Matrix Elimination — In-line Removal of Chloride using InGuard Ag and Na Cartridges
The Application Notebook
In ion chromatography, the presence of a large amount of matrix ions makes quantification of the target ions difficult. Selective removal of matrix ions - matrix elimination - can be performed by treating a sample with a solid-phase extractant. Halides can be removed by precipitation with silver, which is present as a counterion in a cation-exchange resin. A subsequent treatment with a cation-trapping column removes residual dissolved silver ions.
Bernard G. Sheldon,1 Rida Al-Horr2 and Rosanne Slingsby,1
1Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, California, USA,
2Dow Chemical, Houston, Texas, USA.
In ion chromatography, the presence of a large amount of matrix ions makes quantification of the target ions difficult. Selective removal of matrix ions — matrix elimination — can be performed by treating a sample with a solid-phase extractant. Halides can be removed by precipitation with silver, which is present as a counterion in a cation-exchange resin. A subsequent treatment with a cation-trapping column removes residual dissolved silver ions.
When analysing a sample for nitrite, it is important to maintain a high pH to preclude oxidation of nitrite to nitrate, which occurs readily at low pH. Therefore, sodium ion (Na+) should be used as the counterion on the silver-trapping column.
Solid-phase manual extraction columns, such as OnGuard II cartridges are useful for processing a limited number of samples; they are discarded after use with a single sample. Newly introduced InGuard cartridges provide automated in-line matrix elimination capabilities, which reduce sample-processing costs, increase processing reliability and enhance ease-of-method documentation and transfer.
InGuard cartridges are used in an ion chromatograph to treat samples before they are injected. The sample is metered with a sample loop and transferred to a concentrator column after being passed through the InGuard cartridge or cartridges. While InGuard cartridges have capacities similar to their OnGuard analogues, the InGuard cartridges will only be exposed to a small amount of sample per injection and, therefore, can be used many times before they are exhausted.
Experimental
A Dionex ICS-3000 system with a DP dual pumping system and a detector compartment equipped with two 6-port valves was used here.
The first valve was a standard high-pressure 6-port injection valve equipped with a 100 μL sample loop. The second valve was a 6-port high-pressure valve installed on the automation manager of the DC. An InGuard Ag and an InGuard Na cartridge were plumbed in series between the two valves. The second pump transferred the sample from the sample loop through the cartridges and onto a concentrator column (Figure 1).
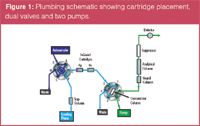
Figure 1
The passage of the sample through the InGuard cartridges may cause some dilution and band-broadening of the sample. A concentrator column traps and concentrates the sample into a small volume before injection onto the analytical column.
Results and Discussion
This application demonstrates the utility of a fully automated method with new InGuard Ag and Na in-line matrix elimination cartridges for removal of chloride from a sample before injection. If not removed, a 1.6% sodium chloride sample, as the one being analysed, would overwhelm the capacity of the analytical column used. The result would be an offscale peak with no resolution of the analytes of interest (Figure 2).

Figure 2
InGuard Ag cartridges contain approximately 5 mEq of silver ion, which is sufficient to remove the chloride from approximately 100 injections of 100 μL each of a 1.6% sodium chloride solution.
OnGuard, IonPac and ASRS are registered trademarks and InGuard is a trademark of Dionex Corporation.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, PO Box 3603, Sunnyvale, California, USA
tel. +1 408 737 0700 fax +1 408 730 9403
Website: www.dionex.com

The Next Frontier for Mass Spectrometry: Maximizing Ion Utilization
January 20th 2025In this podcast, Daniel DeBord, CTO of MOBILion Systems, describes a new high resolution mass spectrometry approach that promises to increase speed and sensitivity in omics applications. MOBILion recently introduced the PAMAF mode of operation, which stands for parallel accumulation with mobility aligned fragmentation. It substantially increases the fraction of ions used for mass spectrometry analysis by replacing the functionality of the quadrupole with high resolution ion mobility. Listen to learn more about this exciting new development.
Liquid Chromatography to Analyze Vitamin D Proteins in Psoriasis Patients
January 21st 2025Can a protein involved in delivering Vitamin D to target tissues have an altered serum profile in psoriasis patients with cardiovascular disease? Researchers used liquid chromatography (LC) to help find out.
The Complexity of Oligonucleotide Separations
January 9th 2025Peter Pellegrinelli, Applications Specialist at Advanced Materials Technology (AMT) explains the complexity of oligonucleotide separations due to the unique chemical properties of these molecules. Issues such as varying length, sequence complexity, and hydrophilic-hydrophobic characteristics make efficient separations difficult. Separation scientists are addressing these challenges by modifying mobile phase compositions, using varying ion-pairing reagents, and exploring alternative separation modes like HILIC and ion-exchange chromatography. Due to these complexities, AMT has introduced the HALO® OLIGO column, which offers high-resolution, fast separations through its innovative Fused-Core® technology and high pH stability. Alongside explaining the new column, Peter looks to the future of these separations and what is next to come.
A Guide To Finding the Ideal Syringe and Needle
January 20th 2025Hamilton has produced a series of reference guides to assist science professionals in finding the best-suited products and configurations for their applications. The Syringe and Needle Reference Guide provides detailed information on Hamilton Company’s full portfolio of syringes and needles. Everything from cleaning and preventative maintenance to individual part numbers are available for review. It also includes selection charts to help you choose between syringe terminations like cemented needles and luer tips.