Superheated Water as an Extraction Solvent in Sample Preparation
The current status of superheated water extraction is reviewed, and the extraction methods, applications, and problems encountered are discussed.
Pressurized high temperature or superheated water is a green extraction solvent used in food, environmental, and traditional medicine studies for the extraction of non-polar and polar analytes including essential oils and spices, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals. The technique can be used on both the analytical and preparative scale to give a clean, solvent-free product for chromatographic analysis. This article reviews the current status of superheated water extraction, discussing extraction methods, applications, and, briefly, problems encountered with this approach.
Water at high temperature is often forgotten as a potential extraction solvent for sample preparation, yet it can be used in a wide range of applications, including the extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from soil and nutraceuticals from plant materials, for both non-polar and polar analytes. Unlike many other solvents, water is readily available in high purity at minimal cost, with minimal disposal costs and a negligible environmental impact. Its potential as a solvent is the result of it's unique properties when heated — the polarity changes from a polar solvent at room temperature with a specific permittivity of ε = 80 to ε = 30 at 220 °C in a pressurized system, which is comparable to many organic solvents at room temperature, such as methanol ε = 33. Mechanically it is easy to handle because only low pressures (15 bar at 200 °C) are required to maintain the liquid state. Unlike most organic solvents, it presents no danger from ignition or toxicity, and, although it is more volatile than ionic liquids, its vapours are environmentally benign.
Hot water is not often thought of as a typical extraction solvent but it is used every day at 100 °C to extract tea leaves and coffee beans. When we raise the temperature further, the polarity decreases and extraction power increases. From 100 °C up to around 300 °C under low pressures it is referred to as either superheated water, subcritical water, or pressurized hot water and has found application as an extraction solvent, as a chromatographic eluent, and as a solvent for organic synthesis. The recent interest in sample preparation and extraction was aroused in the 1990s by Hawthorne and co-workers who used superheated water as an extraction solvent in environmental studies for the extraction of PAHs from soils (1) and compared it to alternative extraction methods (2). They found that for non-polar analytes the change in extraction power with temperature can be dramatic. For example, the solubility of anthracene, chrysene, and perylene in water increased by 20,000-fold over the range 25–200 °C.
In later studies by a number of groups a wide range of analytes and matrices have been examined and these have been presents in reviews by Smith in 2002 (3); by Kronholm, Hartonen, and Riekkola in 2007 (4); and most recently in 2010 by Teo and co-workers (5) and Smith (6).
Extraction Methods
In common with other solvents, superheated water is most suitable for the extraction of solid samples such as soils, environmental solids, and dried plant material but can be difficult to apply to tissues, impervious food samples, or clinical samples. The equipment (shown in Figure 1) is fairly simple, consisting of a water supply, pump, an oven containing an extraction vessel, and post-oven restrictor to maintain the pressure. Typically, an old gas chromatograph (GC) oven can be used that will have good temperature control up to 300 °C. An empty column or similar configuration can act as the extraction vessel. Extraction can either be performed in a static or dynamic mode. In the latter case, a system as simple as a capillary or narrow-bore tube can provide sufficient restriction and back pressure to maintain the water in the liquid phase in the oven. The solvation power of high temperature water is effectively independent of the pressure, so an accurate control is usually not needed. Some recent extractions have used commercial accelerated solvent extraction systems but these are limited to 200 °C.
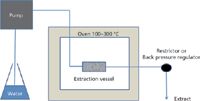
Figure 1: Superheated water extraction system.
After the extraction, the eluent water is cooled to room temperature and if sufficiently concentrated can be analyzed directly either by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography (GC). The extraction can also be linked directly to HPLC or superheated water chromatography, for example, to determine herbicides in compost (7). In that study, a single stream of water steam performed a sequential extraction, fractionation, and chromatographic separation by using temperature control.
For less concentrated samples, analytes can be extracted from the polar aqueous phase and concentrated before an assay using either a small volume of organic solvent, or a solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibre, adsorbent disc, stir-bar, hollow fibre, or a solid-phase extraction (SPE) cartridge before assay. Post extraction derivatization or modification can also be performed in the aqueous solution (8).
Applications
The wide scope of superheated water extraction is shown in the range of environmental, food, and herbal extracts that are listed in the many examples given in the earlier reviews (3–6). Some recent examples from the areas of environmental and petrochemical samples and from the rapidly growing area of food and plant materials illustrate the possible roles for the technique.
These studies include non-polar samples, such as aliphatic hydrocarbons from petroleum source rocks (9) and hydrocarbons from Huadian oil shale in China (10), and more polar PAH metabolites and pesticides (Table 1). Other environmental studies have included the determination of parabens from house dust (14) and personal care products in marine sediments. In a related study, superheated water has been used to release DDE and related compounds, which had been trapped and concentrated on a nanospun fibre (17).

Table 1: Recent examples of the use of superheated water extraction for environmental analysis and related topics.
This ability to extract non-polar analytes has also led to the use of superheated water in soil remediation as it does not markedly disrupt the soil structure unlike some alternative techniques. For example, in recent studies Islam and co-workers removed PAHs (18) and lubricating oils (19) from soils; and superheated water has been evaluated for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soil (20).
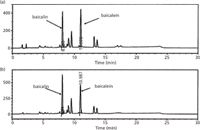
The main growth in recent years in superheated water extraction has been for the extraction of plant materials to yield natural products, such as essential oils or nutraceuticals (Table 2). Although similar to other methods that can be slower, such as steam distillation or solvent extraction, the proportions of polar and non-polar compounds can differ, altering the quality of the extracts. In a recent study by two-dimensional gas chromatography (2D–GC), the essential oil from Rosa damascena Mill obtained by superheated water extraction was compared with steam distillation and direct thermal desorption (27). With the growth of interest in the identification of traditional Chinese medicines and related products, it has become increasingly important to identify the composition and sources of the constituent plant materials. Superheated water extraction was found by Ong and co-workers (36) to give comparable characteristic biomarkers to conventional Soxhlet extraction (Figure 2).
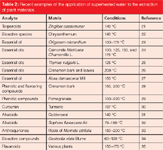
Table 2: Recent examples of the application of superheated water to the extraction of plant materials.
As well as analytical sample preparation for chromatographic analysis, many of these applications have been used in large-scale extraction processes of materials, such as onion skins (37), to provide potential commercial products. These applications often include HPLC or GC assays and have been reviewed by Mustafa and Turner (38), Chemet and co-workers (39), Mukhopadhyay and Panja (40), and Shi and co-workers (41). One advantage is that the absence of an organic solvent means that potential issues associated with solvent residues are avoided, particularly important if the product is intended for human consumption.
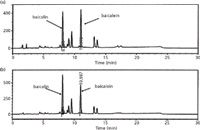
Figure 2: Comparison of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chromatograms obtained for baicalin and baicalein in Scutellariae radix by: (a) Soxhlet extraction; and (b) pressurized hot water extraction. Adapted and reproduced with permission from Elsevier (36).
Because superheated water extraction is generally unsuitable for clinical tissues or aqueous samples, it has not been widely applied in the pharmaceutical area. However, Wang and co-workers found that water at 100 °C could be used to extract oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol antibiotics from animal feeds for HPLC analysis (42). In another study Murakami and co-workers used superheated water up to 225 °C to rapidly extract fluoxetine-hydrochloride from capsules for HPLC analysis (43). Superheated water can also be used for inorganic analysis and Morado Piñeiro and co-workers determined arsenic and arsenic species in scalp hair by using superheated water extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LC–ICP–MS) (44).
Problem Areas
One concern that is always present when high temperatures are used is the potential degradation of analytes, but there are few reported examples. Although some degradation of hydrastine and berberine was observed by Mokgadi and coworkers (31) during the extraction of Goldenseal at 160 °C and 180 °C, this was not an issue at 140 °C. Leppänen and co-workers reported that at 240 °C, cellulose in Norway spruce samples could break down and be extracted (45) but not at lower temperatures.
Conclusion
Superheated water extraction between 100 °C and 250 °C can provide an environmentally friendly method of extraction for both polar and non-polar analytes from a wide range of matrices, more rapidly than Soxhlet methods, and without the problems of flammable and often toxic organic solvents.
Roger M. Smith is a Professor of Chemistry at Loughborough Univerisity, Loughborough, UK. Please direct correspondence to: R.M.Smith@lboro.ac.uk
References
(1) S.B. Hawthorne, Y. Yang, and D.J. Miller, Anal. Chem. 66(18), 2912–2920 (1994).
(2) S.B. Hawthorne, C.B. Grabanski, E. Martin, and D.J. Miller, J. Chromatogr. A 892(1–2), 421–433 (2000).
(3) R.M. Smith, J. Chromatogr. A 975(1), 31–46 (2002).
(4) J. Kronholm, K. Hartonen, and M.L. Riekkola, Trends Anal. Chem. 26(5), 396–412 (2007).
(5) C.C. Teo, S.N. Tan, J.W. Yong, C.S. Hew, and E.S. Ong, J. Chromatogr. A 1217(16), 2484–2494 (2010).
(6) R.M. Smith, Superheated Water Extraction in: Handbook of Sample Preparation (Wiley, New York, USA, 2010) pp. 181.
(7) R. Tajuddin and R.M. Smith, J. Chromatogr. A 1084(1–2), 194–200 (2005).
(8) A.M. Carro, P. Gonzalez, and R.A. Lorenzo, J. Chromatogr. A 1296, 214–225 (2013).
(9) A. Akinlua and R.M. Smith, Energy Fuels 23(12), 6020–6025 (2009).
(10) S. Deng, Z. Wang, Q. Gu, F. Meng, J. Li, and H. Wang, Fuel Proc. Tech. 92(5), 1062 –1067 (2011).
(11) V. Fernández-González, E. Concha-Graña, S. Muniategui-Lorenzo, P. López-Mahía and D. Prada-Rodríguez, J. Chromatogr. A 1196, 65–72 (2008).
(12) O. Chienthavorn and P. Su-in, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 385(1), 83–89 (2006).
(13) Z. Xiao, Y. Yang, Y. Li, X. Fan, and S. Ding, Anal. Chim. Acta 777, 32–40 (2013).
(14) N. Ramírez, R.M. Marcé, and F. Borrull, J. Chromatogr. A 1218, 6226–62231 (2012).
(15) X. Wang, L. Lin, T. Luan, L. Yang, and N.F. Tam, Anal. Chim. Acta 753, 57–63 (2012).
(16) S. Morales-Muñoz, J.L. Luque-García, M.J. Ramos, A. Fernández-Alba, and M.D. Luque de Castro, Anal. Chim. Acta 552(1–2), 50–59 (2005).
(17) D. Adeyemi, J. Mokgadi, J. Darkwa, C. Anyakora, G. Ukpo, C. Turner, and N. Torto, Chromatographia 73(9–10), 1015–1020 (2011).
(18) M.N. Islam, Y.T. Jo, and J.H. Park, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 8(5), 1689–1693 (2012).
(19) M.N. Islam, Y.T. Jo, and J.H. Park, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. (2013) (Available on-line: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.07.040).
(20) M.N. Islam, Y.T. Jo, S.K. Jung, and J.H. Park, Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 244, 1652 (2013) (DOI: 10.1007/s11270-013-1652-8).
(21) O. Chienthavorn, T. Poonsukcharoen, and T. Pathrakorn, Sep. Sci. Technol. 46(4), 616 –624 (2011).
(22) F. Liu, E.S. Ong, and S.F.Y. Li, Food Chem. 141(3), 1807–1811 (2013).
(23) F. Gogus, M.Z. Ozel, and A.C. Lewis, J. Chromatogr. Sci. 43(2), 87–91 (2005).
(24) M. Khajenoori, A.H. Asl, and H.N. Bidgoli, IJE Trans. B. Appl. 26(5), 489–494 (2013).
(25) A.L. Dawidowicz, E. Rado, and D. Wilanowska, J. Sep. Sci. 32(17), 3034–3042 (2009).
(26) B. Jayawardena and R.M. Smith, Phytochem. Anal. 21(5), 470–472 (2010).
(27) M.Z. Özel, F. Göğüs, and A.C. Lewis, Anal. Chim. Acta 566(2), 172–177 (2006).
(28) P. Khuwijitjaru, N. Sayputikasikorn, S. Samuhasaneetoo, P. Penroj, P. Siriwongwilaichat, and S. Adachi, J. Oleo Sci. 61(6), 349–355 (2012).
(29) L. He, X. Zhang, H. Xu, C. Xu, F. Yuan, Ž. Knez, Z. Novak, and Y. Gao, Food Bioprod. Process. 90(2), 215–223 (2012).
(30) M.A. Euterpio, C. Cavaliere, A.L. Capriotti, and C. Crescenzi, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 401(9), 2977–2985 (2011).
(31) J. Mokgadi, C. Turner, and N. Torto, Amer. J. Anal. Chem. 4, 398–403 (2013).
(32) H. Wang, Y. Lu, J. Chen., J. Li, and S. Liu, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 58, 146 (2012).
(33) B. Pongnaravane, M. Goto, M. Sasaki, T. Anekpankul, P. Pavasant, and A. Shotipruk, J. Supercritic. Fluids, 37, 390–396 (2006).
(34) C.C. Teo, S.N. Tan, J.W.H. Yong, C.S. Hew, and E.S. Ong, J. Chromatogr. A 1182(1), 34–40 (2008).
(35) M.J. Ko, C.I. Cheigh, and M.S. Chung, Food Chem. 143, 147–155 (2014).
(36) E.S. Ong, J.S.H. Cheong, and D. Goh, J. Chromatogr. A 1112(1–2), 92–102 (2006).
(37) M.J. Ko, C.I. Cheigh, S.W. Cho, and M.S. Chung, J. Food Eng. 102(4), 327–333 (2011).
(38) A. Mustafa and C. Turner, Anal. Chim Acta 703(1), 8–18 (2011).
(39) F. Chemat, M.A. Vian, and G. Cravotto, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13(7), 8615–8627 (2012).
(40) M. Mukhopadhyay and P. Panja, Ind. Chem. Eng. 51(4), 311–324 (2010).
(41) J. Shi, S.J. Xue, Y. Ma, Y. Jiang, X. Ye, and D. Yu, in Green Technologies in Food Production and Processing, J.I. Boye and Y. Arcand, Eds. (Food Engineering Series, Springer, New York, USA, 2012) pp. 273–294.
(42) L. Wang, H. Yang, C. Zhang, Y. Mo, and X. Lu, Anal. Chim. Acta 619(1), 54–58 (2008).
(43) J.N. Murakami, K.B. Thurbide, G. Lambertus, and E. Jensen, J. Chromatogr. A 1250, 80–84 (2012).
(44) A. Morado Piñeiro, J. Moreda-Piñeiro, E. Alonso-Rodríguez, P.López-Mahía, S.Muniategui-Lorenzo, and D. Prada-Rodríguez, Talanta 105, 422–428 (2013).
(45) K. Leppänen, P. Spetz, A. Pranovich, K. Hartonen, V. Kitunen, and H. Ilvesniemi, Wood Sci. Technol. 45(2), 223–236 (2011).

Evaluating Body Odor Sampling Phases Prior to Analysis
April 23rd 2025Researchers leveraged the advantages of thermodesorption, followed by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC/TOF-MS), to compare and assess a variety of sampling phases for body odor.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)









