Absolute Molar Masses for Phenol Formaldehyde Resins with GPC/SEC-ESI
The Application Notebook
Phenol formaldehyde resins are formed by a step-growth polymerization. GPC/SEC with RI and UV detection is often used to characterize resins and to quantify the amount of different oligomeric species.
Introduction
Phenol formaldehyde resins are formed by a step-growth polymerization. GPC/SEC with RI and UV detection is often used to characterize resins and to quantify the amount of different oligomeric species. Additional information is available if a ESI-MS-spectrometer is on-line attached to the GPC/SEC system. This technique combines the separation ability of GPC/SEC with the sensitivity and specificity of detection from MS and allows the identification of oligomeric species and gives information about the degree of CH2-OH substitution.
Experimental
GPC/SEC analysis was performed on a PSS SECcurity 1200 system consisting of:
- an isocratic pump
- an autosampler with variable injection volume
- a differential refractometer (RI)
- a Thermo Fisher LXQ ESI spectrometer
Conditions
Columns: PSS SDV, 5 µm, 50 + 100 + 1000 Å, 8 × 300 mm each + precolumn
Solvent: THF
Flow rate: 0.3 mL/min
Inject volume: 20 µL
Software: PSS WinGPC Unity 7.4, Thermo Fisher Excalibur 2.07

Figure 1: RI trace oligomeric phenol formaldehyed resin, degree of polymerization identified from corresponding mass spectrum.
Results
Figure 1 shows the elugram of an oligomeric phenol formaldehyde resin, separated into three different peaks with 1, 2 and 3 repetition units. The mass spectra are then measured for each species. Figure 2 shows as example the mass spectrum for peak n = 1 while Table 1 summarizes the masses possible in theory and identified (green) or not detected (grey). This combined approach can be used for molar masses up to approx. 2000 Da, higher degrees of polymerization have also been investigated.
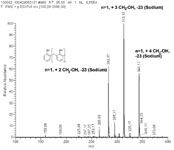
Figure 2: Mass spectrum for n = 1 showing the 3 different species (CH2âOH substitution).
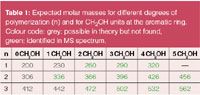
Table 1

PSS Polymer Standards Service GmbH
In der Dalheimer Wiese 5, D-55120 Mainz, Germany
tel. +49 6131 96239 50 fax +49 6131 96239 11
E-mail: fgores@polymer.de
Website: www.analyzepolymers.com

A Guide to (U)HPLC Column Selection for Protein Analysis
April 16th 2025Analytical scientists are faced with the task of finding the right column from an almost unmanageable range of products. This paper focuses on columns that enable protein analysis under native conditions through size exclusion, hydrophobic interaction, and ion exchange chromatography. It will highlight the different column characteristics—pore size, particle size, base matrices, column dimensions, ligands—and which questions will help decide which columns to use.
The Benefits of Custom Bonded Silica
April 1st 2025Not all chromatography resins are created equal. Off-the-shelf chromatography resins might not always meet the rigorous purification requirements of biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Custom bonded silica from Grace can address a wide range of separation challenges, leading to real performance improvements. Discover more about the latest innovations in chromatography silica from Grace, including VYDAC® and DAVISIL®.
5 Things to Consider When Selecting a Chromatography Silica
April 1st 2025Particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, drug purity isn’t just a goal – it’s essential for achieving safety, stability and efficacy. However, purification is easier said than done, especially with challenging molecules like DNA and RNA “oligonucleotides,” due in large part to their diversity and the range of impurities that can be generated during production. Enter DAVISIL® chromatographic silica, with a wide range of pore diameters and particle sizes to meet your specific application, performance and sustainability requirements. Before you choose the chromatography resin for your next purification application, take a look at these 5 considerations.
Automating Protein Purification: Efficiency, Yield, and Reproducibility
March 27th 2025Recent advancements in automated protein purification stress the importance of efficiency, scalability, and yield consistency. This eBook compares different purification platforms, highlighting their impact on downstream applications and demonstrating how automation enhances throughput and process control.














