A Three-Pronged Template Approach for Rapid HPLC Method Development
LCGC North America
HPLC method development can be accelerated by using three distinct method templates of increasing complexity.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method development is an arduous process requiring considerable experience and scientific judgment. This column installment presents a road map for rapid HPLC method development using a three-pronged approach. In this approach, three distinct method templates of increasing complexity are defined: fast LC isocratic methods, generic broad gradient methods, and multi-segment gradient stability-indicating methods. The characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each template are described, and case studies are used to illustrate their applications. The use of this template approach is expected to expedite the method development process, particularly during early-phase drug development.
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method development is a labor-intensive and time-consuming task performed mostly by more-experienced scientists. Paradoxically, the best method development strategy is actually no method development — that is, if an acceptable method can be found elsewhere. In many cases, method development is unavoidable such as to support the development of new chemical entities (NCE) (for example, new drugs or chemicals). An HPLC analytical method typically consists of two major parts: the sample preparation procedure and the HPLC operating conditions. This column installment focuses on the latter part of the process by first summarizing a systematic method development strategy and by proposing a simple three-pronged template approach.
There is no shortage of information on HPLC method development. Useful information can be found in chapters of HPLC books (1,2), specialized books on method development (3–5) and pharmaceutical analysis (6,7), journal publications, short courses, and web resources.
An abbreviated synopsis of a "common method development strategy," extracted from references 2 and 3, is included here for the convenience of our readers. The reader is referred to the original sources for a fuller description of the steps highlighted below.
Defining Method Goal and Sample Type
The most important question for the analytical method's goal is: Is the method for quantitation of the main component only (potency methods) or for purity determination (stability-indicating)? Another important question is: Is the method for quality control (QC)? QC methods and testing in a regulated environment typically have more-stringent method performance and robustness requirements. Sample type is also important because sample complexity dictates the column length and HPLC operating conditions, whereas the sample matrix may impose additional requirements in sample preparation and detection.
Gathering Sample and Analyte Information
A thorough literature search can often provide a ready-to-use method or at least some useful starting points for method development. Knowledge of the analytes such as their chemical structure, molecular weight, purity, solubility, LogD value, number of acidic and basic functional groups and chiral centers, pKa, absorbance maximum (λmax), toxicity, degradative pathways, reactivity, and stability are useful. Other valuable resources are material safety data sheets (MSDS), certificates of analysis (COA), and suppliers' technical packages. Unfortunately, information about the physicochemical properties of the molecule, while useful to avoid pitfalls, does not necessarily lead to an easier path for method development.
Initial Method Development
Before initiating method development to obtain the first chromatograms of the sample, some immediate decisions are needed: selection of HPLC mode, detection technique, column, and mobile phases. In many cases, some default or standard conditions appear to work well for the first "scouting" method; for instance, reversed-phase LC mode with a C18 column, UV detection (for chromophoric compounds), mobile-phase A: 0.1% acid in water and mobile-phase B: acetonitrile or methanol. The most common mobile-phase A additives are: trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid, or phosphoric acid. The actual column dimension and particle size of the packing are dictated by the complexity of the sample and the method's goals (2,3). For nonchromophoric analytes, refractive index, evaporative light-scattering, charged-aerosol, or mass spectrometry (MS) detection can be used. For isocratic analysis, a process of sequential isocratic steps is generally effective (2,8). This is accomplished by lowering the solvent strength of the mobile phase until all key analytes are retained and resolved. For purity testing or separation of more complex mixtures, a broad linear gradient separation from 5% to 100% mobile-phase B is used to generate the first chromatograms. Typically, this approach reveals the number of components and overall purity of the sample. The molecular weights and λmax values of the analytes are easily obtained using MS and photodiode-array detection, respectively.
Method Fine-Tuning and Optimization
For purity analysis, test mixtures (cocktails) of process precursors, impurities, degradants, additives, and excipients are used to confirm that the method is able to separate all of these components (that is, to establish that the method is specific). Mother liquors from the final crystallization step and forced degradation samples are used if reference standards of impurities are not available (2,6,7). The use of forced degradation samples is required to establish the stability-indicating nature of a method. Screening of different columns and mobile phases (pH, buffers, organic solvents), and adjustment of operating conditions (temperature, flow rate, gradient time [tG], gradient range — that is, starting and ending %B, and single or multiple-segment gradients) are used to resolve all key analytes. Finally, the HPLC conditions are optimized for sensitivity, peak shapes, and analysis time.
The fine-tuning step, often called "selectivity tuning," is the most time-consuming step in the method development process. According to Lloyd Snyder, a pioneer in HPLC and a champion in simulation software, the "trial-and-error" approach of varying one factor at a time (OFAT) still reigns in HPLC method development (9). This often "graduates" to an "enlightened trial-and-error" approach for the experienced scientist with a good understanding of chromatographic principles who can establish the final method conditions in fewer steps. With the numerous factors controlling retention during gradient elution, this OFAT strategy is clearly not a very efficient process, even for the expert. Here, the use of simulation software (such as DryLab [Molnar Institut or ChromSword Group]) and automation systems (for example, a column–mobile phase screening system, Fusion AE QbD [S-Matrix], or AutoChrom [ACD/Labs]) is particularly helpful for the optimization process of methods for difficult samples (2,8–10). For the primary stability-indicating assays used in drug development and QC, a systematic and thorough method development process is increasingly becoming a regulatory expectation if not yet a requirement (11). It is worthwhile to note that HPLC method development during clinical development of new drugs is often an iterative process, repeated many times to accommodate the resolution of unexpected impurities found in new synthetic routes or formulations. To conserve resources, a proactive "stage-appropriate method development and validation approach" is adopted by many pharmaceutical laboratories (2,6).
Method Prequalification
Method validation (or qualification) is needed to ensure data accuracy and "fit for purpose." It is a mandatory requirement for quality control or regulated testing to demonstrate that the method is "suitable for its intended use." Therefore, the last step of method development is often a prequalification step (checking for specificity, linearity, precision, and sensitivity) to demonstrate that the method is "validatable." Method validation is a good manufacturing practice (GMP) process and method development is not a GMP activity. Thus, it is prudent to make sure that the newly developed method can be validated before the execution of the formal method validation protocol.
Shortcomings and Potential Improvements of the Common Method Development Strategy
The common strategy described above (or other similar process) is generally accepted by most practitioners. Nevertheless, some shortcomings and potential improvements of the process are noted here:
- The systematic strategy may be too arduous for less-critical samples (such as raw materials or simpler mixtures) or for potency assays.
- The use of generic methods may be "good enough" for many samples or applications. This approach is fairly common in high-throughput or process chemistry laboratories but is less common in analytical development or QC operation. Benefits of such generic or platform methods include time savings in method development, method validation, and method transfer in addition to efficiency gains from standardization.
- Developing a stability-indicating method of a complex molecule or sample is the most challenging task and well suited to a systematic method development strategy. Nevertheless, the availability of a method template with useful gradient profiles and operating guidances can facilitate the method fine-tuning step in the development process.
The Three-Pronged Template Approach: What Is It?
The three-pronged template approach is a concept that helps to expedite the method development process by providing three common method templates and a set of practical ground rules for the selection of templates, columns, and operating conditions. It is a simple, pragmatic approach with a focus on reversed-phase HPLC using UV detection. Figure 1 illustrates the concepts of the three templates of increasing complexity (fast isocratic LC, generic broad gradient, and multisegment gradient). Characteristics, applications, and limitations of each method template are described and illustrated with case studies below.
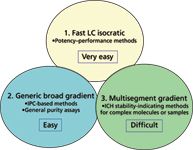
Figure 1: Diagram depicting the three method templates in the three-pronged approach and their relative ease for implementation. ICH = International Conference on Harmonization. IPC = in-process control.
Fast LC Isocratic Potency and Performance Methods
For potency testing (that is, quantitative determination of the main component), a fast LC isocratic method is recommended for simplicity and speed. Figure 2 is an example of a fast LC isocratic method using a short column (for example, a 50 mm × 4.6 mm C18 column) with UV detection at λmax of the analyte. A recommended retention factor (k) of ~1–2 with an analysis time <2 min appears to be feasible in most cases. Application examples are potency assays such as dosing solutions analysis, and content uniformity and dissolution testing of drug products. Method development is very quick using sequential isocratic steps to retain the analytes away from the solvent front (2). Alternately, the optimum isocratic %B can be obtained from a linear broad-gradient (for example, 5–100% B) scouting run. Higher retention may be needed to separate the main component from major interferences. These potency methods can be developed and prequalified in hours. However, they are not stability-indicating methods and have limited resolution or peak capacities. One potential pitfall of a fast LC method is the possible interference from a hydrophobic component such as antioxidant additives in drug product formulations. The use of gradients or isocratic runs with column purging steps is recommended in such cases.
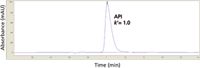
Figure 2: An example of the "fast LC isocratic potency and performance method template" used for content uniformity and dissolution (performance) testing of a drug product (capsule). Column: 50 mm à 4.6 mm, 3-µm dp Waters X-Bridge C18; mobile phase: 30% acetonitrile, 70% water with 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min at 30 °C; detection: 280 nm (λmax of the API); sample: 10 µL of a drug product extract containing ~0.1 mg/mL of API in 1 N hydrochloric acid. Note this potency method is nonstability-indicating with k = 1.0 for the analyte.
Generic Broad Linear Gradient Methods
The use of generic broad-gradient HPLC methods to monitor reaction progress is very common in organic synthesis laboratories. Broad, linear gradients in reversed-phase mode are typically used (for example, 5–95% B or 100% B) because they usually can elute all components and separate most of them in the sample. Generic gradient methods are also the standard practices in process scale-up laboratories for in-process control (IPC) testing and in medicinal chemistry laboratories for rapid characterization or purification of crude compounds. Multiple UV wavelength monitoring (such as 220, 254, and 280 nm) or mass spectral data are typically recorded.
In contrast, scientists in analytical development or QC laboratories tend to develop custom methods for each NCE in their project, leading to a proliferation of methods with myriad combinations of columns and mobile phases. It appears that the generic gradient approach can be readily applied to purity analysis of many sample types (such as drug substances, drug products, raw or starting materials, and reagents) and other applications (for example, cleaning verification). Figure 3 shows an example of a purity assay method for a starting material (Boc-β-amino acid) using HPLC conditions similar to those used in a typical IPC method. Figure 3a is a chromatogram of a cocktail mixture of the starting material reference standard (F) and all its synthetic precursors. Figure 3b is a chromatogram of a starting material with a purity value of ~98% using an area percent calculation.
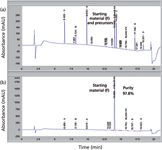
Figure 3: A case study of the "generic broad-gradient method template" used for the purity analysis of a starting material used in the synthesis of a new chemical entity: (a) Chromatogram of a standard solution containing the starting material (F) with its precursor compounds (A to E and G) at ~0.1 mg/mL each. (b) Chromatogram showing the purity profile of the starting material (F) at 0.5 mg/mL with an area percent of 97.8%. Column: 150 mm à 4.6 mm, 3-µm dp ACE-3-C18; mobile-phase A: 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid in water; mobile-phase B: 0.03% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min at 35 °C; gradient program: 5â95% B in 15 min, 95% for 2 min, 95â5% B in 0.1 min; detection: 220 nm.
The selection of detection wavelength in HPLC–UV analysis is rarely discussed in the literature (2). The use of λmax of the main component offers a sensitive and selective detection of the main component and its related substances, but can miss impurities without similar chromophores. A low-UV detection wavelength such as 220 nm offers more universal detection of most components, though it may have lower sensitivity when using MS-compatible mobile phases with end UV absorbance. For low chromophoric compounds (such as raw materials or reagents), a more universal detection wavelength of 200 nm can be used with phosphate buffers (or phosphoric acid) and acetonitrile.
Recently, a universal 10-min generic HPLC method for cleaning verification was developed and qualified for GMP use (shown in Figure 4). Here, a gradient of 10–60% B was found to work well for many drug candidates (12). Two 1.5-min methods using ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) equipment and short 2.1-mm i.d. columns packed with sub-2 µm porous or sub-3-µm core-shell particles (12) were demonstrated to have equivalent sensitivity to the 10-min HPLC method.
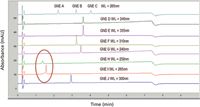
Figure 4: Another case study of the "generic broad-gradient method template" used as a universal platform method for clean verification. The red circle indicates two compounds with peak symmetry issues. Column: 50 mm à 3.0 mm, 3-µm dp Waters X-Bridge C18; mobile-phase A: 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid in water; mobile-phase B: 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min at 30 °C; gradient program: 10â60% B in 7 min, 60â10% B in 0.1 min; detection: UV wavelength labeled in the inset corresponding to λmax of each NCE (GNE A to J); sample: NCE at 0.1 µg/mL in 50:50 methanolâmobile-phase A with a 20-µL injection. Adapted with permission from reference 12.
This generic broad-gradient approach is applicable to the purity analysis of most compounds as well as in IPC testing and cleaning verification. Because the same standard methods are used with little or no modifications, they can be developed, qualified, and transferred quickly, leading to major productivity gains and time-savings from standardization. Very fast high-throughput screening methods (1–2 min methods with ballistic gradients) are expected to become increasingly popular for many applications. One can even argue that a universal HPLC–UV or HPLC–charged-aerosol detection approach could be adopted as a general potency method in most cases. Nevertheless, this generic broad-gradient approach appears to be less amenable to methods for complex samples or molecules with isomeric impurities, which would require a more elaborate method development process.
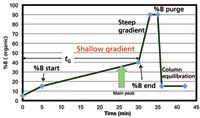
Figure 5: An example of a gradient profile of the multisegment gradient method template showing a shallow middle segment (15â40% B in 25 min) with the main component eluted toward the end. This segment is preceded by an early segment (5â15% B in 5 min) and followed by a steep segment (40â90% B in 3 min) with a 2-min purging step at 90% B.
Multisegment Gradient Methods for New Chemical Entities or Complex Samples
A literature review for stability-indicating methods of NCEs, active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), or complex samples indicated that many final methods follow a multisegment gradient pattern shown in Figure 5. Rationales for using these more complex operating conditions are as follows:
- Isomers, impurities, and degradants of the API usually have structures similar to the parent molecule and, therefore, would have similar HPLC behavior.
- A shallow gradient with the API (or the main component) eluted toward the end of the shallow gradient (or an isocratic segment) would maximize resolution around the API region. The ending %B of this segment is defined by the hydrophobicity of the API.
- A steep gradient segment plus a purging step is typically used to elute highly retained components (for example, dimers or hydrophobic additives).
- An initial low-strength gradient segment or an isocratic step may be needed to retain polar impurities (for example, hydrolytic degradants or hydrophilic impurities).
Figure 6 shows UHPLC chromatograms of a complex multichiral molecule in a standard solution spiked with potential impurities and in a drug product extract using a three-segment gradient (13). The middle shallow gradient segment (15–40% B in 10 min) allows separation of the API (with an absolute configuration of SRR) from its diastereomers (SRS and RRR) and other closely eluted impurities (M416, ketone, M456, and M399 — designated parent MS ions); the first low-strength segment allows the retention of a hydrolytic degradant (M235); the final steep gradient segment allows the determination of the antioxidant — butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and other hydrophobic impurities. Note that the single, broad, linear gradient is still the norm during initial method development and column screening, but it is unlikely to provide sufficient resolution around the API to resolve these close-eluted impurities. The selection of a narrower gradient range is often a secondary next step in the systematic strategy (2). Understanding the rationale behind the multisegment gradient program in the final methods offers helpful insights in the fine-tuning step during method development.
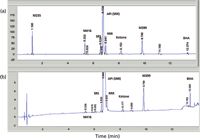
Figure 6: A case study of the multisegment gradient method template of a composite method (potency and purity) of a drug product. Shown are UHPLC chromatograms of (a) a retention marker solution and (b) a three-month accelerated stability sample (extract of a tablet kept at 50 °C and 75% RH). Column: 100 mm à 3.0 mm, 2-µm dp ACE Excel 2 C18; mobile-phase A: 20 mM ammonium formate, pH 3.7; mobile-phase B: 0.05% formic acid in acetonitrile; flow rate: 0.8 mL/min; temperature: 40 °C; pressure: 450 bar; gradient: 5â15% B in 2 min, 15â40% B in 10 min (middle segment), 40â90% B in 1 min; detection: UV absorbance at 280 nm; sample: tablet extract in 20% acetonitrile in 0.1 N hydrochloric acid (aq.) with a 3-µL injection. Adapted with permission from reference 13.
Figure 7 shows an HPLC chromatogram for a final stability-indicating method of another NCE using a two-segment gradient program (14). This method development case study started with a rapid UHPLC column screening with broad linear gradient (5–95% B in 5 min) to identify an optimum column with a polar-embedded phase, and progressed toward method fine-tuning with a narrower gradient range (5–50% B in 10 min) on a longer column to arrive at an acceptable UHPLC method. Next, the UHPLC method was "back-transferred" to a more universally applicable HPLC method shown in Figure 7. The HPLC method was then validated for GMP use (14). Note that the use of a multisegment gradient program does present additional complications for simulation software using the linear-solvent-strength model (2,15) and for selectivity optimization using different organic solvents (that is, acetonitrile and methanol because of their disparate chromatographic strengths resulting in different gradient ranges). Nevertheless, multisegment gradient methods appear to be quite typical for the separations of diastereomers in molecules with multiple chiral centers, which are increasingly common as new small molecule drug candidates. The number of gradient segments is dependent on the impurity profiles of the molecules and can be as high as four or five for combination drug products with multiple APIs (16). Additional applications of the multisegment gradient programs are LC–UV methods for peptide mapping of protein biopharmaceuticals (17) and drug products from natural material (16).
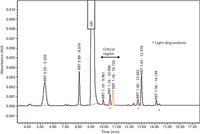
Figure 7: A case study of a composite HPLC method of a new drug substance. This final HPLC method using a two-segment gradient was "back-transferred" from a set of UHPLC conditions. Column: 150 mm à 3.0 mm, 3-µm dp Waters X-Bridge C18; mobile-phase A: 20 mM ammonium formate, pH 3.7; mobile-phase B: acetonitrile; flow rate: 0.8 mL/min; temperature: 30 °C; pressure: 250 bar; gradient: 10â40% B in 25 min, 40â100% B in 3 min; UV detection: 253 nm; sample: API in mobile-phase A at 0.2 mg/mL with a 3-µL injection. Note that only a portion of the chromatogram (3â17 min) is shown here. RRT = relative retention time; * designates light degradants. Adapted with permission from reference 14.
Concluding Remarks
The systematic method development strategy is effective for critical or complex samples and can be facilitated by software tools or automated systems. The three-pronged template approach proposed here offers a practical starting point for method development by focusing on the goals and attributes of the final methods. It provides easy templates for method development of potency assays and simpler samples, and offers a targeted pathway during method fine-tuning for difficult samples. This simple, rapid three-pronged template approach leads to a more efficient method development strategy for our busy colleagues, particularly for those in early-phase drug development.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to Dr. Raphael Ornaf of Vertex Pharmaceuticals; Dr. Lloyd Snyder (retired, Orinda, California); Professor Davy Guillarme of University of Geneva, University of Lausanne; Ross Woods of University of Texas at Arlington; and Eileen Zhao and Dr. Sam Yang of Genentech for their suggestions and comments to the manuscript. The opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and bear no reflections on those of LCGC North America or other organizations.
References
(1) L.R. Snyder, J.J. Kirkland, and J.W. Dolan, Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography, 3rd Ed. (John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2010), pp. 405–497.
(2) M.W. Dong, Modern HPLC for Practicing Scientists (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2006), pp. 193–220.
(3) L.R. Snyder, J.J. Kirkland, and J.L. Glajch, Practical HPLC Method Development (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1997).
(4) S. Matthew, Analytical Method Development by HPLC for Starters, 1st Ed.(E-book from Amazon.com, Amazon Digital Services, Inc., Seattle, Washington, 2012).
(5) M.E. Swartz and I. Krull, Analytical Method Development and Validation, 1st Ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1997).
(6) H.T. Rasmussen, Q.Y. Li, D. Redlich, and M.I. Jimidar, in Handbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis by HPLC, S. Ahuja and M.W. Dong, Eds. (Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2005), pp. 145–191.
(7) R. LoBrutto, in HPLC for Pharmaceutical Scientists, Y.V. Kazakevich and R. LoBrutto, Eds. (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2007), pp. 347–454.
(8) D. Guillarme and M.W. Dong, Amer. Pharm. Rev. 16(4), 36–43 (2013).
(9) L.R. Snyder, LCGC North Am. 25(8), 437–444 (2012).
(10) Y. Li, G.T. Terfloth, and A.S. Kord, Amer. Pharm. Rev. 12(4), 87–95 (2009).
(11) ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline, Impurities in new drug substances, Q3A (R2), 25 October 2006, ICH Expert Working Group.
(12) M.W. Dong, E.X. Zhao, D.T. Yazzie, C.C. Gu, and J.D. Pellett, Amer. Pharm. Rev. 15(6), 10–17 (2012).
(13) M.W. Dong, LCGC North Am. 31(6), 472–479 (2013).
(14) M.W. Dong, LCGC North Am. 25(7), 656–666 (2007).
(15) L.R. Snyder and J.W. Dolan, High-Performance Gradient Elution: The Practical Application of the Linear-Solvent-Strength Model (Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2006).
(16) M.W. Dong, D. Guillarme, S. Fekete, R. Rangelova, J. Richards, D. Prudhomme, and N.P. Chetwyn, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., submitted.
(17) J. Ruta, D. Guillarme, S. Rudaz, and J.L. Veuthey, J. Sep. Sci. 33, 2465–2477 (2010).
Michael W. Dong is a senior scientist in Small Molecule Drug Discovery at Genentech in South San Francisco, California. He is responsible for new technologies, automation, and supporting late-stage research projects in small molecule analytical chemistry and QC of small molecule pharmaceutical sciences. He holds a PhD in analytical chemistry from the City University of New York and a certificate in Biotechnology from U.C. Santa Cruz. He has conducted numerous courses on HPLC/UHPLC, pharmaceutical analysis, HPLC method development, drug development process, and drug quality fundamentals. He is the author of Modern HPLC for Practicing Scientists and a co-editor of Handbook of Pharmaceutical Analysis by HPLC. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of LCGC.

Michael W. Dong

Extracting Estrogenic Hormones Using Rotating Disk and Modified Clays
April 14th 2025University of Caldas and University of Chile researchers extracted estrogenic hormones from wastewater samples using rotating disk sorption extraction. After extraction, the concentrated analytes were measured using liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection (HPLC-PDA).
Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.