Automated Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) and GC–MS Analysis of Pond Water Samples According to EN16691 for PAHs
The Application Notebook
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are found worldwide and are emitted from a number of sources including fossil fuel, coal and shale oil derivatives, coke production, and burning wood for home heating, and generally arise from incomplete combustion. Surface water supplies, such as water in ponds, may be used for recreational purposes or become a drinking water source. Characterization of PAHs and their concentration is of interest in maintaining public health.
Alicia Cannon and Michael Ebitson, Horizon Technology, Inc.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are found worldwide and are emitted from a number of sources including fossil fuel, coal and shale oil derivatives, coke production, and burning wood for home heating, and generally arise from incomplete combustion. Surface water supplies, such as water in ponds, may be used for recreational purposes or become a drinking water source. Characterization of PAHs and their concentration is of interest in maintaining public health.
PAH measurement in water should be accurate, precise, and sensitive enough to measure low concentrations. Method EN 16691 is a recently developed method that uses solid-phase extraction to isolate organic compounds from 1 L of water using a divinylbenzene (DVB) solid-phase extraction disk. PAHs are eluted from the disk with dichloromethane and dried to remove water before evaporation, solvent exchange into toluene, and introduction into GC–MS. The method specifies the use of the whole water sample, ensuring that any analyte adsorbed on the particulate matter will be extracted along with the water sample. Disks are a particularly well suited SPE format for samples containing particulates because the increased surface area does not become clogged with particulate as easily as a cartridge format might, even for larger water samples, such as 1 L. In addition, the particulates are rinsed with solvent at the same time as the bottle is rinsed in an automated system (SPE-DEX® 4790 or new SPE-DEX 5000), including compounds adsorbed on the particulate surfaces in the extraction process (1).
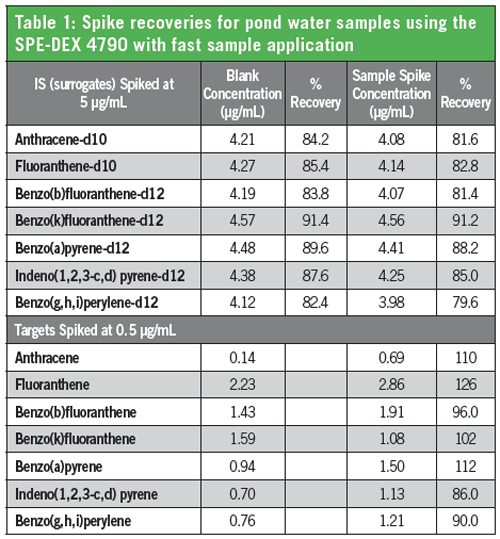
The recoveries of a suite of PAH compounds spiked into a pond water sample using this methodology are shown in Table 1 (2). A slow flow rate through the disk (25 mL/min) is specified in the method and excellent recoveries are shown in the full application note. However, the flow rate through a disk does not need to be limited in the same way as a cartridge for good equilibrium. The recoveries shown in Table 1 result from extraction at full speed (approximately 100 mL/min). Recoveries of the surrogate compounds are very good ensuring the method is operating properly. The recoveries of spiked compounds from the matrix is excellent.
The performance of the SPE-DEX 4790, using Atlantic® DVB disks for the extraction of PAHs, was shown to comply with method requirements and provided excellent recoveries of the full suite of PAH analytes.
References
- Application Note AN1091606_01, Automated Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) and GC/MS Analysis of Whole Water Samples According to EN16691 for PAHs, available from www.horizontechinc.com.
- Application Note AN1101606_01, Automated Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) and GC/MS Analysis of Pond Water Samples According to EN16691 for PAHs.

Horizon Technology, Inc.
16 Northwestern Drive, Salem, New Hampshire 03079 USA
Tel.: +1 603 893 3663 Fax: +1 603 893 4994
E-mail:spe@horizontechinc.comWebsite:www.horizontechinc.com

New Study Reviews Chromatography Methods for Flavonoid Analysis
April 21st 2025Flavonoids are widely used metabolites that carry out various functions in different industries, such as food and cosmetics. Detecting, separating, and quantifying them in fruit species can be a complicated process.
Quantifying Terpenes in Hydrodistilled Cannabis sativa Essential Oil with GC-MS
April 21st 2025A recent study conducted at the University of Georgia, (Athens, Georgia) presented a validated method for quantifying 18 terpenes in Cannabis sativa essential oil, extracted via hydrodistillation. The method, utilizing gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) with selected ion monitoring (SIM), includes using internal standards (n-tridecane and octadecane) for accurate analysis, with key validation parameters—such as specificity, accuracy, precision, and detection limits—thoroughly assessed. LCGC International spoke to Noelle Joy of the University of Georgia, corresponding author of this paper discussing the method, about its creation and benefits it offers the analytical community.