Novel Malaria Vaccine Candidates
The Application Notebook
Malaria remains one of the world's most deadly diseases, killing a child under five years of age every 30 s. Our branch aims to produce and characterize recombinant protein vaccines for Phase I and II human trials.
Malaria remains one of the world's most deadly diseases, killing a child under five years of age every 30 s. Our branch aims to produce and characterize recombinant protein vaccines for Phase I and II human trials. We use Wyatt instruments coupled to a Waters HPLC to characterize these recombinant proteins. Wyatt instruments facilitate our understanding of purity, identity and aggregation states of recombinant protein vaccine candidates.
The solution profile of a candidate antigen was analyzed using analytical size exclusion chromatography with on-line multi-angle light scattering (SECMALS- HPLC), refractive index (RI) and ultraviolet (UV) detection. A Waters 2695 HPLC and 2996 PDA detector was connected in series to a Wyatt EOS and an Optilab RI detector run by the ASTRA V software suite. An isocratic elution at 0.5 mL/min was performed using a Tosoh Biosciences TSK gel G3000PWxl column (Part#:08021) and TSK gel Guard PWxl column (Part#:08033) with 0.04 mM KH2PO4, 2.97 mM Na2HPO4·7H2O, 308 mM NaCl, 0.5 M urea, pH 7.4, 0.02% sodium azide for mobile phase.
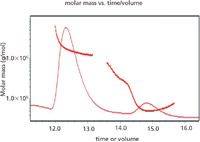
Figure 1: MALS results of the sample showing tetramers and dimers mixed in with monomer populations. The expected mass should be about 43 kDa.
The SEC-MALS trace in Figure 1 suggests the solution state of our vaccine candidate was comprised of three populations. Using the supportive resources at Wyatt Tech. Inc., we concluded that we did not have complete separation of monomer and dimer on the leading edge of the monomer peak. In addition, and perhaps more importantly, there appears to be a large Mw species (whose peak max shows up early — at 12.5 min) that is bleeding onto everything afterward, as seen in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Interpretation of the results which suggest there is a mixture of monomer and aggregate forms of the vaccine.
The Wyatt SEC-MALS results clearly indicated the presence of three populations, monomer, dimer and tetramer, which was later verified by boundary sedimentation equilibrium studies.
Application note courtesy of Richard L. Shimp, Jr., David L. Narum, and Peter F. Duggan, Malaria Vaccine Development Branch (NIAID/NIH).
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, CA 93117
tel. (805) 681-9009, fax (805) 681-0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.















