Determination of Diethylene Glycol in Sorbitol Solutions Used for Pharmaceutical Formulations
Ingestion of DEG-adulterated glycerin excipients in pharmaceuticals and personal care products, such as toothpaste, mouth wash, and medicinal syrups has caused systemic alcohol intoxication, acidosis, and subsequent multi-organ failure that have led to hundreds of fatalities of children and adults (1). To help prevent future adulterations, the U.S. FDA requested that the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) revise the USP 32 NF 26 monograph to identify and quantify EG and DEG in sorbitol solutions at the maximum limit of 0.1%. The revised monograph (USP 33-NF 28) meets these criteria using GC-FID (2).
Terri T. Christison, Brian M. De Borba, and Jeffrey S. Rohrer, Dionex Corporation
Ingestion of DEG-adulterated glycerin excipients in pharmaceuticals and personal care products, such as toothpaste, mouth wash, and medicinal syrups has caused systemic alcohol intoxication, acidosis, and subsequent multi-organ failure that have led to hundreds of fatalities of children and adults (1). To help prevent future adulterations, the U.S. FDA requested that the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) revise the USP 32 NF 26 monograph to identify and quantify EG and DEG in sorbitol solutions at the maximum limit of 0.1%. The revised monograph (USP 33-NF 28) meets these criteria using GC-FID (2). To minimize the possibility of false positives, we used a confirmatory liquid chromatography method to determine 0.1% DEG in sorbitol solutions (3).
Here, we describe the determination of 0.1% DEG in a sorbitol solution using a mixed-mode separation with an ion-exclusion (ICE) guard and a cation-exchange analytical column with pulsed amperometric detection (PAD) and a Pt working electrode. The method takes advantage of the selectivity of combining ion-exclusion, cation-exchange, and reversed-phase properties to fully resolve DEG from other glycols and the large sorbitol matrix peak. Additionally, PAD provides a sensitive, selective, and direct detection of DEG without cumbersome derivatization.
Experimental
A Dionex ICS-3000 system was used in this study. DEG (25 μL) was separated using an IonPac® ICE-AS1 guard column (4 × 50 mm) and IonPac CS14 analytical column (2 × 250 mm) with 100 mM methanesulfonic acid at 0.2 mL/min (3). DEG was detected using PAD with a disposable platinum electrode and three-potential waveform. Chromeleon® 6.8 Chromatography Data System (CDS) software (Dionex) was used for system control and data processing. The 50 mg/mL sorbitol samples were spiked with 0.050 mg/mL DEG and diluted 1:4 for analysis.
Results
Figure 1 shows the determination of 0.013 mg/mL DEG in 13 mg/mL sorbitol solution using a mixed-mode separation and PAD with 107% recovery. DEG is easily resolved from the large sorbitol peak and small unknown peaks (peaks 3 and 5). The method was sensitive with an LOD and LOQ of 3.1 and 10 μg/mL, respectively. This corresponds to 0.024 and 0.077% in a 13 mg/mL sorbitol solution. The calibration from 0.013 to 0.10 mg/mL DEG produced a correlation coefficient (r2 ) of 0.9993. The retention time and peak area precisions of 0.013 mg/mL DEG (n = 7) produced RSDs of 0.17 and 2.2, respectively.
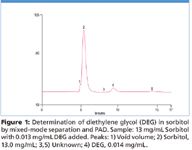
Figure 1
This method can be used as a primary method for determining DEG in sorbitol solutions or to confirm the results obtained by GC-FID. The method directly, accurately, and selectively determines DEG in mg/mL sorbitol solutions at concentrations below the USP monograph limit of 0.1% DEG. Samples suspected of adulteration need only be diluted and analyzed to evaluate their safety.
References
(1) K. L. O'Brien, J. D. Selanikio, C. Hecdivert, M-F. Placide, M. Louis, D. B. Barr, J. R. Barr, C. J. Hospedales, M. J. Lewis, B. Schwartz, R. M. Philen, S. St. Victor, J. Espindola, L. L. Needham, K. Denerville, Acute Renal Failure Investigation Team. Epidemic of Pediatric Deaths From Acute Renal Failure Caused by Diethylene Glycol Poisoning, JAMA, 279 (15), 1175–1180 (1998).
2. United States Pharmacopeial. Sorbitol Solution, Pharmacopeial Revision Bulletin. To be printed in USP 33, NF 28 First Supplement, released 1 February 2010, official 1 August 2010.
3. Dionex Corporation. Determination of ethylene glycol and diethylene glycol in a sorbitol solution, Application Note 246, LPN 2505, Sunnyvale, CA, 2010.
IonPac and Chromeleon are registered trademarks of Dionex Corporation.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088
tel. (408)737-0700; fax (408)730-9403
Website: www.dionex.com.

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.














