HPLC Separation of Anabolic Steroids on ZirChrom-PBD
The Application Notebook
ZirChrom Separations, Inc.
This note shows the separation of three closely related anabolic steroids, boldenone, nandrolone, and testosterone, using a ZirChrom®-PBD column. A typical analysis of these compounds involves derivatization and subsequent quantitation by GC–FID or GC–MS, however these methods tend to be labor intensive, and analytically unreliable. Baseline resolution of all three compounds was obtained on ZirChrom®-PBD at slightly elevated temperature in under 10 min using isocratic conditions.
Introduction
The rapid and accurate detection of anabolic steroids is crucial in today's sporting world. Historically the structural similarity of these compounds has made quantitative analysis by reversed-phase HPLC difficult at best. These steroids are very difficult to separate on silica ODS phases and provide nearly identical mass spectra. This method capitalizes on the unique temperature stability and surface chemistry of a zirconia-based stationary phase to achieve baseline resolution of these compounds in less than 10 min.
Experimental
A mixture of anabolic steroids was separated at 60 °C using a ZirChrom®-PBD column (see Figure 1) using the following conditions.
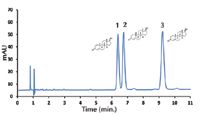
Figure 1: Separation of anabolic steroids on ZirChrom®-PBD, 1-Boldenone, 2-Nandrolone, 3-Testosterone.
Column: 150 mm × 4.6 mm i.d. ZirChrom®-PBD
Mobile Phase: 15/85 ACN/Water
Flow Rate: 1.5 mL/min
Injection Vol.: 5 μL
Pressure Drop: 160 bar
Temperature: 60 °C with Metalox™ 200-C Column Heater
Detection: UV at 215 nm
This separation allows for clear identification and quantification of these compounds without the use of expensive MS detection. The separation also requires no complex buffers and uses a minimum of organic modifier.
Acknowledgments
(1) Walter Hyde, Iowa State University.
Visit www.zirchrom.com for more application notes using ultra-stable, high efficiency ZirChrom columns.

ZirChrom Separations, Inc.
617 Pierce Street, Anoka, MN 55303
tel. 1-866-STABLE-1
Website: support@zirchrom.com


.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













