Chromatography Fundamentals, Part VI: The Gaussian Distribution and Moment Analysis
LCGC North America
How well do Gaussian-shaped profiles represent injected solute peaks after they are eluted through a chromatographic column? This question is explored along with a discussion of moment analysis for determining retention time, variance, and shapes of peaks.
During elution through a chromatographic column, injected solutes develop into Gaussian-shaped profiles, caused by diffusion processes. In this article, we show how the Gaussian distribution model is used for measuring retention time and peak width, or broadening. Also included is a discussion of moment analysis for determining retention time, variance, and shapes of chromatographic peaks.
The key to high-resolution separations is using chromatographic columns that generate large numbers of theoretical plates,

or have minimal plate heights,

where tr is retention time, L is column length, and σ2 is peak variance, topics that were previously covered in Parts IV and V in this series (1,2). The connection between statistical theory and chromatography stems from the fact that the two variables in equations 1 and 2, retention time and peak variance, are also the same two statistical parameters that characterize the Gaussian distribution.
This month's article reviews the properties of the Gaussian distribution, with emphasis on its relationship to retention time and peak broadening. Also included is a discussion of moment analysis of chromatographic peaks, and its application to chromatography.
Chromatographic Peaks as Gaussian Distributions
Immediately after injection, retained solute molecules begin to separate into discrete populations based on their chemical composition, while those that are unretained elute early as a single population. When a sample is injected, solute molecules form a binomial distribution; as peaks encounter more plates during elution, they morph into a Poisson distribution, and finally elute from the column as Gaussian distributions.
Each chromatographic peak, therefore, consists of a population of molecules that are spatially and temporally distributed randomly about a mean retention time with a standard deviation. This Gaussian distribution model, first proposed by Nobel laureates Martin and Synge, is one of the key elements of chromatographic theory.
Properties of the Gaussian Distribution
The Gaussian, or normal, distribution, also known as the most probable distribution or error function, is the limiting form of the binomial distribution, consisting of a large population of random, independent events. Most physical phenomena involving molecules can be modeled by this type of distribution.
The Gaussian distribution describes the deviation of random events from a central or average value. This function, which is based on statistical theory, assumes that the probability of finding an event close to the mean is high, and decreases exponentially outwards from the mean. An event is a statistical term equivalent to a data point, or a solute molecule located a certain distance from the mean. The totality of events forms a chromatographic peak.
Equation 3 is the normalized form of the Gaussian distribution equation used for statistical analysis of data populations:
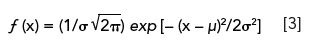
This equation has been normalized so that the total area under the curve is unity, that is,
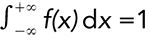
; a derivation that was accomplished by setting the pre-exponential term to 1/σ√2π). The ordinate y is the peak height at a distance or location x from the mean µ, which is referenced to zero. Since the theoretical limits of this equation are x ± ∞, the curve never reaches baseline, but approaches it asymptotically. Peak shape is defined by the exponential term in equation 3, and the standard deviation, σ. As we shall see later in this article, moment analysis can also be used to study peak shape.
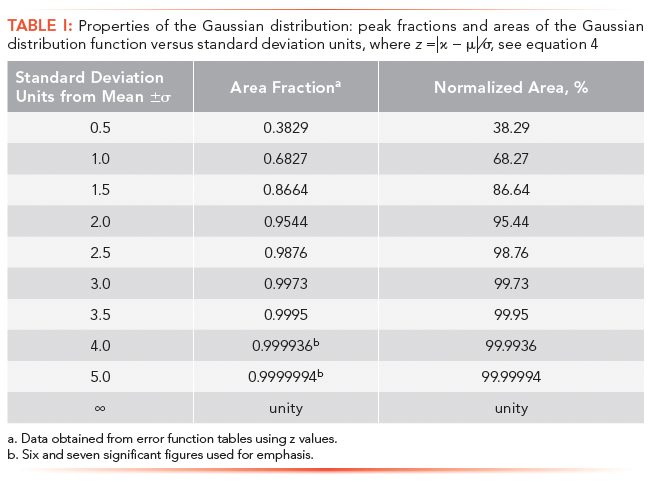
The Gaussian distribution shown in Figure 1 is represented by coordinates that places the center or origin of the distribution (x = 0); a format typically reserved for statistical analysis. In chromatography, the origin or reference point is the time of injection, t = 0. Each standard deviation unit of the Gaussian distribution, working outwards from the mean, represents a fraction of the total area or the probability of finding a molecule at a location specified by the standard deviation. For example, the probability of finding a solute molecule beyond ± 4σ units from the mean is only 6.4 × 10-3 % (see Table I). In chromatography, however, we are mainly concerned with an area of 95.4%, bounded by ± 2σ.
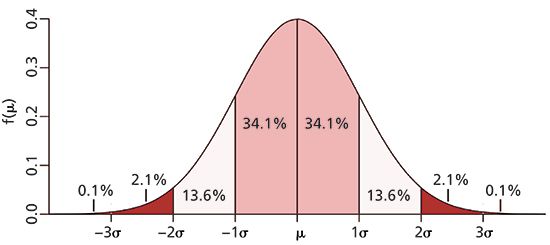
Figure 1: Gaussian distribution with peak area normalized to unity. Areas under the curve are indicated for each standard deviation, σ. Although difficult to see, the peak approaches baseline asymptotically. Ordinate is the correct height for a normalized area. Adapted from http://www. muelaner.com/wp.
Gaussian Distribution Integral
Since the total area under a Gaussian distribution is unity, we can determine relative peak areas with the integral form of equation 3 (3):
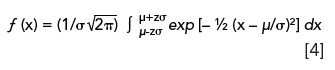
where the dimensionless variable z is equal to |x-µ|/σ. Equation 4 is used for statistical analysis, but shown here represents an idealized chromatographic peak.
Since equation 4 cannot be evaluated analytically, we must rely on probability tables (3). For example, the relative peak area encompassed by ± 1σ units from the mean, would have a z value of 1.0. Based on tabulated data or appropriate software, the peak area fraction would be 0.683 or 68.3%. For convenience, some z-values and corresponding areas are given in Table I; seven significant figures are shown for emphasis. (Note that the z-value is a mathematical construct used by statisticians to ensure that the limits are dimensionless. Thus a z-value of 2.5 is identical to 2.5σ units).
Mean, µ
The mean value, also referred to as an arithmetic average, is the first moment of the distribution, which is presented below. In statistics and for many problems in physics, the mean is used as a reference point; however, in chromatography, the first moment is referenced with respect to the point of injection, that is, t0.
The peak maximum, or mode, of the distribution is routinely used as an indicator of retention time, because it is an easily measured parameter; however, since the peak maximum is dependent on injection concentration, as well as other experimental parameters, the mean or first moment should be used instead. As discussed in Part I of this series (4), the mean retention time is the location where the distribution coefficient is at thermodynamic equilibrium. The mean, rather than the mode, should be used, for asymmetric or tailed peaks, or for measurements involving physiochemical properties of solutes, such as partition coefficients, equilibria, and free energy (for documentation, readers may want to check their chromatographic software to see if retention time is measured at peak maximum, or the mean).
Standard Deviation, σ
Methods of measuring the standard deviation from a population of experimental data are exactly the same as for a chromatographic peak. These approaches are given in Table II and illustrated by Figure 2. The choice of method depends upon baseline quality, such as noise and drift, and peak symmetry or tailing. Also included in this table and discussed in the next main section is the second moment.
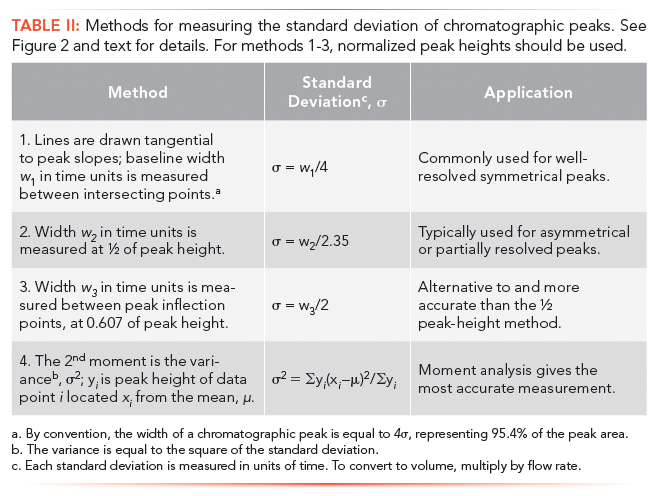
One standard deviation unit, σ, of a Gaussian distribution is defined as the distance or location between the mean, µ, and the inflection point on either side of a symmetrical distribution; the peak height of the inflection points is equal to 0.606 or e-½, see Figure 2. The standard deviation can also be measured at one-half of the peak height, w½ = 2.35σ. The third method, commonly used in chromatography, especially before the introduction of computers, is to draw tangential lines along the steepest portions of the slopes of a peak. For symmetrical peaks, the distance between points where the tangents intersect the baseline is equal to 4σ. The last method in Table II uses moment analysis to compute the peak variance, which is the square of the standard deviation.
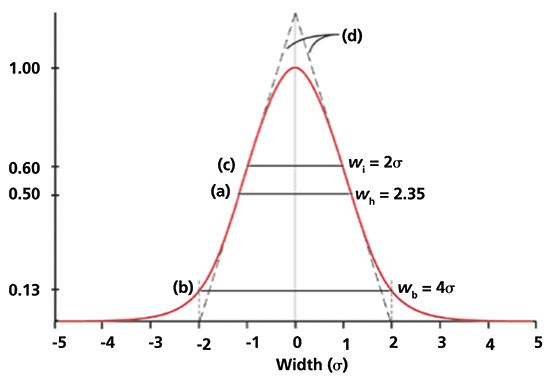
Figure 2: Chromatographic peak centered at µ = 0. Peak height of maximum is set equal to 1.00. (a) Peak width at 50% height, wh = 2.35Ä ; (b) Peak width at baseline, wb = 4Ä, which is equivalent to 13% of peak height; (c) Peak width at the inflection points, wi = 2Ä, which is equivalent to 60% of peak height. (d) lines drawn tangentially to the inflection points intersect baseline at 4Ä. Adapted and used with permission from J. V. Hinshaw, LCGC Eur., 26(10), 575-582 (2013).
From a mathematical perspective, an infinite number of sigma units are required to encompass 100% of all random events that comprise a population (see Table I), a chilling prospect for chromatographers. For most physical phenomena, a range of µ ± 4σ is typically used, which includes >99.99% of all values under the curve (see Table I). In chromatography, however, the width of a chromatographic peak is relaxed even further by setting peak width at ± 2σ, which includes 95.4% of the peak area; a reasonable value considering that chromatographic peaks may not be symmetrical nor follow an exact Gaussian distribution (please note that the number of theoretical plates, which is calculated from peak width measurements, are approximations, and should be reported to two or three significant figures).
Additive Properties of the Standard Deviation
If two or more Gaussian peaks merge, the resultant peak width or standard deviation, σt, does not equal to the sum of the individual standard deviations,

because of the statistical nature of Gaussian distributions. To combine either discrete or populations of data points, only peak variances, σ2, can be used,

from which the standard deviation is obtained,,

A conceptual explanation why the variance, and not the standard deviation, is used for addition (or subtraction) is as follows: Within a population of molecules undergoing random motion, one-half of all molecules will, at some time, diffuse to the right, and one-half will diffuse to the left. If we add all the vectors of diffusing molecules in an instant of time, the sum total would be zero, not a satisfying answer. To eliminate this problem, absolute values are used which necessitates the use of squared terms; the basis of which is the random-walk model, to be presented in Part VIII of this series.
Combining variances, either in theoretical or practical situations, is used when multiple sources of peak broadening are considered or when two or more peaks merge. For example, when two chromatographic peaks with baseline widths of 20 µL and 40 µL are added or merged, the net peak volume would be: Vt = (202+402)½ = 45 µL, not 60 µL. Note that total peak width in chromatography encompasses four sigma units. Applications of this concept to peak broadening will be given in Part VII.
Moment Analysis in Chromatography
Moment analysis is a mathematical procedure of determining properties of distributions, including, of course, chromatographic peaks. The term "moment" originates from "moment of inertia" (not momentum), I, which is the torque or the resistance of an object to angular acceleration,

where m is the mass of the object, and r is the radial distance from the object to the point where the force is being applied. When moments are used for the statistical analysis of distributed data, however, the following equation applies (5):
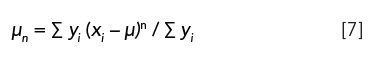
where µn is the nth moment about the mean or arithmetic average, µ, of the distribution, and yi is the magnitude of a data point at distance xi from the mean. The denominator, Σyi, is required for peak area normalization.
In chromatography, retention time is used for xi, referenced with respect to the point of injection, µ = t0 = 0, except for the 2nd moment, in which case the mean of the peak is used as reference. We must also introduce the number of data points, N, taken across a peak. In addition, yi has units of detector response per data point, and xi is the time per data point,
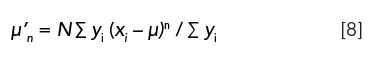
Although any number of moments can be employed, we are only interested in moments that range from 0 to 4 with respect to chromatographic peaks:
µ0: The zeroth moment of a chromatographic peak is simply the normalized peak area, µ0 = 1. However, for practical purposes we are most often interested in the absolute peak area, in which case the denominator is set equal to unity,
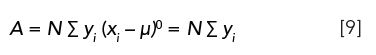
µ1: For a Gaussian distribution, referenced with respect to the mean, µ1 = 0. The first moment of a chromatographic peak, however, is the mean or average retention time of a solute,
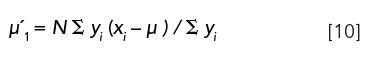
As mentioned above, it is the mean value, not the mode or peak maximum that should be used for accurate retention time measurements.
µ2: The second moment of a chromatographic peak, referenced with respect to the mean, is the peak variance, σ2.
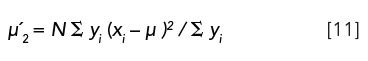
µ3: The third moment of a chromatographic peak, referenced with respect to the mean, measures peak asymmetry or skewness,
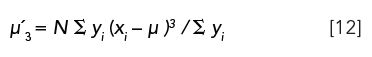
Peak asymmetry towards the front side occurs if µ3 > 0, and on the backside if µ3 < 0. The distribution is symmetrical when µ3 = 0. Skewness in statistics is defined as (µ3)â . It would be of interest to compare accuracy and precision of the third moment with standard methods of measuring peak asymmetry or tailing (6).
Several other formulae of skewness are available consisting of ratios of other moments, called beta coefficients (5)
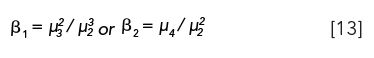
µ4: The fourth moment, referenced with respect to the mean, is the kurtosis, a measure of the peakedness or flatness of the peak. For a symmetrical distribution, µ4 = 0. When µ4 > 0, the peak is sharper or more peaked than a normal distribution. When µ4 < 0, the peak is flatter or has a broader peak maximum than a normal distribution. Other kurtosis definitions based on moment ratios are available (5).
Moment Analysis in Size Eclusion Chromatography
Moment analysis is also used in size exclusion chromatography (SEC) for determining average molecular weights of a polymer. In this technique, an SEC column is calibrated by injecting a series of polymer standards of known molecular weights Mi. Using an SEC calibration curve in which log Mi is plotted against elution volume (or retention time), the abscissa is transformed into log Mi or Mi.
Depending upon the ordinate that is used for describing the molecular weight distribution (MWD), the following molecular-weight averages can be computed from the first moment of the MWD:
Mn: The number-average molecular weight is the first moment of a distribution in which the number of moles, N, is plotted against molecular weight, M:

Mw: The weight-average molecular weight is the first moment of a distribution in which NM or weight (w) is plotted against molecular weight, M:
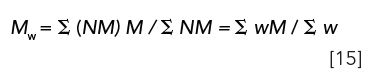
Mz: The z-average-molecular weight is the first moment of a distribution in which NM2 is plotted against molecular weight, M:
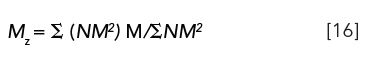
Although these three average molecular weights can be computed with equations 14 to 16, they can be graphically represented using first moments of the distribution.
Conclusions
Chromatographic peaks consist of solute molecules being carried through a column with excursions into and out from the stationary phase or packing. These populations can be modeled as Gaussian distributions, governed by the laws of statistics, where the probability density is highest in the center and decreases exponentially as we move outwards from the center. Based on chromatographic theory, there are only two parameters that define the behavior of solutes: the mean and standard deviation or variance of the peak.
Since peaks are considered as statistical distributions, moment analysis can also be used to determine peak properties. Thus, the zeroth moment is peak area, the first moment is the mean, and the second moment is peak variance. The ratio of the first moment squared and the second moment gives us an accurate measurement of column efficiency. The third moment reflects peak asymmetry or skewing, and the fourth moment describes the shape of the top-most portion of a peak; that is, its peakedness or flatness. Moment analysis can also be used in SEC for calculating average molecular weights provided that the correct ordinates of the molecular weight distribution are employed.
Next month's installment will describe the influence of peak broadening on resolution, as well as detection sensitivity.
References
(1) H.G. Barth, LCGC North Am., 36(8), 532-535, 538 (2018).
(2) H.G. Barth, LCGC North Am., 36(11), 830-835 (2018).
(3) P.R. Bevington and D. K. Robinson, Data Reduction and Error Analysis, (McGraw-Hill Education, New Delhi, India, 3rd Ed., 2003).
(4) H.G. Barth, LCGC North Am., 36(3), 200-202 (2018).
(5) J.G. Smith and A. J. Duncan, Elementary Statistics and Applications (McGraw-Hill Book Publishers, New York, New York, 1944).
(6) L.R. Snyder, J.J. Kirkland, and J.W. Nolan, Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography (Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 3rd Ed., 2010), p. 51.
Howard G. Barth is with Analytical Chemistry Consultants, Ltd. in Wilmington, Delaware. Direct correspondence to: howardbarth@gmail.com

Analyzing Vitamin K1 Levels in Vegetables Eaten by Warfarin Patients Using HPLC UV–vis
April 9th 2025Research conducted by the Universitas Padjadjaran (Sumedang, Indonesia) focused on the measurement of vitamin K1 in various vegetables (specifically lettuce, cabbage, napa cabbage, and spinach) that were ingested by patients using warfarin. High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) equipped with an ultraviolet detector set at 245 nm was used as the analytical technique.
Removing Double-Stranded RNA Impurities Using Chromatography
April 8th 2025Researchers from Agency for Science, Technology and Research in Singapore recently published a review article exploring how chromatography can be used to remove double-stranded RNA impurities during mRNA therapeutics production.
The Effect of Time and Tide On PFAS Concentrations in Estuaries
April 8th 2025Oliver Jones and Navneet Singh from RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia discuss a recent study they conducted to investigate the relationship between tidal cycles and PFAS concentrations in estuarine systems, and offer practical advice on the sample preparation and LC–MS/MS techniques they used to achieve the best results.
Assessing Safety of Medications During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding with LC–MS/MS
Published: April 8th 2025 | Updated: April 8th 2025Researchers conducted a study on medications used in psychiatry and neurology during the perinatal period, assessing how antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) affect placental functions, including transport mechanisms, nutrient transport, and trophoblast differentiation. Several quantitative methods, such as those for antianxiety and hypnotic drugs, were established to evaluate the safety of pharmacotherapy during breastfeeding using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS).











