Determination of Lactose in Lactose-Free Milk Products
Lactose, a major disaccharide found in milk products, is catabolized into glucose and galactose by the enzyme lactase. Lactose-intolerant individuals have a lactase deficiency; therefore lactose is not completely catabolized.
Pranathi Perati, Brian De Borba, and Jeffrey Rohrer, Dionex Corporation
Lactose, a major disaccharide found in milk products, is catabolized into glucose and galactose by the enzyme lactase. Lactose-intolerant individuals have a lactase deficiency; therefore lactose is not completely catabolized. While lactose intolerance is not a dangerous condition, the global prevalence has created a large market for lactose-free products. Commercially available lactose-free products are produced by breaking down lactose into glucose and galactose using enzymatic hydrolysis. However, the resulting milk products can contain varying amounts of residual lactose, thus creating the need for simple, reliable, and accurate analytical methods to quantify low concentrations of lactose.
This article describes a sensitive and accurate method to determine lactose in dairy products, including lactose-free products, using high-performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD).
Experimental
A Dionex ICS-3000 chromatography system consisting of a Dual or Single Pump, electrochemical detector, AS Autosampler, and Chromeleon® Chromatography Data System (CDS) software was used. All samples and standards were prepared according to the procedures described in Dionex Application Note 24 (1).
Results and Discussion
Figure 1a shows the separation of carbohydrates in a prepared whole milk sample diluted 1:10 to prevent overloading with lactose. The diluted milk sample shows some galactose and glucose, and 56 mg/L or 0.0056% of lactose. Figure 1b shows the separation of carbohydrates in lactose-free milk. The chromatogram shows that lactose-free milk contains high concentrations of galactose and glucose and trace amounts of lactose (0.6 mg/L or 0.00006%). To evaluate accuracy, we spiked the sample of lactose-free milk with 10 mg/L each of lactose and lactulose. The recoveries were 97.6% for lactose and 94.5% for lactulose, suggesting method accuracy.
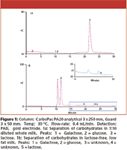
Figure 1
Conclusion
The method demonstrates that HPAE-PAD determines low levels of lactose in lactose-free milk and eliminates errors associated with analyte derivatization, which is needed to detect low concentrations of lactose when using other techniques.
References
(1) "Determination of lactose in lactose-free milk products by high–performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD)," Application Note 248, LPN 2507, Dionex Corporation, Sunnyvale, CA.
Chromeleon is a registered trademark of Dionex Corporation.
Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088
tel. (408)737-0700; fax (408)730-9403
Website: www.dionex.com


.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













