Hyaluronic Acid (Polysaccharides)
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a ubiquitous, very high molar mass polysaccharide that has been of particular importance in opthalmic surgery. HA acts as a molecular "shock-absorber" and stabilizer for cells and its visco-elastic properties are valuable for separating tissue and maintaining shape.
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a ubiquitous, very high molar mass polysaccharide that has been of particular importance in opthalmic surgery. HA acts as a molecular "shock-absorber" and stabilizer for cells and its visco-elastic properties are valuable for separating tissue and maintaining shape. It is a critical component in tissue lubrication and is believed to play a leading role in wound repair. Finally, HA's property of non-pyrogenicity makes it an ideal sheath for implants, whose presence might cause the body to suffer an immune response.
Among the many benefits high molecular weight HA hold are
- the maintenance of tissue space for surgery
- the protection of cells and tissue
- therapeutic effectiveness.
HA's therapeutic effectiveness depends critically on molecular weight: the higher the molecular weight, the longer its benefit. However, because of its visco-elastic properties, standards-based GPC analysis is inappropriate for characterizing HA. There exist no standards identical to HA and the desirability of altering experimental conditions renders conventional GPC/SEC impractical.
Combining a DAWN with HPLC separation, however, provides an ideal platform for absolute characterization, since the light-scattering measurements do not depend on pump speed, polymer standards, or molecular conformation.
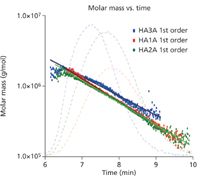
Figure 1: From the molar mass versus time plot, subtle differences can be seen among the samples.
A DAWN was connected to a GPC/SEC line (100 mM NaN03 buffer, TSK-Gel G6000PW column, Optilab DSP refractometer, Waters 510 pump) and generated the data required to determine not only absolute molar mass, but also molecular size, for a variety of HA products.
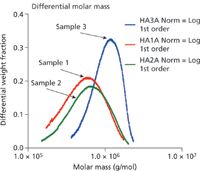
Figure 2: The differential molar mass distributions calculated by ASTRA immediately confirm the large differences among the three HA samples.
Figure 1 shows the molar mass versus time (with the 90° lights-cattering chromatograms in the background) for the three samples, ranging from approximately 2 million to less thasn 200K Daltons. Figure 2 illustrates how profoundly different the samples are by revealing their differential molar mass distributions. These indicate that the samples will behave in different ways when used medically, depending on the content of their high molecular weight HA.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117
tel. +1 (805) 681-9009, fax +1 (805) 681-0123
E-mail: info@wyatt.com Website: www.wyatt.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.














