Determination of Methacholine Chloride and Potential Impurities Using a Reagent-free Ion Chromatography System
The Application Notebook
Methacholine chloride is a synthetic analogue of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine used to assess bronchial asthma of subjects in respiratory function labs and epidemiological field studies.
Richard Kornfeld and Jeffrey Rohrer, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, California, USA.
Methacholine chloride is a synthetic analogue of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine used to assess bronchial asthma of subjects in respiratory function labs and epidemiological field studies.1 Methacholine has been shown to decompose over time.2 Hydrolysis will yield β-methylcholine and acetic acid. Acetylcholine, a potential synthetic impurity, may also be present in the powder.
Choline and its analogues have been determined using ion chromatography (IC) in various matrices such as prescription and nonprescription medications, milk and infant formula, and vitamin and mineral formulations (3 and references cited therein). This contribution demonstrates that a cation RFIC system can determine methacholine, acetylcholine and β-methylcholine with high precision, high recovery and excellent day-to-day reproducibility. We use anion IC to determine acetate. The first method can assay methacholine and the combination of both methods can determine methacholine's related substances.
Experimental
Analyses are performed using a Dionex ICS-2100, AS autosampler and Chromeleon Chromatography Data System software. Cation separations use an IonPac CG/CS17 column set with electrolytically generated MSA eluent, while anion separations use an IonPac AG/AS22 column set with manually prepared carbonate/bicarbonate eluent. For detailed experimental conditions, see Dionex Application Note 249.
Results and Discussion
The method for methacholine assay includes diluting the initial solution (25 g/L methacholine in 0.9% sodium chloride with or without 0.4% phenol) 1000-fold with water. Excellent linearity (R2 > 0.9999), spike recovery (97–100%), 5-day retention time (<0.05%), and peak area (<0.4%) RSDs were observed for methacholine.
The method for potential methacholine impurities includes diluting the initial methacholine solution 100-fold with water. Figure 1 shows the cation IC of 2.5 mg/L acetylcholine in diluted methacholine-containing matrix. A peak for β-methylcholine is observed in both the matrix blank and acetylcholine-spiked matrix at approximately 0.1% of the methacholine concentration. MDL estimates for β-methylcholine and acetylcholine are at single-digit µg/L levels while the estimate for acetate MDL is 75 µg/L. Excellent linearity (R2 > 0.9998) for target impurities are observed. Recoveries of target impurities spiked at 2.5 mg/L range from 85–95%. Highly reproducible retention times (0.1% or less) and peak areas (<0.8%) are observed for the choline-based analytes over a 5-day study.
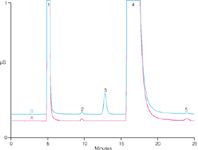
Figure 1: Cations in 100:1 dilution of 25 g/L methacholine + 0.9% NaCl + 0.4% phenol matrix. Conditions: IonPac CG/CS17 (4 mm) column set at 30 °C, 5 mM methanesulphonic acid, 1.0 mL/min, 25 µL injection, suppressed conductivity (recycle mode). Trace A: matrix blank. Trace B: 2.5 mg/L acetylcholine in diluted matrix. Peaks: 1 = sodium, 2 = β-methylcholine, 3 = acetylcholine, 4 = methacholine and 5 = calcium.
Conclusions
This note presents IC-based methods for the detection and quantification of methacholine and potential impurities in solutions used to assess bronchial asthma. These assays only require simple dilutions with deionized water and demonstrate excellent precision and accuracy for both methacholine and for potential impurities present in amounts approaching 1%.
References
1. Guidelines for Methacholine and Exercise Challenge Testing – 1999. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 161, 309–329 (2000).
2. R.D. Hayes et al., Eur. Respir. J., 11, 946–948 (1998).
3. Dionex Corporation. Application Note 194 (LPN 1967, April, 2008).
Chromeleon and IonPac are registered trademarks of Dionex Corporation.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, PO Box 3603, Sunnyvale, California 94088, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.
New Guide: Characterising Impurity Standards – What Defines “Good Enough?”
April 25th 2025Impurity reference standards (IRSs) are essential for accurately identifying and quantifying impurities in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Yet, with limited regulatory guidance on how much characterisation is truly required for different applications, selecting the right standard can be challenging. To help, LGC has developed a new interactive multimedia guide, packed with expert insights to support your decision-making and give you greater confidence when choosing the right IRS for your specific needs.
Using the Carcinogenic Potency Categorisation Approach (CPCA) to Classify N-nitrosamine Impurities
April 25th 2025Learn how to manage nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals with our free infographic. Discover how the CPCA approach establishes acceptable intake limits and guides the selection of NDSRI reference samples. Stay compliant and ensure safety with our ISO-accredited standards.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)


















