Universal Analytical Method Development for Various HPLC Systems
The Application Notebook
This application note describes a combined approach of analytical method development and method transfer by direct emulation of different target HPLC systems.
Edgar Naegele and Andreas Borowiak, Agilent Technologies, Inc.
This application note describes a combined approach of analytical method development and method transfer by direct emulation of different target HPLC systems.
Method development facilities face the challenge to develop LC methods for a diversity of target systems used across different departments, or even within one analytical laboratory, because systems differ in manufacturer or LC generation. To overcome the need for many method development systems, this application note presents a workflow that combines analytical method development supported by Agilent Method Scouting Wizard with on-the-fly target system emulation using Agilent Intelligent System Emulation Technology (ISET). One of the emulated target systems was a Waters Acquity H-Class.
Experimental Conditions
For method development, an Agilent 1290 Infinity II Method Development Solution was used. This solution included a solvent selection valve and a Multicolumn Thermostat (MCT) with an eight-column selection valve. Methods necessary for column and gradient screening as well as for instrument flushing and column equilibration were created automatically using Agilent Method Scouting Wizard. Emulation of the target systems was done using Agilent Intelligent System Emulation Technology. To achieve a separation method suitable for the target LC system, C8, C18, phenyl-hexyl, and pentafluorophenyl (PFP) phases with small particles (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.9 μm) were used. The initial campaign was run with methanol and acetonitrile as organic solvents and at three different temperatures. The initial generic gradient had a length of 20 min and the organic solvent increased from 5% to 70%.
Results
As expected, C8 and C18 columns showed similar separation. Surprisingly, the PFP phase showed a dramatically earlier elution with slightly different selectivity. All compounds were already separated and the last peak eluted at a retention time of 12 min. In a second campaign, different flow rates and gradients were tested to separate the pesticide sample on the PFP column in a shorter run time and with optimum resolution. Finally, the separation could be achieved in only 7.4 min applying a gradient from 10% to 47% acetonitrile at a flow rate of 0.85 mL/min. The identity of the retention times could be seen in the comparison of the chromatograms obtained on the Agilent 1290 Infinity II Method Development System and the Waters H-Class system. Typical standard deviations of retention times below 0.01 min could be found. Corresponding RSD values were typically below 0.2%. The differences in retention time between the development system and the target system were typically below 2%. The complete method development workflow took approximately 37 h.
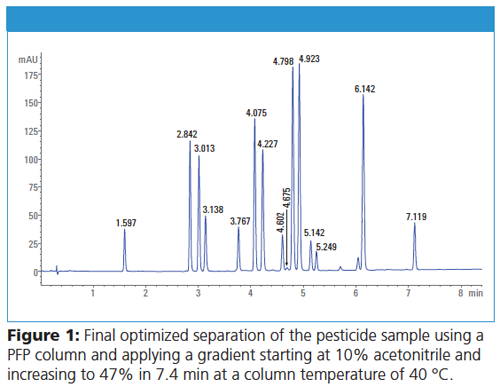
Conclusions
This application note demonstrates the use of the Agilent 1290 Infinity II Method Development Solution with Agilent Method Scouting Wizard for direct development of analytical separation methods under ISET control for a chosen target system. The results showed excellent correlation between the method developed on the Agilent 1290 Infinity II Method Development Solution and the target system. The retention time deviation was typically below 2%.

Agilent Technologies, Inc.
5301 Stevens Creek Blvd., Santa Clara, California 95051, USA
Tel.: (800) 227 9770
Website:www.agilent.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.
Accelerating Monoclonal Antibody Quality Control: The Role of LC–MS in Upstream Bioprocessing
This study highlights the promising potential of LC–MS as a powerful tool for mAb quality control within the context of upstream processing.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)










