Improvement in LC–MS-MS Analysis of Vitamin D Metabolites in Serum Using Column Selectivity and Effective Sample Prep
LC–MS-MS has become an important tool to assess an individual's vitamin D status. Chromatographic resolution of the various homologs of vitamin D2 is necessary for accurate quantitation since several key metabolites are isobaric and not distinguishable by MS alone.
LC–MS-MS has become an important tool to assess an individual's vitamin D status. Chromatographic resolution of the various homologs of vitamin D2 is necessary for accurate quantitation since several key metabolites are isobaric and not distinguishable by MS alone. Additionally, effective sample prep is required since the hydrophobic character of vitamin D metabolites requires high organic mobile phases that also elute endogenous interferences, like phospholipids.
Materials and Methods
HPLC: Ascentis® Express F5, 10 cm × 2.1 mm i.d., 2.7 µm (Supelco, 53569-U). Sample Prep: HybridSPE® -Phospholipid, 96-well plates, 50 mg/well (Supelco, 575656-U). Solvents and Additives (for sample prep and chromatography): LC-MS Ultra CHROMASOLV® water (Fluka, 14263), methanol (Fluka, 14262) and ammonium formate (Fluka, 14266). Standards: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D2 (Cerilliant, H-087), 25 Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Cerilliant, H-083), 1α, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D2 (Cerilliant, H-090); 3-epi-25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 (Aldrich, 705993). HybridSPE® -Phospholipid 96-well method: Apply 100 µL of spiked plasma to the well, followed by 300 µL of 1% v/v formic acid in acetonitrile. Agitate via vortex for 4 min, place on vacuum manifold and apply 10" Hg vacuum for 4 min. Collect filtrate and analyze directly.
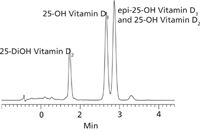
Figure 1: HPLC Separation of 25-dihydroxyvitamin D2, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, and epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3. Column: Ascentis Express F5, 10 cm à 2.1 mm i.d., 2.7 µm (Supelco, 53569-U). Mobile Phase: 5 mM ammonium formate in water:methanol (25:75), Flow Rate: 0.4 mL/min., Temperature: 40 °C, Detection: ESI(+), m/z 100-1000, Sample: 1 µL, each compound 20 µg/mL in methanol.
Results
Figure 1 shows the separation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D2, 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 and epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 on the Ascentis Express F5 column. The pentafluorophenyl phase resolved the vitamin D homologs that a C18 could not. (Note that the coelution of 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and 3-epi-25-hydroxyvitamin D3 is not an issue because they are resolved by the mass spec.) The effectiveness of sample prep using HybridSPE-Phospholipid is demonstrated in Figure 2. The unique HybridSPE-Phospholipid selectively depleted the phospholipid matrix and precipitated proteins, providing no matrix interference (1). For further details of this method, please see reference 2.
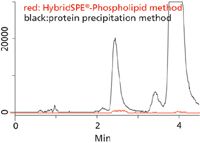
Figure 2: Monitoring phospholipids. Serum extracted using HybridSPE-Phospholipid (red trace) or protein precipitation (black trace). Conditions as in Figure 1 except phospholipid monitoring (m/z): lysophosphatidylcholines, 496.3, 524.3 m/z; glycerophosphocholines, 758.5, 786.5, 806.5, 810.5 m/z.
References
(1) C.R. Aurand, D.S. Bell, and M. Wright, Bioanalysis 4 (22), 2681–2691 (2012).
(2) C. Aurand, Supelco Reporter 30.2, 10–12 (2012).
Ascentis, CHROMASOLV, and HybridSPE are registered trademarks of Sigma-Aldrich Co LLC.
Supelco/Sigma-Aldrich
595 North Harrison Road, Bellefonte, PA 16823
tel. (800) 787-3526, (814) 359-3441
Website: sigma-aldrich.com/analytical

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.














