Size-Exclusion Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Insulin
The Application Notebook
Insulin was the first recombinant pharmaceutical produced. Currently, one of the critical quality control attributes of therapeutic insulin in the US and European Pharmacopoeia (USP and EP) monograph is the level of covalent high molecular weight (HMW) insulin as determined by HPLC size-exclusion chromatography.
Insulin was the first recombinant pharmaceutical produced. Currently, one of the critical quality control attributes of therapeutic insulin in the US and European Pharmacopoeia (USP and EP) monograph is the level of covalent high molecular weight (HMW) insulin as determined by HPLC size-exclusion chromatography. Presented in this application are the advantages that may be realized using a 125 Å pore size, sub-2-µm ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) silica packing material and Waters Ultra Performance liquid chromatography (UPLC®) instrumentation for the pharmacopoeial analysis of covalent HMW impurities in therapeutic insulin samples. Among these advantages are faster run times, higher sensitivity, and higher resolving separations of insulin and covalent insulin HMW, while at the same time greatly reducing acetonitrile containing waste-stream volumes.
Instrumentation & Consumables
LC Conditions
Instrument: ACQUITY® UPLC H-Class Bio System with TUV detector and titanium flow cell
Columns: ACQUITY UPLC® BEH125 SEC, 1.7 µm, 4.6 × 300 mm (part number 186006506)and Insulin HMWP HPLC, 10 µm, 7.8 × 300 mm (part number WAT201549)
Mobile Phase: L-arginine (1.0 g/L)/acetic acid (99%)/acetonitrile; 65/15/20 (v/v/v)
Column Temp.: 25 °C
Sample Temp.: 10 °C
Flow Rate: 0.4 mL/min for the ACQUITY® UPLC BEH125 SEC column and 0.5 mL/min for the HMWP HPLC column
Detection: UV @ 276 nm
Injection Volume: 10 µL for ACQUITY® UPLC BEH125 SEC column and 100 µL for the Insulin HMWP HPLC column
Results and Discussion
For this application a comparison was performed between two SEC columns with particle sizes of 1.7 µm (UPLC) and 10 µm (HPLC) that are of comparable 125 Å pore size and equivalent 30 cm length (Figure 1). While both columns met the EP and USP HMW peak-to-valley ratio (P/V) system suitability criterion of NLT 2, and produced comparable HMW peak quantitation, the average HMW P/V for the UPLC® column (P/V = 37) was more than four times higher than that of the HPLC column (P/V = 8) and an insulin fragment was partially resolved at the tail of the monomer peak. In addition to dramatically increased resolution, the UPLC column also provides a smaller total elution volume (~ 5 mL) than the HPLC column. This decrease in total elution volume provides the analyst with increased sample throughput in addition to a decrease in mobile-phase use.
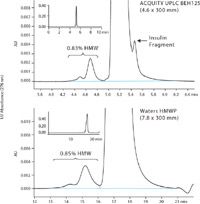
Figure 1: Zoomed view of chromatograms of a biotherapeutic insulin sample (analyzed past expiry) generated by the ACQUITY UPLC BEH125 and the Waters HMWP columns. The complete chromatographic profiles are presented in the insets.
Conclusions
The use of 125 Å pore size, sub-2-µm ethylene-bridged hybrid (BEH) silica packing material and Waters Ultra Performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) instrumentation for this traditional SEC-based analysis provides significant improvements in resolution compared to traditional SE-HPLC methods while reducing analysis time and mobile-phase use.
©2012 Waters Corporation. Waters, ACQUITY UPLC, UPLC, Alliance are trademarks of Waters Corporation.
Waters Corporation
34 Maple Street Milford, MA
tel. (508) 478 2000, fax (508) 872 1990
Website: www.waters.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















