An Improved SPE–LC–MS–MS Platform for the Simultaneous Quantification of Multiple Amyloid β Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid for Preclinical or Biomarker Discovery
Waters Application Note
Introduction
Fast, flexible platforms for peptide quantification are needed, particularly for a discovery setting. This type of methodology would be especially advantageous in the case of amyloid beta (aβ) peptides. The deposition/formation of insoluble aggregates, or plaques, of aβ peptides in the brain is considered to be a critical event in the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and thus has the attention of many researchers. A previous Waters application note (720003682en) described in detail the development of a fast, flexible SPE–LC–MS–MS platform for the quantification of multiple aβ peptides from human or monkey CSF for use in a biomarker or preclinical discovery setting. In this work, the mass spectrometry platform has been updated from the Xevo TQ MS to the Xevo TQ-S mass spectrometry system. This change facilitated both a 4× reduction in required sample size and a 4–5× increase in assay sensitivity. This work focuses on methods for the 1-38, 1-40 and 1-42 aβ (Table 1).

Table 1: Sequence, MW and pI information for amyloid peptides.
Experimental Conditions
SPE-LC–MS–MS Conditions
LC system: Waters ACQUITY UPLC System
Column: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 300 Å, 2.1 × 150 mm, 1.7 µm, Peptide Separation Technology
SPE: Oasis MCX µElution 96-well plate, 50 µL human or animal CSF
MS system: Waters Xevo TQ-S, ESI+
Results and Conclusions
• An improved SPE–UPLC–MS–MS bioanalytical method was developed and validated for the simultaneous quantification of multiple amyloid β peptides in human CSF.
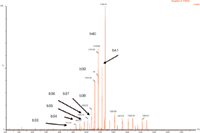
Figure 1: Representative ESI+ MS-MS spectrum for amyloid 1-42 with fragment sequence ions labelled.
• MS was performed in positive ion mode since CID of the 4+ precursor ion yielded several distinct product ions corresponding to inherently specific b sequence ions (representative spectrum shown in Figure 1).
• UPLC separation of the three amyloid β peptides is shown in Figure 2.
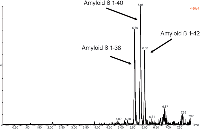
Figure 2: Representative UPLCâMSâMS analysis of amyloid 1-38, 1-40 and 1-42 peptides extracted from artificial CSF + 5% rat plasma.
• The increased sensitivity of the Xevo TQ-S triple quadrupole mass spectrometer facilitated the use of 4× less sample and a 4–5× improvement in quantification limits (Table 2).

Table 2: Comparison of Standard Curve and QC range using Xevo TQ and TQ-S MS.
• Average basal levels and RSD values for all 3 aβ peptides in 2 sources of human CSF are shown in Table 3 and are lower or equal to 5%.
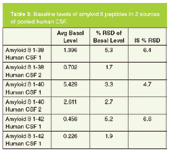
Table 3: Baseline levels of amyloid peptides in 2 sources of pooled human CSF.
• Overspiked QC samples were prepared in triplicate in 2 sources of pooled human CSF at 0.04, 0.075, 0.15, 0.2, 0.8, 2 and 6 ng/mL. Accuracy and precision values met the regulatory criteria for LC–MS–MS assays. Results from QC sample analysis are shown in Table 4. Average deviation from expected is 2.3%.

Table 4: Average deviation values for all overspike QC samples
• The method described herein eliminates time-consuming immunoassays or immunoprecipitation steps for pre-clinical work.
• The use of a single UPLC–MS–MS assay represents a significant advantage over an ELISA assay, which would require multiple assays with multiple antibodies to quantify each of the relevant peptides.
Copyright 2011: ACQUITY UPLC, Oasis, The Science of What's Possible, Xevo are trademarks of Waters Corporation.

Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street, Milford, Massachusetts 01757, USA
tel. +1 508 478 2000 fax +1 508 478 1990
Website: www.waters.com

Silvia Radenkovic on Her Research and Passion for Scientific Collaboration
April 3rd 2025Radenkovic is a PhD candidate at KU Leuven and a member of FeMS. Her research focuses on inborn metabolic disorders (IMD), like congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG), omics techniques such as tracer metabolomics, and different disease models.
Study Explores Thin-Film Extraction of Biogenic Amines via HPLC-MS/MS
March 27th 2025Scientists from Tabriz University and the University of Tabriz explored cellulose acetate-UiO-66-COOH as an affordable coating sorbent for thin film extraction of biogenic amines from cheese and alcohol-free beverages using HPLC-MS/MS.
Quantifying Microplastics in Meconium Samples Using Pyrolysis–GC-MS
March 26th 2025Using pyrolysis-gas chromatography and mass spectrometry, scientists from Fudan University and the Putuo District Center for Disease Control and Prevention detected and quantified microplastics in newborn stool samples.


















