Why Should Bioanalysts Use Microflow LC–MS?
This article looks at the practical benefits of microflow liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) in bioanalysis applications.
Photo Credit: Aqwees/Shutterstock.com

Anthony G. Marcello, Waters Corporation, Milford, Massachusetts, USA
This article looks at the practical benefits of microflow liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) in bioanalysis applications.
Why are bioanalysts at leading pharmaceutical companies using microflow liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) for more routine applications (1–7)? The answer is simple: an overarching need to do “more with less”. They are working with more complex analytes, with limited sample, often requiring both improved sensitivity and high throughput. Although microflow LC–MS has historically been perceived as a tradeoff between high sensitivity and throughput, recent advances are enabling analysts to collect highly sensitive data with cycle times comparable to analytical scale (8,9). As a result, microflow LC–MS is being increasingly adopted, particularly for large molecule quantification.
More with Less
The highly competitive drug and biomarker space demands rapid commercialization to stay competitive, making assay efficiency and throughput critically important. Competition drives the need for instrument platforms with higher performance, throughput, and flexibility. Every year, sensitivity requirements continue to escalate because of the increased use of microdosing and higher potency drug candidates. Microdosing aims to determine pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of a new drug by administering subtherapeutic levels less than 1% of the target dose (10). Low dosed drugs, limited sample availability, and increased sample sharing among groups also drive sensitivity needs. In addition, the rapid expansion into large molecule development challenges bioanalysts, with reduced signal as a result of multiply charged species and high background from endogenous interferences, among others. With a changing landscape, bioanalysts need a choice of sensitive and flexible platforms than ever before.
When searching for viable biomarker candidates, significantly high sensitivity has been accessible in proteomics laboratories for decades, through microflow and nanoflow liquid chromatography (LC). Tasked with characterizing large numbers of unknown proteins with limited sample, these applications require extremely high sensitivity and separation of many closely related species, which is achieved with low flow rates. In this environment, longer cycle times, sometimes up to 90 min, are acceptable. This is in stark contrast to routine bioanalytical laboratories that require cycle times of 2–5 min. As a result of complex homebrewed methods and limited throughput of traditional low-flow LC, nano- and microflow LC have not been realistic in high-throughput discovery laboratories until recently. Today, tradeoffs between sensitivity and throughput remain, but with improvements in technology, they are much less extreme. Modern microflow systems have the flexibility to handle a variety of application needs, including high sensitivity and routine applications, which has eased the adoption of contemporary microflow LC–MS by leading drug development companies.
Integrated Microfluidic Platforms
The gains in sensitivity that microflow LC–MS affords compared with standard flow can be attributed to smaller column diameters, increased sampling efficiency, lower flow rates, and improved chromatographic separation. However, widespread adoption of the technology has been hampered by the need for highly skilled analysts and the limited reproducibility across users and between laboratories.
Making connections with fused-silica tubes requires considerable expertise, and narrower silica-based tubing adds to robustness issues because it easily cracks when tightened. To address these issues, an array of fully integrated tile and “plug-and-play” microfluidic platforms have been introduced with aims of simplifying workflows, increasing robustness, and better positioning microflow for routine analyses (5). Tile, chip-based, or other integrated devices are typically made of composite plates with bead-packed channels, which contain inlet and outlet ports, an emitter, and a heating element. Having a fully integrated device reduces void volumes and eliminates the need to make multiple capillary connections. Integration improves reproducibility among users and laboratories because it reduces variability, a necessity for labs performing absolute quantification. In the pharma industry, an essential requirement is the effective transfer of methods to contract research organizations (CROs). Modern microflow platforms are easier to use and much more robust, and consequently, pharma and CROs are more readily adopting integrated microfluidic platforms (1–7).
Sensitivity Gains for Peptides and Proteins
Microflow can facilitate sensitivity gains for a wide variety of analytes, but the greatest benefit has been for peptide and protein quantification (11). Although two-thirds of drugs in development are small molecules, a record number of peptide and protein therapeutics were approved in 2015, and large molecule drug approvals are growing at a faster rate (12). Over the past few years, the majority of the top 10 selling drugs were biologics, and this trend will likely continue. Not only have biologics proven to be effective therapies to key diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders, but they are often also easier to patent compared to small molecules, and they produce higher returns on investment, which increases their attractiveness. As a result, drug companies, CROs, and small molecule bioanalysis laboratories are now working with large molecule therapeutics, and dealing with the challenges associated with making the transition.
Peptide and protein bioanalysis comes with a myriad of complexities compared to small molecule analysis. High background noise from endogenous peptides and proteins can reduce signal and requires more complex sample preparation. Larger molecules have more multiply charged species, increased fragmentation patterns, and a variety of lower abundance fragments, all of which reduce signalâtoânoise ratios. In addition, a significant number of biologics have longer half-lives than small molecules, and are therefore dosed at lower concentrations. Many of these issues support the need for the increased analytical sensitivity afforded by microflow.
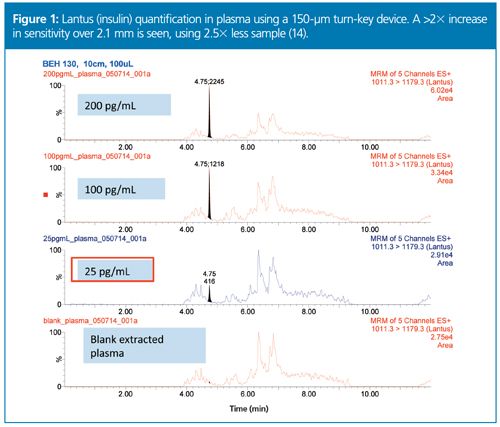
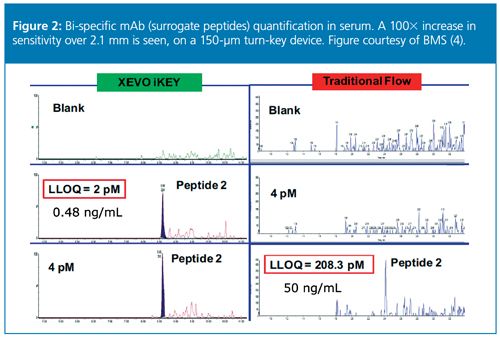
The increased sampling efficiency of microflow LC–MS is a major contributor to the increased sensitivity it yields, and this is especially true for larger molecules (11). Peptides tend to be more surfaceâactive on ionized droplets because of their hydrophobic moieties, and they have a greater ability to protonate, making them more easily ionized than small molecules. Although the degree of increased ionization is analyte-dependent, in some cases, picogram levels of detection are readily achievable, even without immunoaffinity purification (Figure 1) (13,14). With optimization of sample preparation techniques, sensitivity gains can be significantly increased. Also, single- or dualâpump column trapping allows the flexibility to concentrate and clean up larger sample volumes. When sample prep and column trapping are employed together, sensitivity gains of 100× over standard flow have been reported (Figure 2) (4). Overall, modern microflow LC–MS is enabling laboratories to address sensitivity issues associated with large molecule bioanalysis.
Is High-Throughput Microflow LC–MS Possible?
Pharma and CROs know that time is the most valuable currency, and speed to market is crucial to stay competitive. To increase the throughput of a robust microflow LC–MS method, three strategies can be used to balance the tradeoff with sensitivity: modulation of flow rate, pressures, and column internal diameter.
In a recent study published by Alelyunas et al., an integrated microflow LC system with a 150-µm tile was coupled with a QTOFâMS, and a cycle time of 4 min (including sample injection) was achieved by increasing the flow rate to 7 µL/min (8). The resulting microflow LC–MS method yielded sensitivity of 1–10 pg/mL range for a panel of small molecules and a peptide. Also, the cycle times were comparable to that of traditional reversed-phase ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) using 2.1 mm scale, and were fit for routine bioanalysis with a high degree of reproducibility, linearity, precision, and robustness.
Increasing throughput with microflow LC–MS can also be achieved by using wider internal diameter columns in combination with higher flow rates. In a recent white paper from Donegan et al., a panel of six small molecules in plasma were tested using a prototype 300-µm turn-key microfluidic device on a tandem quadrupole MS. The resulting method yielded sensitivity gains up to 6× with an average of 3× and cycle times of less than 3 min (Figure 3) (9).
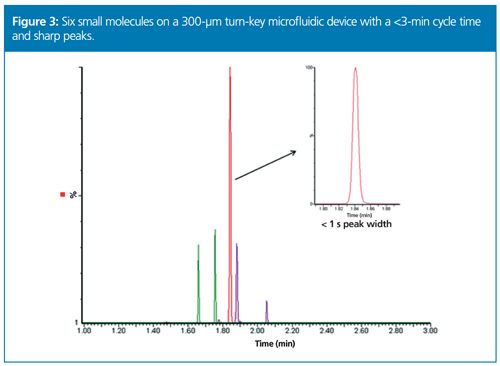
Both examples address the perceptions that microflow is too slow for routine applications. Each study shows the flexibility to use microflow at routine speeds with injection-toâinjection cycle times between 3–5 min - a common requirement in a routine bioanalysis laboratory. Now, microflow enables one to not only conduct ultra-sensitive applications but also higher throughput applications comparable to analytical scale cycle times.
Conclusion
Top bioanalysts at leading pharma and CRO companies are using modern microflow LC–MS systems to address key challenges, such as high sensitivity needs, and for more routine applications (1–7). The balance between achieving high-sensitivity and high-throughput capabilities has been demonstrated in the literature, and this approach is suitable to address the sensitivity challenges associated with analyzing peptides and proteins.
References
- Paul D. Rainville et al., The Analyst140(16), 5546–556 (2015).
- Derek L. Chappell et al., Bioanalysis8(22), 2341–349 (2016).
- Chris Holiman, “Microsampling and the Bioanalytical Challenges in Their Routine Analysis Webinar,” (Bioanalysis Zone, Future Science Ltd., 2015).
- E. Ciccimaro (BMS) et al., “Achieving Maximal Sensitivity Gain When Scaling a Protein Immunocapture Assay from Traditional to Microflow LC-MS/MS,” poster presented at ASMS, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, 2014.
- Morse Faria et al., Journal of Chromatography B1001, 156–68 (2015).
- Anne J. Kleinnijenhuis et al., Bioanalysis8(9), 891–904 (2016).
- Thomas D. Olgesby, “The changing landscape of large molecule bioanalysis by LC-MS/MS and the use of new tools to improve sensitivity Webinar,” (Bioanalysis Zone, Future Science Ltd., 2015).
- Yun Wang Alelyunas et al., J. Appl. Bioanal. 1(4), 128–35 (2015).
- Michael Donegan et al., High Throughput Microflow LC-MS: Sensitivity Gains on a Practical Timescale. App Note, Waters Corp., (2016).
- US Food and Drug Administration, Guidance for Industry, Investigators, and Reviewers (FDA, Rockville, Maryland, USA, 2006).
- James P. Murphy et al., Enhancing Mass Spec Sensitivity by Reducing Chromatographic Flow Rates with ionKey/MS. White Paper, Waters Corp., (2014).
- US Food and Drug Administration, Novel Drugs 2015 (FDA, Rockville, Maryland, USA, 2016).
- Erin E. Chambers et al., Reducing Sample Volume and Increasing Sensitivity for the Quantification of Human Insulin and 5 Analogs in Human Plasma Using ionKey/MS. App Note, Waters Corp., (2016).
- Catalin E. Doneanu et al., Ultrasensitive Quantification Assay for Oxytocin in Human Plasma Using the ionKey/MS System. App Note, Waters Corp., (2016).
Anthony G. Marcello is a Business Development Manager for Waters Corporation’s Global Pharmaceutical Business, with a focus on LC–MS technologies for bioanalysis. He has experience with marketing, partnering, and licensing of large molecule and cell-based therapies, bioinformatics platforms, medical devices, and LC–MS technologies. His education includes a B.Sc. in biotechnology and an MBA in strategic innovation both from the University of Rhode Island.
E-mail: Anthony_Marcello@waters.com
Website: www.waters.com

Understanding FDA Recommendations for N-Nitrosamine Impurity Levels
April 17th 2025We spoke with Josh Hoerner, general manager of Purisys, which specializes in a small volume custom synthesis and specialized controlled substance manufacturing, to gain his perspective on FDA’s recommendations for acceptable intake limits for N-nitrosamine impurities.














