Seamless Method Transfer from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC
The Application Notebook
This application note describes the transfer of a conventional LC method for the analysis of antihistaminic drugs from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC, and demonstrates that equivalent results can be obtained.
Introduction
Instrument-to-instrument method transfer is an important topic for all laboratories throughout different industries (1). One example is the transfer of conventional LC methods from older equipment such as the Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC, to new instruments such as the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC. This application note (2) describes the analysis of antihistaminic drugs using an 1100 Series Quaternary LC. The method is transferred without any changes to the 1260 Infinity II LC, and equivalent results in terms of retention time and resolution are obtained. Furthermore, the conventional LC analysis of antihistaminic drugs can be transferred to UHPLC conditions, optimized for resolution as well as for speed, using the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC.
Experimental Conditions
Conventional LC analysis of the antihistaminic drugs tripelenamine, chlorpheniramine, tetracaine, and promethazine was achieved with the Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC as well as the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC. An Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5-μm) was used with a gradient of 25 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate in water (pH 3) and acetonitrile at a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min and a temperature of 40 °C. Diode array detection was performed at 204 nm.
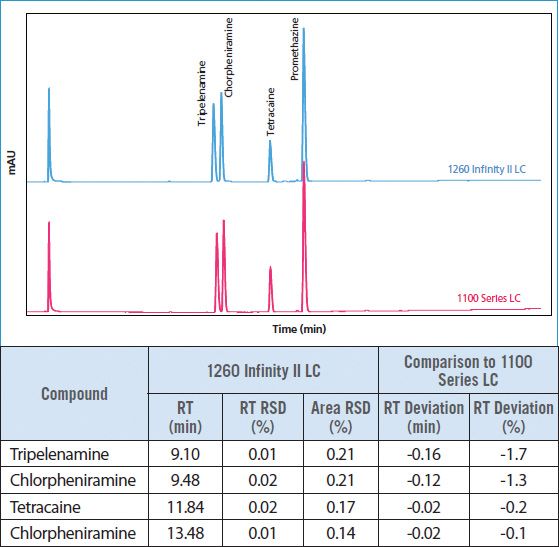
Figure 1: Conventional LC analysis of antihistaminic drugs on an
Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC and an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC.
Results
The conventional LC analysis of antihistaminic drugs was transferred without any method changes from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC. By using the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC, excellent retention time and area precision was achieved. Figure 1 compares the retention times of the antihistaminic drugs obtained using the Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC and the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC. With a maximum deviation of -1.7%, excellent agreement of retention times was observed. Further, a slight increase in resolution was achieved using the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC. This proves the equivalency of the 1260 Infinity II LC compared to the 1100 Series Quaternary LC for the analysis of antihistaminic drugs.
With a pressure range of up to 600 bar, the Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC also enables UHPLC analyses to be performed using Agilent InfinityLab Poroshell columns. The transfer of the conventional LC analysis of antihistaminic drugs to UHPLC conditions, optimized for resolution as well as for speed, offers the option to increase peak resolution and at the same time reduce analysis time and solvent use.
Conclusions
The transfer of a conventional LC method for the analysis of antihistaminic drugs from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC showed a maximum retention time deviation of -1.7% as well as a slight increase in resolution, and thereby proves the equivalency of the 1260 Infinity II LC compared to the 1100 Series Quaternary LC for the analysis of antihistaminic drugs.
References
(1) Agilent 1290 Infinity with ISET, Agilent Technologies User Manual, part number G4220-90314 (2015).
(2) S. Krieger, Method Transfer from an Agilent 1100 Series Quaternary LC to an Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC, Agilent Technologies Application Note, publication number 5991-6914EN (2016).

Agilent Technologies, Inc.
5301 Stevens Creek Blvd., Santa Clara, CA 95051
Tel: (800) 227 9770
Website: www.agilent.com

SEC-MALS of Antibody Therapeutics—A Robust Method for In-Depth Sample Characterization
June 1st 2022Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective therapeutics for cancers, auto-immune diseases, viral infections, and other diseases. Recent developments in antibody therapeutics aim to add more specific binding regions (bi- and multi-specificity) to increase their effectiveness and/or to downsize the molecule to the specific binding regions (for example, scFv or Fab fragment) to achieve better penetration of the tissue. As the molecule gets more complex, the possible high and low molecular weight (H/LMW) impurities become more complex, too. In order to accurately analyze the various species, more advanced detection than ultraviolet (UV) is required to characterize a mAb sample.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)










