Analysis of Fumonisins in Grains and Feeds
The Application Notebook
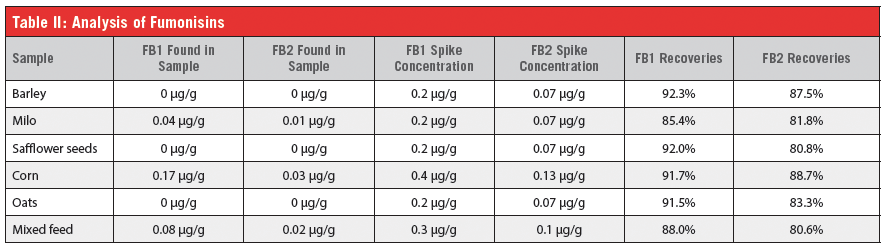
Fumonisins are naturally occurring mycotoxins produced by Fusarium mold species. Fumonisins contamination happens worldwide in many agricultural commodities, especially in corn, and is usually associated with dry and hot weather followed by periods of high humidity. Out of more than 10 types of Fumonisins, Fumonisin FB1 is the most prevalent and toxic, followed by Fumonisins FB2 and FB3. Fumonisins are classified as possibly carcinogenic for humans and also cause health problems in animals, especially in equids and swine. FDA sets total Fumonisins limits in human foods between 2–4 µg/g and in animal feed between 5–100 µg/g.
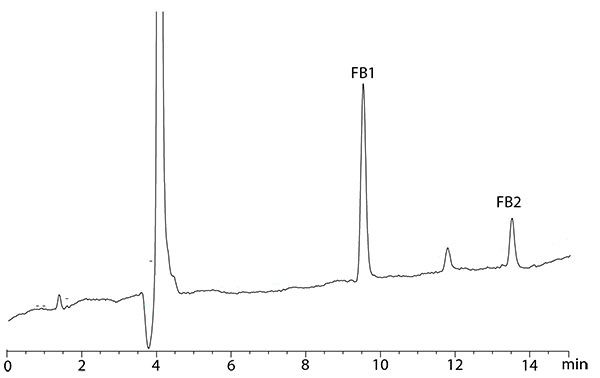
Figure 1: Chromatogram of corn sample contaminated with 0.17 µg/g of FB1 and 0.03 µg/g of FB2.
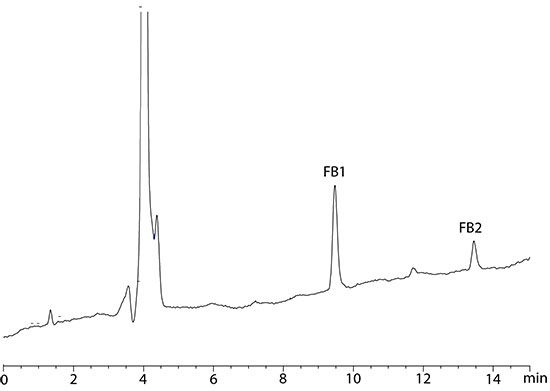
Figure 2: Chromatogram of mixed feed sample contaminated with 0.08 µg/g of FB1 and 0.02 µg/g of FB2.
Since Fumonisins don't have a chromophore and don't fluoresce, derivatization is needed to achieve the required sensitivity of detection. We developed a fast and sensitive HPLC method with post-column derivatization that is capable of analyzing Fumonisins in grains and animal feed at levels as low as 0.01 µg/g.
Method
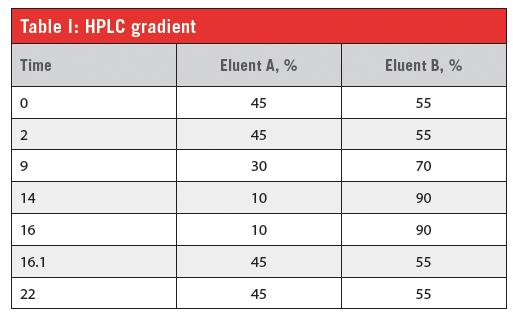
Analytical Conditions

Post-Column Conditions

Sample Extraction and Clean-Up
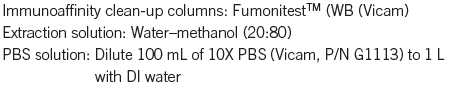
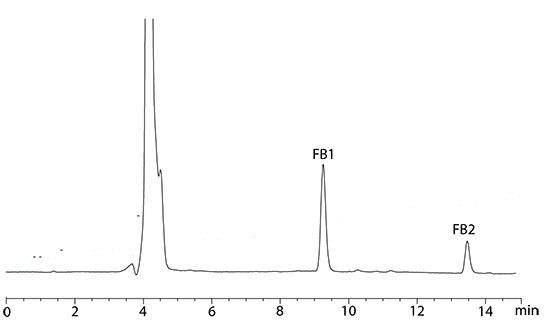
Figure 3: Chromatogram of barley sample spiked with 0.2 µg/g of FB1 and 0.07 µg/g of FB2.
To 25 g of finely ground sample add 2.5 g of NaCl and 50 mL of extraction solution. Blend at high speed for 5 min, filter through fluted filter. Take 10 mL of extract and add 40 mL of PBS solution, mix well, filter through microfiber filter. Load 10 mL of diluted extract to Immunoaffinity column, let the solution pass through at the flow rate about 1–2 drops/s. Wash the column with 10 mL of PBS solution, elute with 1 mL of methanol followed by 1 mL of DI water. Evaporate the solution to dryness under the stream of nitrogen, reconstitute in 1 mL of methanol–water (50:50). Inject 10–50 µL.
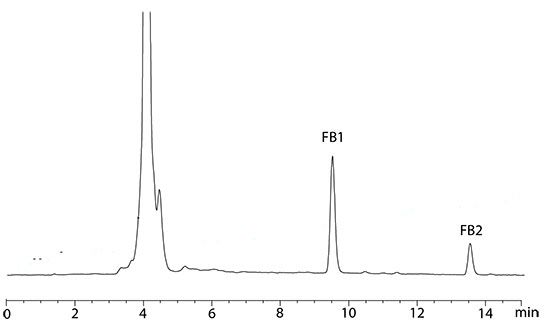
Figure 4: Chromatogram of safflower seeds sample spiked with 0.2 µg/g of FB1 and 0.07 µg/g of FB2.

Pickering Laboratories, Inc.
1280 Space Park Way, Mountain View, CA 04043
tel. (800) 654-3330, (650) 694-6700
Website: www.pickeringlabs.com

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.















