Direct Determination of Endothall in Water Samples by IC–MS
The Application Notebook
Dionex Application note
Endothall is a widely used herbicide for both terrestrial and aquatic weeds. Exposure to endothall in excess of the maximum contamination level (MCL) can cause illness. Endothall is regulated by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) at 100 ppb in drinking water, and by the California EPA at 0.58 mg/L, or 580 ppb, as the Public Health Goal. Current analytical methods described in EPA method 548.1 for the quantification of endothall in water samples involve time-consuming sample preparation and derivatization followed by a 20-min analysis by GC–MS or GC–FID.
This study describes the direct analysis of trace levels of endothall in water samples by ion chromatography–mass spectrometry (IC–MS). Water samples were directly injected for analysis and chromatographic separation was reduced to 10 min. The MSQ Plus mass spectrometer was operated in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode, allowing minimum sample cleanup and ensuring sensitive (low ppb) and selective quantification. Isotope labelled glutaric acid (Glutarate–d6) was used as the internal standard to ensure quantification accuracy.

Results and Conclusion
As seen in Figure 1, endothall was retained and separated from seven commonly seen anions within 10 min, and was detected with great sensitivity and selectivity using SIM acquisition. This method features direct analysis without sample pretreatment and significantly reduces run time relative to GC methods, thus improving throughput. Sufficient sensitivity was achieved in this study to allow the routine quantification of endothall below the lowest regulated level (100 ppb by US EPA standards).
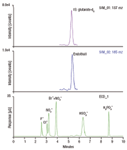
Figure 1: ICâMS of 20 ppb endothall spiked in a seven anions matrix: 0.2â1.5 ppm.
IonPac is a registered trademark of Dionex Corporation. MSQ Plus is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, PO Box 3603, Sunnyvale, California 94088, USA
tel: +1 408 737 0700 fax: +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Characterizing Plant Polysaccharides Using Size-Exclusion Chromatography
April 4th 2025With green chemistry becoming more standardized, Leena Pitkänen of Aalto University analyzed how useful size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) and asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) could be in characterizing plant polysaccharides.
Investigating the Protective Effects of Frankincense Oil on Wound Healing with GC–MS
April 2nd 2025Frankincense essential oil is known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and therapeutic properties. A recent study investigated the protective effects of the oil in an excision wound model in rats, focusing on oxidative stress reduction, inflammatory cytokine modulation, and caspase-3 regulation; chemical composition of the oil was analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).


















