Determination of Selected Pesticides and Flame Retardants in Drinking Water by SPE for UCMR2 and EPA Method 527 Using the Atlantic 527 Disk
The Application Notebook
The second unregulated contaminant monitoring regulation (UCMR2) program was developed to monitor US drinking water sources for currently unregulated compounds. EPA Method 527 is categorized under List 1; Assessment Monitoring in the UCMR2 program. EPA Method 527 focuses on a wide range of semi volatile organic contaminants, including pesticides that were deferred during the first UCMR, flame retardants, and pyrethroid pesticides. This application for EPA Method 527 employs SPE with analysis by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).
Horizon Technology, Inc.
The second unregulated contaminant monitoring regulation (UCMR2) program was developed to monitor US drinking water sources for currently unregulated compounds. EPA Method 527 is categorized under List 1; Assessment Monitoring in the UCMR2 program. EPA Method 527 focuses on a wide range of semi volatile organic contaminants, including pesticides that were deferred during the first UCMR, flame retardants, and pyrethroid pesticides. This application for EPA Method 527 employs SPE with analysis by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS).
The Atlantic EPA 527 Disk was used to capture the compounds of interest. The disk must be conditioned, using acetone, methanol, and ultra pure water prior to the extraction step. The extraction solvents used are acetone and hexanes, and the extracts are then analyzed using GC–MS.
Automated sample handling equipment manufactured by Horizon Technology, Inc. was used in this method. The SPE-DEX® 4790 Automated Extraction System with the Envision™ Platform are designed to streamline the sample handling required for analyzing environmental samples. The SPE-DEX 4790 provides automatic extraction of liquid samples by solid phase extraction methods. It can handle samples that range from 20 ml to 4 L. The Envision Platform provides a user- friendly, web-based controller capable of interacting with up to eight extractors through your PC.
Instrumentation
- Horizon Technology SPE-DEX 4790 Automated Extractor System
- Horizon Technology Atlantic EPA 527 Disks (47 mm)
- Horizon Technology Envision Platform
Method Summary
1) A 1000 mL aliquot of sample is used.
2) Residual chlorine must be reduced at the time of sample collection with 100 mg of ascorbic acid per liter.
3) Trisodium EDTA (0.35 g/L) must be added to inhibit metal-catalyzed hydrolysis of the target compounds.
4) Sample buffered to pH 3.8 using potassium dihydrogen citrate (9.4 g/L).
5) Agitate bottles by hand until preservatives are dissolved.
6) Spike surrogate compounds and standards into samples.
7) Adjust the low vacuum cartridge regulator to 5 in. Hg
8) Start extraction method, collect extract (approx 20 ml). Concentrate extract to approx 0.7 mL under a gentle stream of nitrogen in a warm water bath (at ~ 40°C).
9) Add internal standard and quantitatively bring the extract volume to 1.0 ml with ethyl acetate.
10) Transfer a portion of the extract to a GC vial with insert.
11) Analyze by GC–MS.
Results
DI water was spiked with Method 527 standard at a theoretical concentration of 0.3 μg/ml. The surrogate standard was spiked at 2.0 μg/ml. Seven 527 compounds were included in the target compound list. Table I and Figure 1 show the compound names, amount recovered, and percent recovery.
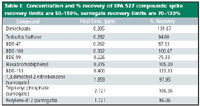
Table I: Concentration and % recovery of EPA 527 compounds: spike recovery limits are 50â150%, surrogate recovery limits are 70â130%
Conclusions
This data demonstrates that when using the Atlantic EPA 527 Disk and Horizon Technology automated equipment the results are both accurate and precise.
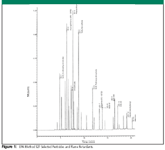
Figure 1
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Craig Caselton, from Northern Lake Services, Crandon, Wisconsin.

Horizon Technology, Inc.
45 Northwestern Dr., Salem, NH 03079
Tel: (603) 893-3663; Fax: (603) 893-4994

Separation of Ultra-Short and Long Chain PFAS Compounds Using a Positive Charge Surface Column
December 11th 2024A separation of ultra-short and long chain PFAS (C1-C18) is performed on a HALO®PCS Phenyl-Hexyl column along with a HALO®PFAS Delay column which demonstrates excellent retention for both hydrophilic and hydrophobic analytes.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














