Rapid Determination of Azo Dyes from Textile Samples Using Dionex ASE and U3000 HPLC-UV Instruments with MSQ Plus Detection
The Application Notebook
Azo dyes are used widely in the manufacture of various consumer goods such as leather, textiles, plastics, paper, hair care products, and cosmetics. On September 11, 2003, the European Union enacted European Parliament Directive 2002/61/EC, prohibiting the manufacture and sale of consumer goods containing specified azo dyes (1). The azo dyes of concern are those that can be reduced to aromatic amines. There are 22 aromatic amines classified as carcinogenic or potentially carcinogenic to humans.
Azo dyes are used widely in the manufacture of various consumer goods such as leather, textiles, plastics, paper, hair care products, and cosmetics. On September 11, 2003, the European Union enacted European Parliament Directive 2002/61/EC, prohibiting the manufacture and sale of consumer goods containing specified azo dyes (1). The azo dyes of concern are those that can be reduced to aromatic amines. There are 22 aromatic amines classified as carcinogenic or potentially carcinogenic to humans.
Current sample preparation and analysis methods for these compounds are time and labor intensive and consume large volumes of solvent (2). Combining an Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE®) system for sample preparation with an UltiMate® 3000 HPLC-UV-MS system for analysis has proven to be an advantageous alternative to previous methods, saving time, labor, and solvent. This article describes methods for extracting textile samples using ASE as well as analytical methods for determination of aromatic amines, including the 22 restricted aromatic amines.
Equipment
ASE 200 system
UltiMate 3000 HPLC system consisting of:
SRD-3600 solvent rack degasser
LPG-3600 low pressure gradient pump
WPS-3000T well plate autosampler
TCC-3000 thermostatted column compartment
UVD 340U UV detector
MSQ™ Plus MS detector
Chromeleon® 6.80 Chromatography Workstation
Glass fiber filters
ASE Conditions
Preheat: 20 min (purge closed)
Pressure: 1500 psi
Static: 5 min
Temp: 100 °C
Cycles: 2
Purge: 100 s
Flush: 30%
Solvent: 90% CH3OH with 10% 1 M KOH
Extraction time per sample: 40 min
Solvent amount used per sample: 17 mL
Analytical Conditions
Column: Acclaim® 120 C18, 3 μm, 120 Å, 2.1 × 150 mm
Column Temperature: 30°C
Injection Volume: 10 μL
Gradient: See Dionex Application Note 360 (3)
UV: 240 nm, 278 nm
Ionization Mode: APCI, positive polarity
Nitrogen: 3 bar
Corona Current: 10 μA
Source Temperature: 400°C
Cone Voltage: Varies per analyte. See Table I.
Sample Prep
Soak 1.0 gram of material in 3 mL citrate buffer (pH 6.0) and 3 mL of sodium dithionite (200 mg/mL) for two min. Transfer the mixture and solution to an ASE 11 mL cell containing a glass fiber filter.
Extraction
Place the extraction cells onto the ASE 200 and extract with the ASE conditions listed above. When the extraction is complete, record total volume of the extract and inject 10 μL onto the UltiMate 3000 HPLC-MS-UV.
Results and Discussion
Experimentation with the photodiode array detector demonstrated that wavelengths 240 and 278 nm were best suited for aromatic amine detection. A standard comprising 22 aromatic amines at 5 mg/L concentrations (Azo Dyes Mix-6, Ehrenstorfer Laboratories) was separated on the Acclaim 120 column and detected at UV wavelength 278 nm. (Figure 1). The 22 restricted azo dyes are labeled.
Figure 1
Individual standards of the Ehrenstorfer dyes were ordered from Sigma-Aldrich. These standards were run to determine the optimal mass spectrometer detection conditions (Table 1).
Table I: Optimized detection conditions of Azo Dye standards for amine analysis
A leather sample known to contain a forbidden dye was prepared, extracted, and determined using UV and MS detection (Figure 2). The presence of 2-anisidine and o-toluidine peaks in single ion monitoring (SIM) detection mode confirmed the identification of the peaks in the UV trace.
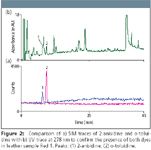
Figure 2
Conclusions
Extracting aromatic amines from samples is a bottleneck for most azo dye test procedures. ASE in combination with the UltiMate 3000 HPLC-MS-UV is a powerful tool in extraction and analysis of azo dyes, saving both time and solvent.
References
(1) Directive 2002/61/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 July 2002 Amending for the Nineteenth Time Council Directive 76/769/EEC Relating to Restrictions on the Marketing and Use of Certain Dangerous Substances and Preparations (Azocolourants). Official J. Eur. Commun. 2002, 45 (L243), 15–18.
(2) Ahlström, L.; Eskilsson, C. S.; Björklund, E. "Determination of Banned Azo Dyes in Consumer Goods." Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2005, 24, 49–56.
(3) Dionex Corporation. "Application Note 360: Rapid Determination of Azo Dyes in Textiles Using Dionex ASE and UltiMate 3000 HPLC Systems with MSQ Plus and UV Detection." Sunnyvale, CA, 2008.
Acclaim, ASE, Chromeleon, and UltiMate are registered trademarks of Dionex Corporation. MSQ is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088-3603
tel. (408) 737-0700, fax (408) 730-9403

Pick Your Poison. Isolation of Paclitaxel (Mar 2025)
March 7th 2025The diterpenoid, paclitaxel, which was identified as a potent chemotherapy agent for breast and ovarian cancer originates from the Pacific Yew tree. The isolation of paclitaxel from its major impurities is shown with the use of Hamilton’s PRP-1 (5 µm) HPLC column.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













