Taking Advantage of Sub-2 ?m Core–Shell Technology for Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Efficient Urinary Excretion Profiling
Throughout the drug development process, potential new drug candidates (or new chemical entities; NCEs) and their metabolites must be subjected to rigorous and extensive pharmacokinetic evaluations to determine their rates accumulation, metabolism, and excretion from the body. With regards specifically to the excretion, urinary excretion is typically the predominant route for the elimination of drugs and their metabolites, and urinary excretion profiling is an integral portion of the pharmacokinetic characterization of NCEs.
Throughout the drug development process, potential new drug candidates (or new chemical entities; NCEs) and their metabolites must be subjected to rigorous and extensive pharmacokinetic evaluations to determine their rates accumulation, metabolism, and excretion from the body. With regards specifically to the excretion, urinary excretion is typically the predominant route for the elimination of drugs and their metabolites, and urinary excretion profiling is an integral portion of the pharmacokinetic characterization of NCEs.
Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectroscopy (LC–MS-MS) allows scientists to rapidly and accurately quantify specific drugs and their metabolites at extremely low levels from various biological matrices, such as urine. On the liquid chromatography side, the ultra-high efficiency delivered by sub-2 μm UHPLC core–shell media provides analysts with the ability to run their samples in extremely short periods of time while maintaining excellent resolution from sample interferences. In this application note, we present an example of the ability of the Kinetex® 1.7 μm core–shell particle to deliver significantly improved performance over larger core–shell particles and conventional fully porous media.
Experimental Conditions
LC–MS-MS conditions
Column: Kinetex 1.7 μm C18 30 × 2.1 mm Fused-core 2.7 μm C18 50 × 2.1 mm Fully porous 3.5 μm C18 50 × 2.1 mm
Mobile Phase: A: 10 mM Ammonium formate B: Acetonitrile
Gradient: (95:5) A/B to (0:100) A/B in 2 min, then re-equilibrate at (95:5) A/B for 1 min
Flow Rate: 700 μL/min
Temperature: Ambient
Detection: MS using API 4000 detector
HPLC system: Agilent 1200 SL
Concentration: 100 ng/mL for active drug and 50 ng/mL for metabolite
Analytes: Lorazepam-glucuronide spiked into urine at a concentration of 50 ng/mL

Figure 1: XIC for oxazepam glucuronide (MRM 463.1 -> 287.0) in urine.
Results
In many instances, suitable MRM transitions for an analyte of interest are hidden because of significant matrix interference. Oxazepam-glucuronide did not suffer from urinary interference (Figure 1), however the 497.2 -> 320.9 MRM transition for the glucuronide metabolite of lorazepam does show significant isobaric interference (Figure 2). In cases such as this, the ultra-high efficiency of the core–shell Kinetex 1.7 μm particle can provide significantly greater peak capacity than standard fully-porous media (3.5 μm in this case) and a larger fused-core particle (2.7 μm fused-core).
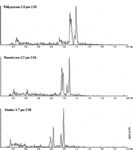
Figure 2: Comparison of the performance of the Kinetex 1.7 μm C18 (30 à 2.1 mm) column versus a fused-core 2.7 μm column (50 à 2.1 mm) and a fully porous 3.5 μm C18 column (50 à 2.1 mm) for the glucuronide metabolite of lorazepam (MRM 497.2 -> 320.9).
Phenomenex Inc.
411 Madrid Avenue, Torrance, CA 90501
tel. (310) 212-0555, (310) 328-7768
Website: www.phenomenex.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















