Characterization of PEGylated Lysozyme by Size Exclusion and Ion Exchange Chromatography
The Application Notebook
PEGylation, the process by which polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains are attached to protein and peptide drugs is a common practice in the development of biopharmaceuticals to prolong serum half-life and improve pharmacokinetics of a drug. There is increasing demand for chromatographic methods to separate the modified isoforms from the native protein. This application note describes the use of size exclusion and ion exchange chromatography for the characterization of PEGylated lysozyme.
Werner Conze, Jessica Christel, Achim Sprauer, Volker Noedinger and Egbert Mueller, Tosoh Bioscience GmbH.
PEGylation, the process by which polyethylene glycol (PEG) chains are attached to protein and peptide drugs is a common practice in the development of biopharmaceuticals to prolong serum half-life and improve pharmacokinetics of a drug. There is increasing demand for chromatographic methods to separate the modified isoforms from the native protein. This application note describes the use of size exclusion and ion exchange chromatography for the characterization of PEGylated lysozyme.
Introduction
PEGylation of proteins is a well established method to decrease in vivo clearance rate and reduce toxicity and immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins.1 While the addition of PEG groups to a protein or peptide improves its properties as a therapeutic, the addition also complicates both the separation and purification of such PEG/protein conjugates from the "non-PEGylated" protein species.2,3
The polymeric modification changes the biochemical and physical properties of the protein and will, therefore, influence the behaviour during chromatographic analysis and purification. To facilitate method development for both, analytical and preparative applications, it is important to know the influence of a covalent PEG modification on the performance of a protein on HPLC columns and chromatographic bulk media.
Size exclusion (SEC) and ion exchange chromatography (IEC) are common methods for the separation of proteins. Both modes were used to characterize the PEGylation of hen white egg lysozyme, which was used here as a model protein. The amino acid structure of lysozyme shows six lysine residues, which can serve as PEGylation reaction sides (Figure 1).

PEGylation and Chromatographic Analysis

PEGylated lysozyme was produced out of methoxy-PEG-aldehyde (with a molecular weight of 5 kDa, 10 kDa and 30 kDa) and chicken white egg lysozyme in a phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 6.0) in the presence of sodium-cyano-borohydrid (NaCNBH3) as a reducing agent.4 The product mixture was analysed by SEC on a TSKgel G3000SWXL HPLC column and by IEC on TSKgel SP-5PW (20). Fractions were analysed subsequently by MALDI-TOF-MS.
Chromatographic Conditions:
SEC-HPLC:
Column: TSKgel G3000SWXL (7.8 mm i.d. × 30 cm L, 5 µm, 250 Å)
HPLC-system: Shimadzu LC-20A Prominence
Flow-rate: 1 mL/min
Mobile phase: 0.1 M phosphate buffer; 0.1 M Na2SO4, pH 6.7
Detection: PDA @ 280 nm
Injection volume: 20 µL
IEC-FPLC:
Column: TSKgel SP-5PW (20) (6.6 mm i.d. × 22 cm L, 20 µm, 1000 Å)
Flow-rate: 0.85 mL/min
Mobile phase: Buffer A: 25 mM phosphate buffer; 0.1 M Na2SO4, pH 6.0 Buffer B: A + 0.5 M NaCl
Detection: UV @ 280 nm
Injection volume: 100 µL
Results
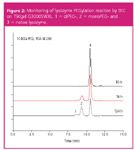
The degree of PEGylation can be easily monitored by analysing the increase in molecular weight by size exclusion analysis, as every covalently linked PEG group adds 10 kDa to the molecular weight of the native protein. TSK-GEL SWXL HPLC columns are renowned for their high efficiency in protein separations by aqueous SEC.5 (1) DiPEG-, (2) MonoPEG- and (3) native Lysozyme species could be resolved by SEC-HPLC analysis on a TSKgel G3000SWXL column (Figure 2).
Figure 3 shows the result of the cation exchange analysis of the final product of the PEGylation process. The isomers of monoPEG lysozyme and diPEG lysozyme can be further separated by ion chromatography. Depending of the affected PEGylation site (Figure 1) the voluminous PEG group shields different areas of the protein. Resulting differences in surface charge distributions are then leading to partial separation of the isoforms in IEC. Fractions 1(a) to 5 were submitted to subsequent MALDI-TOF MS analysis, which confirmed the assignment of the IEC peaks to di-, mono-, and non-PEGylated lysozyme species.
Conclusion
Size exclusion HPLC with TSK-GEL SWXL columns is a fast and efficient tool to monitor time, concentration and temperature depending synthesis of PEGylated lysozyme species. The SEC chromatograms show different elution volumes for monoPEG, diPEG and native lysozyme respectively. PEGylation with other molecular weight polyethylene glycols (e.g., 5 kDa or 30 kDa) could be monitored as well by using the same method parameters (data not shown). The cation exchange resin TSKgel SP-5PW(20) was successfully applied to separate various isoforms of mono-PEGylated and of di-PEGylated lysozyme. The degree of PEGylation in the collected fractions was confirmed by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr H. Lange and K. Darsow, Institute of Bioprocess engineering, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, for MALDI-MS analysis.
References
1. J.M. Harris and R.B. Chess, Nature Reviews, 2, 214–221 (2003).
2. S.P. Monkarsh et al., Anal.Biochem., 247(2), 434–440 (1997).
3. S. Yamamoto et al., J. Biotechnol., 132(2),196–201 (2007).
4. A.S. Morar et al., BioPharm International, 19(4), 34–49 (2006).
5. B. S. Kendrick et al., Analytical Biochemistry, 299(2), 136–146 (2001).

Tosoh Bioscience GmbH
Im Leuschnerpark 4
64347 Griesheim
tel. +49 6155-7043700
fax +49 6155-8357900
E-mail: Info.tbg@tosoh.com
Website: www.tosohbioscience.de

Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.
Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)







