Molecular Weight Determination of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparins: SEC/MALS vs. SEC/UV-RI
Wyatt Application Note
Low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) are obtained by fractionation or depolymerization of natural heparins. They are defined as having a mass-average molecular weight of less than 8000 and for which at least 60% of the total weight has a molecular mass less than 8000.
Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) has been the most common way of measuring the molecular weight and molecular weight distributions of LMWHs by using the two most common detection technologies: ultraviolet (UV) coupled with refractive index (RI) detection. However, these detectors embody a relative method in order to determine molecular weights, requiring calibration standards. A newer, absolute method involves the use of multi-angle light scattering (MALS), which does not require any standards. The European Pharmacopeia (EP) monograph for LMWH specifies the use of the UV/RI detection method and provides a known calibration standard. Many laboratories around the world have adopted this method.
We previously developed an SEC/MALS method and found it to be very suitable for the analysis of LMWHs. We have recently adopted the UV-RI method described in the EP monograph and compared the molecular weight results generated for LMWH using each detection type. The adopted method uses an Agilent LC1200 series HPLC, 0.2 M sodium sulphate pH 5.0 mobile phase, Tosoh TSK-gel G2000 SWxl column with Tosoh TSKgel Guard SWxl, Waters 2487 dual wavelength UV detector, and Wyatt Optilab rEX refractive index detector. For MALS analysis, the UV detector was replaced with a Wyatt miniDAWN TREOS detector; all other methods aspects remained the same.
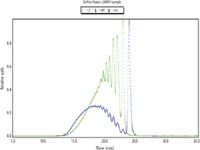
Figure 1: Examples of UV and RI traces for an LMWH sample
The results indicated that both detection types are suitable and acceptable for the analysis of LMWHs. The molecular weight and distribution results generated using each detection type are comparable. This indicates that a SEC/MALS method could be adopted in place of the SEC/UV-RI method currently required by the EP monograph, and that it would result in less time because it obviates the need for calibration standards.
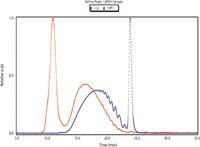
Figure 2: Examples of LS and RI traces for an LMWH sample.
This note was graciously submitted by Lin Rao and John Beirne of Scientific Protein Laboratories LLC.
Wyatt Technology Corporation
6300 Hollister Avenue, Santa Barbara, California 93117, USA
tel. +1 (805) 681-9009, fax +1 (805) 681-0123
Website: www.wyatt.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)

















