The Secrets of Red Wine - Determination of Polyphenols by Comprehensive 2D LC with PDA and MS-MS (IT-TOF) Detection
Shimadzu Application Note
Paola Donato,1 Francesco Cacciola,2 Paola Dugo1,2 and Luigi Mondello,1,2
1Università Campus Bio-Medico, Roma, Italy,
2Dipartimento Farmaco-chimico, Facoltà di Farmacia, Università di Messina, Messina, Italy.
Introduction
Produced and consumed world-wide, red wine is probably the best known "French paradox" contributor, being an excellent source of polyphenols and flavonoids, which confer important health benefits to the heart and blood vessels. In this application, we developed a comprehensive 2D LC technique for the separation of a mixture of 31 bioactive molecules commonly found in wine, whose complexity clearly overwhelms the peak capacity afforded by any single separation approach.
Instrumentation
Comprehensive 2D LC-PDA analyses were performed on a Shimadzu prominence UFLC-XR system, coupled to an ion trap time-of-flight (IT-TOF) mass spectrometer with electrospray ionization interface (ESI).
Chromatographic separation was achieved in the first dimension by the following conditions:
Column: Ascentis Phenyl 250 × 1.0 mm, 5 µm d.p. (SigmaAldrich/Supelco)
Gradient: A: water (pH 3);
B: acetonitrile (pH 3)
0 min: 10% B;
60 min: 70% B;
110 min: 70% B;
111 min: 100% B;
120 min: 100% B;
121 min 10% B.
Flow-rate: 9.7 µL/min.
Fast repetitive gradient was performed in the second dimension by the following conditions:
Column: Ascentis Express 30 × 4.6 mm, 2.7 µm d.p. (Sigma-Aldrich/Supelco)
Gradient: A: water (pH 3);
B: acetonitrile (pH 3);
0 min: 0% B;
0.90 min: 20% B;
1.20 min: 30% B;
1.50 min: 100% B;
1.69 min: 100% B;
1.70 min: 0% B.
Flow-rate: 4 mL/min.
Oven temperature: 45 °C.
Modulation time of the switching valve was 120 sec. ESI was operated both in positive and negative mode, with CDL and block temperature of 200 °C, 1.5 mL/min nebulizer gas (nitrogen) flow, 1.60 kV detector voltage. Data acquisition by LCMSsolution software, ver. 3.50.346; 2D plot elaboration by Chromsquare Ver. 1.4 software (Chromaleont, Messina, Italy).
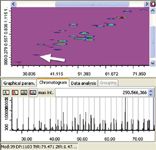
Figure 1: Software window with the 2D plot (top) and the corresponding raw chromatogram (bottom) extracted at 280 nm for the chromatographic separation of 31 bioactive polyphenols.
Results
All of the 31 compounds tested have been separated perfectly by the comprehensive system, as shown in Figure 1. Tandem MS detection by IT-TOF is a powerful tool for confident structure elucidation, thanks to the high mass accuracy and high mass resolution independent of MS mode, as shown in Figure 2.
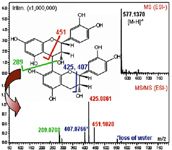
Figure 2: Peak identification of Procyanidin B by Comprehensive 2D LCâMSâMS (IT-TOF). Accuracy: 0.9 ppm. The peak is indicated by arrow in the plot of Figure 1.

Shimadzu Europa GmbH
Albert-Hahn-Str. 6–10, D-47269 Duisburg, Germany
tel. +49 203 76 87 0 fax +49 203 76 66 25
E-mail: shimadzu@shimadzu.eu
Website: www.shimadzu.eu

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.


















