Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Apples using Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS AOAC Kit by LC–MS–MS Detection
The Application Notebook
Based on the QuEChERS AOAC Official Method 2007.01, 16 pesticides were used for evaluating the performance of the Agilent's AOAC buffered extraction and SampliQ QuEChERS dispersive SPE kits for general fruits and vegetables.
Limian Zhao, David Schultz and Joan Stevens, Agilent Technologies Inc., Wilmington, Delaware, USA.
Introduction
Based on the QuEChERS AOAC Official Method 2007.01, 16 pesticides were used for evaluating the performance of the Agilent's AOAC buffered extraction and SampliQ QuEChERS dispersive SPE kits for general fruits and vegetables. Apple was selected as the fruit matrix. The pesticides are from the 'representative pesticides' list.1 A method working well for these representative pesticides should work equally well for the other pesticides that are routinely monitored in multi-class, multi-residue methods. The compounds are from 9 different pesticide classes: including acidic, basic, neutral, base-sensitive and acid-labile pesticides. The selected pesticides are suitable for LC–MS–MS analysis. The MRLs of these pesticides have been set at 10 ng/g or higher.2–4
Experimental-Instrument Conditions
Agilent 1200 HPLC with diode array detector
Agilent 6410 Triple Quadrupole LC–ESI-MS–MS
Agilent SampliQ buffered QuEChERS AOAC extraction kits Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS AOAC dispersive SPE kits: general fruits and vegetables.

Extraction/partitioning: 15 g (±0.05 g) homogenized sample were placed into a 50 mL centrifuge tube from the SampliQ QuEChERS extraction kit. Tubes were capped and vortexed; add 15 mL of 1% HAc in ACN. An Agilent AOAC buffered extraction packet containing 6 g of anhydrous MgSO4 and 1.5 g of anhydrous NaOAc, was added directly to the tubes, vigorously shaken and centrifuged.
Dispersive SPE clean-up: An aliquot of the upper ACN layer was transferred into a SampliQ QuEChERS AOAC dispersive SPE tubes, containing PSA and anhydrous MgSO4, capped, vortexed and centrifuged. Aliquot of the extract was diluted 1:4 and analysed by LC–MS–MS.
Results and Discussion
The unique design of Agilent's SampliQ QuEChERS kits, allows the whole procedure to be even faster and easier, creating time and labour savings, while ensuring consistency. An analyst can process 40–50 samples in just a few hours. Adding a food sample with a high percentage of water directly to the extraction salts containing MgSO4 may create an exothermic reaction that can affect analyte recovery. Agilent's SampliQ QuEChERS extraction salts and buffers are uniquely prepared in anhydrous packages. This allows addition AFTER adding solvent to the sample, as specified in the original QuEChERS methodology. The powerful selectivity of LC–MS–MS multiple reaction monitoring mode, indicate the blank apple extract did not contribute any interferences with the target compounds, Figure 1.
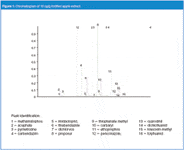
Figure 1
Conclusions
Agilent's QuEChERS AOAC buffered extraction and SampliQ AOAC dispersive SPE kits for general fruits and vegetables provided a simple, fast and effective method for the purification of representative pesticides in apple. The LOQs (5 ng/g or 5 ppb) of the pesticides were lower than their regulated MRLs. The recovery and reproducibility (RSD) for SampliQ QuEChERS were 95.4% and 4.3% (average), respectively. Notoriously base-sensitive pesticides such as dichlorfluanid and tolyfluanid showed excellent recoveries and RSDs; even an acid-labile pesticide, pymetrozine showed acceptable recovery and RSD. The Agilent SampliQ QuEChERS AOAC extraction and dispersive kits for general fruits and vegetables can be used for other pesticides in other similar fruit matrices.
References
1. S.J. Lehotay et al., J. AOAC Int., 88, 615–629 (2005).
2. M. Anastassiades and S.J. Lehotay, J. AOAC Int., 86, 412–431 (2003).
3. S.J. Lehotay et. al., J. AOAC Int., 90, 485–520 (2007).
4. http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/footprint/en/index.htm

Agilent Technologies Inc.
2850 Centerville Road, Wilmington, Delaware 19808, USA
tel. +1 800 227 9770 fax +1 302 633 8901
E-mail: info_agilent@agilent.com
Website: www.agilent.com/chem

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.
Prioritizing Non-Target Screening in LC–HRMS Environmental Sample Analysis
April 28th 2025When analyzing samples using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry, there are various ways the processes can be improved. Researchers created new methods for prioritizing these strategies.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)

















