Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography and Water, Part II: Re-equilibration of the Stationary Phase Following Gradient Elution
LCGC North America
Re-equilibrating a reversed-phase stationary phase following aqueous gradient elution can be achieved much faster than you think.
How long does it take to re-equilibrate reversed-phase stationary phases following gradient elution, especially when starting with a highly aqueous eluent?
A little more than 15 years ago, Adam Schellinger and I started what turned into an extensive series of experiments aimed at better understanding reversed-phase column re-equilibration following solvent gradient elution. We were both graduate students at the time, studying with Professor Peter Carr at the University of Minnesota. Adam was focused on fundamental aspects of gradient elution, including optimization and method transfer, and I was focused on improving the speed of two-dimensional liquid chromatography (2D-LC) separations. I can still recall the place in the lab where I asked Adam why re-equilibration of reversed-phase columns required so much time. Neither of us could come up with a clear answer based on our reading and understanding about how columns worked, so we decided to do some simple experiments and find out for ourselves. The prevailing thought at that time was that reversed-phase columns should be re-equilibrated with about 10 column volumes of the initial eluent used in the gradient following one separation, and before injecting the next sample. A typical 150 mm × 4.6 mm i.d. column has a dead volume of about 1.5 mL. Even using a flow rate of 2 mL/min, this translates into a re-equilibration time of about 8 min; these days, many separations are entirely completed in a fraction of that time.
The essence of what we learned was that, under most circumstances, reliable chromatographic results can be obtained with much shorter re-equilibration times corresponding to re-equilibration with just one to two column volumes of the initial eluent used in the gradient. For conventional LC separations, this can result in tremendous time savings, and improve throughput of gradient elution methods. In 2D-LC, this was a transformative finding, because we realized that this would enable high quality 2D separations on the timescale of an hour or less (1).
In Part I of this "LC Troubleshooting" series earlier this year, I discussed the use of reversed-phase stationary phases designed for use in highly aqueous eluents, and how "dewetting" of traditional reversed-phase stationary phases can occur under these conditions. One question I alluded to in that article, but did not address in detail, was "How long does it take for an aqueous-compatible reversed-phase stationary phase to equilibrate when switching from an eluent containing some organic solvent to a completely aqueous eluent?" This is a question of practical significance, both for isocratic separations involving a completely aqueous eluent, and gradient elution separations that involve an initial eluent that is completely aqueous.
Essential Concepts for Re-equilibration Following Gradient Elution
The results of our initial studies of column re-equilibration several years ago were summarized in a series of journal articles. One was focused primarily on eluents containing acetonitrile and water, and non-ionogenic solutes (2). The other two papers dealt with more complex situations, involving buffered eluents and ionogenic solutes (3,4). Readers interested in the effects of variables on re-equilibration, such as flow rate, temperature, solute retention, and eluent additives are encouraged to read these articles. It is also worthwhile noting here that McCalley has recently published two papers that address questions about the rate of column re-equilibration under HILIC conditions (5,6). The two most impactful outcomes from our own work on reversed-phase separations were:
- Learning that we had to distinguish between two very different "states" of column re-equilibration following gradient elution: i) a state in which retention was highly repeatable as long as the re-equilibration time between separations was fixed and precisely controlled; and ii) a state in which retention was independent of re-equilibration time between separations; we refer to this as a state of full re-equilibration.
- Learning that, in many situations, the time it takes to flush the "strong solvent" (for example, acetonitrile in the case of reversed-phase gradient elution) from the pumping system at the end of a gradient is a big contribution to the apparent required re-equilibration time. This time is a property of the instrument, and has nothing to do with the column itself.
Figure 1 illustrates the exponential flushing out of the strong solvent from the pumping system and connections to the column (in many cases, flushing this strong solvent from the autosampler takes significant time, too) that is observed at the end of the solvent gradient program. For practical purposes, in my laboratory we estimate the flush-out time (tflush) as two times the delay time (td). In many cases, actual re-equilibration of the column requires flushing with just one to two column volumes of initial eluent beyond tflush. This is why it is important to have a sense for this time, especially when using columns with small volumes (that is, diameters of 2.1 mm or less).
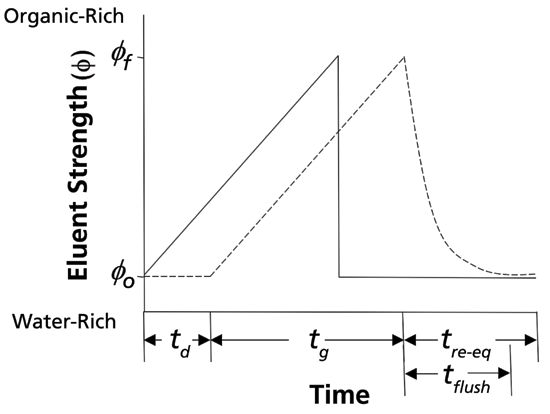
Figure 1: Illustration of reversed-phase solvent program used in gradient elution (solid line), and the eluent composition observed at the column inlet (dashed line). The change is composition is offset in time, due to the delay time (td) that results from the time it takes for a change in composition to travel from the mixing point to the column inlet. Particularly problematic for fast gradient separations is the exponential flush-out of the strong solvent observed at the end of the programmed gradient.
Quantifying the Rate of Re-Equilibration in Aqueous Eluents
To quantify the rate of rate-equilibration of an AQ-C18 column in a completely aqueous eluent following a solvent gradient, I varied the re-equilibration time, and tracked the retention times of six probe compounds, ranging from the hydrophilic tartaric acid to the more hydrophobic 4-butylbenzoic acid. A representative chromatogram for this mixture is shown in Figure 2, where the solvent gradient starts with completely aqueous eluent, and ends with 75% acetonitrile.
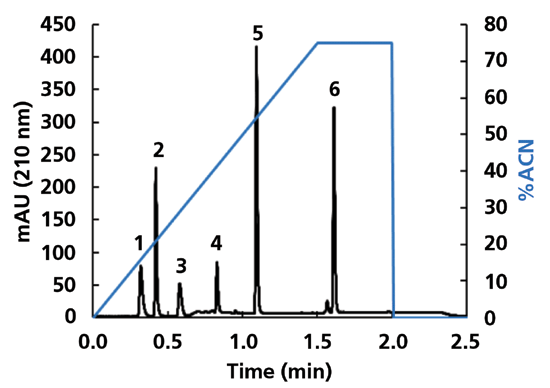
Figure 2: Chromatogram for the separation of six organic acids on an AQ-C18 column. Chromatographic conditions: Column, HALO AQ-C18, 50 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., 2.7 µm superficially porous particles; Eluent A, 10 mM phosphoric acid in water; Eluent B, acetonitrile; Gradient: 0-75% B in 1.5 min, 75% B for 0.5 min, 75-0% B in 0.1 min, 0% B for 4.99 min; Flow rate, 0.50 mL/min; Temperature, 40 °C; Injection volume, 1 µL; Solutes: 1 – tartaric acid, 2 – succinic acid, 3 – propionic acid, 4 – butyric acid, 5 – phenylacetic acid, 6 – 4-butylbenzoic acid. The retention factor of tartaric acid is about 0.5. The pressure at the column inlet at the beginning of the separation was about 160 bar. HALO is a trademark of Advanced Materials Technology, Inc.
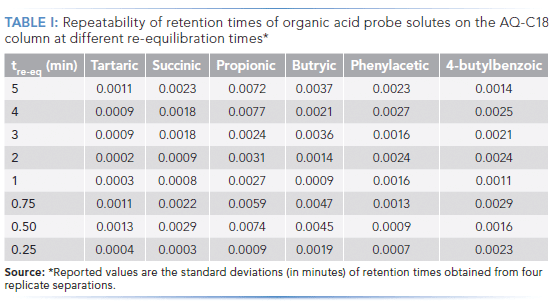
Figure 3 shows the difference between average retention time for a given solute from four replicate separations at a given re-equilibration time, and the retention time for that solute with a re-equilibration time of 5 min (which corresponds to about 25 column volumes of re-equilibriation). We observe that retention of the probe solutes is nominally independent of re-equilibration time all the way down to a re-equilibration time of 0.5 min. The retention of propionic acid appears to vary slightly; however, the retention of this probe is significantly less repeatable than the others, as is indicated by the standard deviations shown in Table I.
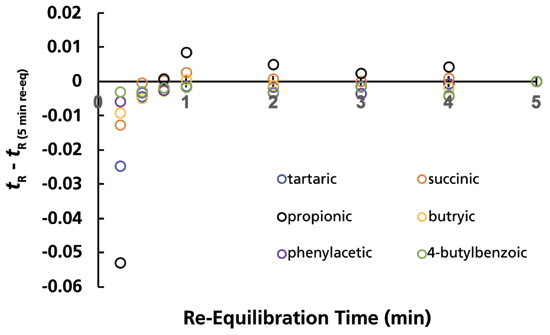
Figure 3: Difference between retention at a given re-equilibration time and the retention time with a re-equilibration time of 5 minutes for the AQ-C18 column. Conditions are the same as those described in Figure 2.
These experiments were carried out using an instrument optimized to reduce the gradient delay volume to about 70 µL. At a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min., the gradient delay time is about 10 s, and the flush-out time is 20 s. Under these conditions, the dead time of the column is about 12 s. Given that the retention times of the probes are already stabilized at a re-equilibration time of 30 s, this means that the column is effectively fully equilibrated after flushing with just one column volume of completely aqueous eluent. Although the retention times of the probes are clearly different, with a re-equilibration time of 15 s compared to 30 s, the separations are still highly repeatable, as shown by the excellent precision of retention time in the last row of Table I, so long as the re-equilibration step is also precise.
What About Re-Equilibration of a Conventional C18 Column in Highly Aqueous Eluents?
Given how fast the AQ-C18 column equilibrates with the completely aqueous eluent as shown above, it is reasonable to ask if a conventional C18 phase behaves differently under these conditions. In the first work Adam and I did on this topic many years ago, the lowest percentage of starting organic solvent we used was 1% acetonitrile. Figure 4 shows the results from the same type of experiment described above, where the initial eluent used in the gradient was 100% aqueous, but with a conventional C18 column. These results are similar to those shown in Figure 2 in that retention times are nominally independent of re-equilibration time down to re-equilibration times as short as 1 min. In this case, however, retention times increase as the re-equilibration time is decreased. It is not immediately obvious to me how we might rationalize this result. Nevertheless, we see again that these separations are highly repeatable, even at the shortest re-equilibration time of 15 s. The conclusion here, then, is that the conventional C18 column requires a bit more time to fully equilibrate with the completely aqueous eluent (that is, four column volumes rather than one), but not dramatically more time.
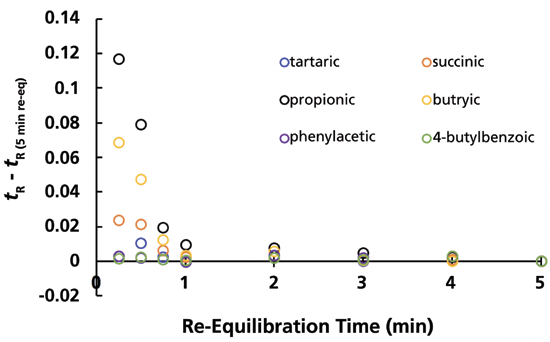
Figure 4: Difference between retention at a given re-equilibration time and the retention time with a re-equilibration time of 5 min. Conditions are exactly the same as those described in Figure 2, except that a HALO C18 column was used. HALO is a registered trademark of Advanced Materials Technology, Inc.
Keeping in mind the result shown in Part I of this series that we only observed dewetting of the C18 phase when the eluent flow through the column was stopped for 10 min, I did one final experiment to check for this effect under these gradient elution conditions. Figure 5 shows chromatograms for the C18 column before and after turning off the flow for 10 min, both with a re-equilibration time of 1 min, and each after a first "warmup" gradient. We observe that there is no statistically significant difference between the retention times observed in these two cases. It seems that, even if the C18 phase does dewet when the flow is turned off, it is re-wetted quickly during the first gradient such that the separations observed thereafter are indistinguishable from those obtained prior to turning off the flow.
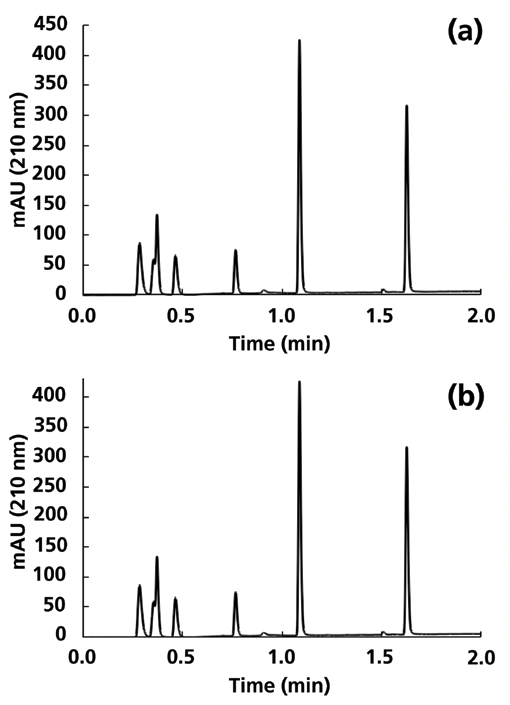
Figure 5: Comparison of chromatograms obtained with the C18 column and a re-equilibration time of 1 min, (a) before, and (b) after turning the flow off for 30 min. The slight splitting of the second peak is due to the partial separation of acetic and succinic acid. Acetic acid was also in the mixture used with the AQ-C18 column, but was not resolved from succinic acid, as shown in Figure 2. Conditions are the same as those described in Figure 4.
Summary
In this installment of "LC Troubleshooting," I have discussed the results of simple experiments aimed at understanding how quickly reversed-phase stationary phases equilibrate with highly aqueous eluents when they are used as the initial eluent in solvent gradient elution. We observe that an aqueous compatible AQ-C18 is effectively fully equilibrated with a completely aqueous eluent after flushing with just one column volume of initial eluent beyond the flush-out time of the instrument, at least for the solutes studied here. It is likely that other solutes that may be more sensitive to the chemical state of the stationary phase might require longer re-equilibration periods. Finally, similar experiments with a conventional C18 column showed that this phase required slightly, though not dramatically, longer times to fully equilibrate with a completely aqueous initial eluent.
Acknowledgments
I'd like to thank Tom Waeghe for our discussion of highly aqueous eluents that eventually led to the experiments described in this article.
References
(1) D.R. Stoll, P.W. Carr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 5034–5035 (2005). doi:10.1021/ja050145b.
(2) A. Schellinger, D. Stoll, P. Carr, J. Chromatogr., A.1064, 143–156 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.12.017.
(3) A.P. Schellinger, D.R. Stoll, P.W. Carr, J. Chromatography A. 1192, 54–61 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.02.049.
(4) A.P. Schellinger, D.R. Stoll, P.W. Carr, J. Chromatography A.1192, 41–53 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.01.062.
(5) J.C. Heaton, N.W. Smith, D.V. McCalley, Analytica Chimica Acta.1045 141–151 (2019). doi:10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.051.
(6) D.V. McCalley, J. Chromatography A. 1554, 61–70 (2018). doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.016.
ABOUT THE COLUMN EDITOR
Dwight R. Stoll

Dwight R. Stoll is the editor of "LC Troubleshooting." Stoll is a professor and co-chair of chemistry at Gustavus Adolphus College in St. Peter, Minnesota. His primary research focus is on the development of 2D-LC for both targeted and untargeted analyses. He has authored or coauthored more than 60 peer-reviewed publications and three book chapters in separation science and more than 100 conference presentations. He is also a member of LCGC's editorial advisory board. Direct correspondence to: LCGCedit@MMHgroup.com

Polysorbate Quantification and Degradation Analysis via LC and Charged Aerosol Detection
April 9th 2025Scientists from ThermoFisher Scientific published a review article in the Journal of Chromatography A that provided an overview of HPLC analysis using charged aerosol detection can help with polysorbate quantification.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.













