A Simple Analysis of 4-Methylimidazole Using Automated Solid-Phase Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography with MS-MS and MS–SIM Detection
Special Issues
This work will demonstrate a simple methodology using automated solid-phase extraction (SPE) and HPLC coupled with mass spectrometric detection. This work will demonstrate a simple methodology using automated solid-phase extraction (SPE) and HPLC coupled with mass spectrometric detection. This work will demonstrate a simple methodology using automated solid-phase extraction (SPE) and HPLC coupled with mass spectrometric detection.
The compound 4-methylimidazole (4-MEI) is formed as a by-product in some foods and beverages. Caramel coloring Type III and Type IV in beverages is one of the ingredients which may contain 4-MEI and it may be found in products such as certain colas, beers, soy sauces, breads, coffee, ammoniated livestock feed, and others. There has been an increase in concern lately about 4-MEI being a suspected carcinogen. Europe has regulated the amount of 4-MEI allowed in coloring used in food products. The state of California has added 4-MEI to its proposition 65 list of known carcinogens. California now requires products with an exposure potential of >29 µg/day to carry warning labels.
This work will demonstrate a simple methodology using automated solid-phase extraction (SPE) and HPLC coupled with mass spectrometric detection.
The SmartPrep® Cartridge Extractor was used with a Waters Oasis® MCX 3 cc (60 mg) cartridge. The extraction method was optimized using a series of conditions and collecting fractions on the SmartPrep (1).
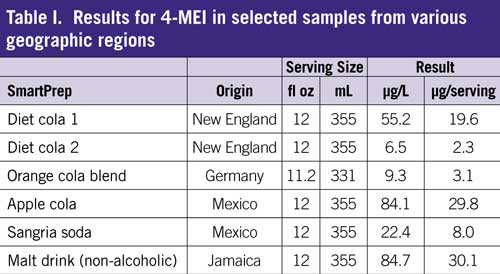
The samples for this experiment were common soft drinks containing caramel coloring. The point of purchase and original product production site are variables in 4-MEI levels. Some of the beverages were purchased in New England and others in California, in common supermarkets and their bottling origin is listed with the results.
Results and Discussion
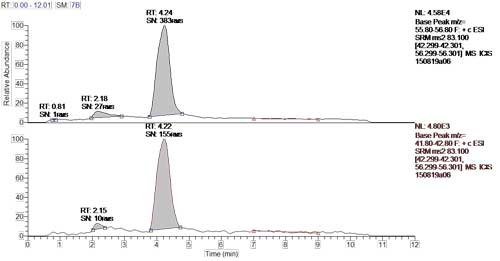
Figure 1: Mexican soda sample, S/N = 383 for quantitation ion.
A sensitive method for 4-MEI detection was developed using HPLC–MS, showing adequate measurement below the California Prop 65 requirements of 29 µg per day. Solid-phase extraction was shown to adequately concentrate the 4-MEI from the soft drinks analyzed and provide clean-up. Two samples were shown to exceed the daily exposure limits in Prop 65 with one serving.
Reference
- “A Simple Analysis of 4-Methylimidazole Using Automated Solid Phase Extraction and High Performance Liquid Chromatography with MS-MS and MS-SIM Detection,” AN1111606_01, available from www.horizontechinc.com.

Horizon Technology, Inc.
16 Northwestern Drive, Salem, NH 03079
tel. (603) 893-3663
Website: www.horizontechinc.com

Understanding FDA Recommendations for N-Nitrosamine Impurity Levels
April 17th 2025We spoke with Josh Hoerner, general manager of Purisys, which specializes in a small volume custom synthesis and specialized controlled substance manufacturing, to gain his perspective on FDA’s recommendations for acceptable intake limits for N-nitrosamine impurities.











