion Mobility Spectrometry
May 6th 2025Ion mobility spectrometers can detect trace compounds quickly, though they can face various issues with detecting certain peaks. University of Hannover scientists created a new system for resolving hyper-fast gas chromatography (GC) peaks.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)












