Separation of Lactulose and Epilactose
The Application Notebook
Lactulose, a semi-synthetic disaccharide, is a useful indicator for heat induced modifications in milk. Lactulose can be derived from lactose by alkaline isomerization or enzymatic transgalactosylation of fructose.
Lactulose, a semi-synthetic disaccharide, is a useful indicator for heat induced modifications in milk. Lactulose can be derived from lactose by alkaline isomerization or enzymatic transgalactosylation of fructose. Once in solution, lactulose is less stable in than lactose in an alkaline environment and can degrade into galactose, tagatose, and low molecular weight acids.
US Pharmacopeia describes the separation of lactulose together with lactose and galactose, as well as traces of other related sugars. The USP method describes HPLC separation is achieved on an L8 amino propyl functionalized silica support column. Herein, we describe an improved separation for lactulose, epilactose, and lactose on Shodex VG-50 4E, an amino HILIC column.
Shodex introduces the VG-50 4E column packed with a durable polymer based packing material modified with chemically stable tertiary amino functional groups. Shodex VG-50 4E is suitable for saccharide analysis and provides a fast reliable method for the determination of lactose and lactulose.
Experimental Conditions
The analysis of three disaccharides is accomplished with Shodex VG-50 4E (4.6 mm ID × 250 mm, 5 μm), a polymer-based amino HILIC column. Column temperature was 40 °C and flow rate was 1.0 mL/min for the VG-50 4E analysis. Eluent conditions are 75/20/5 acetonitrile/methanol/water. Injection volume of 5 μL of 5 mg/mL of each sugar was used for the experiment. The HPLC system was coupled with RI detector.
Results
Lactulose, lactose, and epilactose were analyzed successfully by HPLC and RI detection with VG-50 4E (Figure 1). Shodex VG-50 4E demonstrates baseline separation of the three sugars with an elution volume of less than 15 min with the elution order of lactulose, then epilactose, and finally lactose. The USP monograph describes the elution order as first epilactose, lactulose, and then lactose with resolution between lactulose and lactose not less than 1.5 and resolution between lactulose and epilactose not less than 0.9. The Shodex analysis demonstrates resolution between lactulose and epilactose as 2.29 and resolution between epilactose and lactose as 1.98.
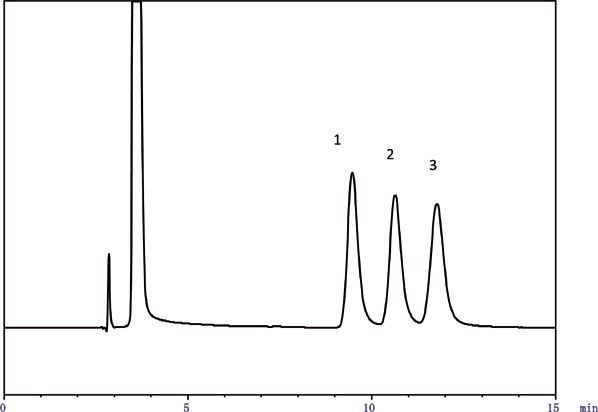
Figure 1: Separation of lactulose and epilactose. Column: Shodex VG-50 4E; column temperature: 40 °C; injection volume: 5 μL; eluent: CH3CN/CH3OH/H2O = 75/20/5; flow rate: 1.0 mL/min; detector: Shodex RI. Sample: 1. lactulose, 2. epilactose, 3. lactose.
Conclusions
Shodex VG-50 4E, a polymer-based hydrophilic interaction (HILIC) chromatography column is suitable for the analysis of lactulose, epilactose, and lactose.

Shodex™/Showa Denko America, Inc.
420 Lexington Avenue Suite 2335A, New York, NY 10170
tel. (212) 370-0033 x109
Website: www.shodex.net


.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)











