Analysis of Limonin in Citrus Juice Using QuEChERS and LC–MS/MS
The Application Notebook
This application note outlines a simple, fast, and cost‑effective QuEChERS-based method for the determination of limonin in citrus juice. Limonin is extracted from a variety of juice samples using acetonitrile and citrate-buffered salts. The sample extract undergoes cleanup by dispersive-SPE (dSPE) using primary‑secondary amine (PSA), C18, and graphitized carbon black (GCB) to remove unwanted matrix components, including sugars, acids, and pigments, and to yield a clear sample extract. Analysis is performed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) using a Selectra® C18 HPLC column (although high performance liquid chromatography [HPLC]–UV can also be used).
Brian Kinsella, UCT, LLC
This application note outlines a simple, fast, and costâeffective QuEChERS-based method for the determination of limonin in citrus juice. Limonin is extracted from a variety of juice samples using acetonitrile and citrate-buffered salts. The sample extract undergoes cleanup by dispersive-SPE (dSPE) using primaryâsecondary amine (PSA), C18, and graphitized carbon black (GCB) to remove unwanted matrix components, including sugars, acids, and pigments, and to yield a clear sample extract. Analysis is performed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) using a Selectra® C18 HPLC column (although high performance liquid chromatography [HPLC]–UV can also be used).
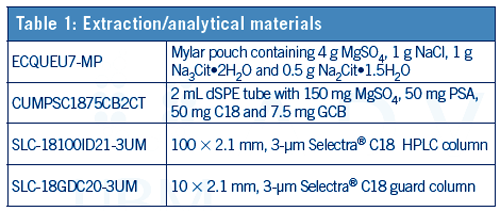
Procedure
1. Sample Extraction:
a) Allow citrus juice to come to room temperature and thoroughly mix the sample before analysis.
b) Transfer 10 mL of juice into a 50-mL polypropylene centrifuge tube.
c) Add 10 mL of acetonitrile.
d) Add the contents of the ECQUEU7-MP Mylar pouch and vortex or shake (manually or mechanically) for 5 min.
• For this work a SPEX® SamplePrep® 2010 Geno/Grinder® was used (1500 rpm).
e) Centrifuge the samples at ≥3000 rcf for 5 min.
2. Sample Clean-up of Extract
a) Transfer 1 mL of supernatant to a CUMPSC1875CB2CT 2 mL dSPE tube.
b) Vortex the samples for 30 s.
c) Centrifuge the samples at ≥3000 rcf for 5 min.
d) Transfer 500–600 µL of purified supernatant into an autosampler vial for analysis.
Instrumental
LC–MS/MS: Thermo Scientific™ Dionex™ Ultimate™ 3000 UHPLC and TSQ Vantage™ (MS/MS)
Column: 100 × 2.1 mm, 3-μm UCT Selectra® C18 HPLC column
Guard column: 10 × 2.1 mm, 3-μm UCT Selectra® C18 guard column
Injection volume: 1 μL
Mobile phase A: D.I. H2O + 0.1% formic acid
Mobile phase B: Methanol + 0.1% formic acid
Column flow rate: 0.30 mL/min
Results
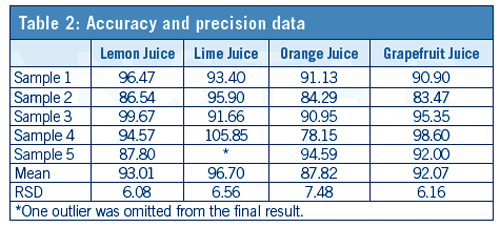
Samples were fortified with limonin at 10 µg/mL (50 µL of a 2 mg/mL acetonitrile standard). Six-point matrix-matched calibration curves were prepared at 1, 2, 5, 10, 15, and 20 µg/mL. Non-fortified juice samples were extracted according to the QuEChERS procedure described above and 1 mL of purified extracts were fortified with 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, and 100 µL of a 200 µg/mL acetonitrile standard.
Conclusion
This application note outlines a simple, fast, and costâeffective QuEChERS-based method for the determination of limonin in citrus juice. Citrus juice samples are extracted with citrateâbuffered QuEChERS salts followed by dSPE cleanup of the supernatant using PSA, C18, and GCB, yielding a clear extract. Analysis was performed by LC–MS/MS using a Selectra® C18 HPLC column. Various citrus juices (lemon, lime, orange, and grapefruit) were evaluated for recovery and repeatability using fortified samples. Excellent recovery (88% to 97%) and repeatability (≤7.5%) were obtained using the outlined method.

UCT, LLC
2731 Bartram Rd, Bristol, Pennsylvania 19007, USA
Tel: (800) 385 3153
E-mail: methods@unitedchem.com
Website: www.unitedchem.com
Determining the Effects of ‘Quantitative Marinating’ on Crayfish Meat with HS-GC-IMS
April 30th 2025A novel method called quantitative marinating (QM) was developed to reduce industrial waste during the processing of crayfish meat, with the taste, flavor, and aroma of crayfish meat processed by various techniques investigated. Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) was used to determine volatile compounds of meat examined.
Accelerating Monoclonal Antibody Quality Control: The Role of LC–MS in Upstream Bioprocessing
This study highlights the promising potential of LC–MS as a powerful tool for mAb quality control within the context of upstream processing.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)










