High Speed Separation of More Than 16 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
The Application Notebook
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are particularly relevant in the analysis of environmental pollution because of their ubiquity, toxicity and persistence. Consequently, the PAHs have become the most intensively studied pollutants in environmental analysis.
S. Marten and A. Knöfel, Wissenschaftliche Gerätebau Dr. Ing. Herbert Knauer GmbH, Berlin, Germany
Introduction
Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are particularly relevant in the analysis of environmental pollution because of their ubiquity, toxicity and persistence. Consequently, the PAHs have become the most intensively studied pollutants in environmental analysis.1,2 Standard and official methods for their analysis are available in guidelines for air, water, solid waste and food analysis.3 To attain the required selectivity of HPLC separations stationary phases specifically designed for PAH analysis are required.
Using standard HPLC for PAH analysis, injection-to-injection cycle times can often exceed 30 minutes. Under optimized conditions, gradient separations of the US EPA recommended standard test mixture of 16 PAH can be performed in about 15 minutes. The aim of this study was to investigate the resolution limit and analysis time for 16 PAH of the EPA standard plus 3 additional related aromatic compounds (1-methylnapthalene, triphenylene and p-terphenyl) using a PLATINblue system with a short BlueOrchid PAH column.
Experimental
The PAH analysis was developed on BlueOrchid PAH 50 × 2 mm column and a PLATINblue UHPLC high pressure gradient system. Please refer to Figure 1 for details.
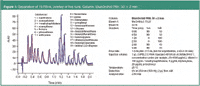
Figure 1
Results
After method optimization for the separation of the standard PAH mixture we spiked the mixture with 3 additional PAHs. To achieve a separation of these 19 PAHs in less than 2 min the method parameters were slightly modified (see Figure 1). In spite of the fast gradient applied (composition change rate of 2% per second), the reproducibility of the method was good with a maximum deviation of ΔtR = 0.012 min. In summary, we would recommend a flow-rate of 1 mL/min for an analysis time of 2.5 min, plus an equilibration time of 0.4 min run at a higher flow-rate of 1.5 mL/min. Side-effect: compared with the standard HPLC method the method above accounted for an eluent savings of 80% per analysis.
Conclusion
By using a shorter column with a smaller inner diameter and a KNAUER PLATINblue UHPLC system, complex mixtures such as the 19 PAHs can be analysed with excellent reproducibility and cycle times of less than 3 minutes. Optimizing the speed and resolution of routine analyses can not only save time but also dramatically decrease eluent costs, particularly important for analyses using acetonitrile.
References
1. M.N. Kayali-Sayadi et al., Fresenius J Anal Chem., 368(7), 697–701 (2000).
2. T. Wenzl et al., Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 25(7), 716–725 (2006).
3. AOAC 973.30; Deutsche DIN TVO; UK ISBN 0 11 752032 2; US EPS Methods TO-13, 550 550.1, 610, 8310 8330.

Wissenschaftliche Gerätebau Dr. Ing. Herbert Knauer GmbH
Hegauer Weg 38, 14163 Berlin, Germany
tel. +49 30 809727 0 fax +49 30 8015010
E-mail: info@knauer.net Website: www.knauer.net

SPE-Based Method for Detecting Harmful Textile Residues
January 14th 2025University of Valencia scientists recently developed a method using solid-phase extraction (SPE) followed by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC–HRMS/MS) for detecting microplastics and other harmful substances in textiles.