Ghost Peak Investigation in a Reversed-Phase Gradient LC System
LCGC North America
Here is a step-by-step approach to investigate the source of ghost peaks in a gradient LC method.
Ghost peaks can be difficult to eliminate when minor peaks are important in an LC separation. This case study shows how to isolate the source of such peaks.
Ghost peaks can be referred to as artifact (erroneous) peaks, system peaks, pseudo peaks, vacancy peaks, eigenpeaks, induced peaks, or spurious peaks (1). These are often observed unexpectedly in a chromatogram and can pose a challenge to analytical scientists. These peaks may arise from unknown impurities or artifacts within the liquid chromatography (LC) system (such as contaminants from a dirty injector needle, an air bubble in the pump, or a trapped contaminant in the guard column), from the mobile phase, from an extractable contaminant, from autosampler vials and caps, or from a contaminant carried over from a previous injection.
The occurrence of ghost peaks is seen more frequently in the gradient mode. The presence of a ghost peak in a sample chromatogram, especially at the elution time of a known impurity, may trigger an out-of-trend (OOT) or out-of-specification (OOS) investigation. An OOT or OOS investigation will lead to efforts to identify an assignable cause, assess the impact of the result, and propose further corrective or preventive action, if required. Because the contamination or artifact causing the ghost peak may come from many sources or may be transient in nature, the investigation can be time-consuming. In certain cases, the cause of the ghost peak may remain unresolved.
Furthermore, in some company standard operating procedures (SOPs) in a good manufacturing practice (GMP) environment, if the cause of a random ghost peak cannot be identified and the peak is ruled out as an impurity unrelated to the sample, the data may need to be reported "as is." In some situations a blank subtraction can be justified when reporting the data with ghost peak problems; however, this is usually not preferred in routine quality control (QC) laboratories. The biggest problem with significant ghost peaks is that they make automatic integration of chromatograms difficult. Hence, when manual integration or blank subtraction is used, ghost peaks can cause inconsistent and inaccurate impurity results. The problem eventually intensifies if the inconsistent impurity result has been used for trending purposes in stability studies.
Many publications (including past installments of this column) have cited ghost peak problems and perspectives (2). Here, we outline a step-by-step approach we have used to investigate the source of ghost peaks in a gradient LC method and share our empirical perspectives as quick approaches for solving ghost peak problems in LC. As a case study, we'll offer our experience with a reversed-phase LC method that was used to analyze a nonpolar, small-molecule active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in an early development stage.
Ghost Peak Issues
Whenever gradient methods are used, it is a good idea to run a blank gradient, in which no injection is made or only the sample diluent is injected, to check for any ghost peaks that might be present. In this study, acetonitrile was used as the sample diluent. An overlay chromatogram is shown in Figure 1 that compares injections of an acetonitrile blank with multiple ghost peaks and an injection of the API sample containing related substances. The analyses were performed on a Waters LC Alliance 2695 and Waters photodiode-array detector model 2996 (Waters Corporation, Milford, Massachusetts) with a 250 mm x 4.6 mm, 5-µm Luna C8 column (Phenomenex, Torrance, California) operated at 25 °C and 1 mL/min, with 264-nm UV detection. A linear gradient was run from 95% 50 mM ammonium acetate buffer (pH 4.75) (mobile phase A) to 95% acetonitrile (mobile phase B) in 30 min, with a final 5-min hold at 95% acetonitrile.
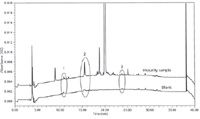
Figure 1: Overlay of chromatograms with ghost peaks (circled) from a blank (lower chromatogram) that interfere with an impurity sample analysis (upper chromatogram).
The overlay chromatogram of Figure 1 clearly shows that some of the ghost peaks in the blank (lower chromatogram) were eluted at the same time as some of the related substances (upper chromatogram); these will interfere with the determination of the related substances.
As shown in Figure 2, multiple runs on different days indicated that these ghost peaks showed up inconsistently in various acetonitrile blank injections. This random appearance of ghost peaks made related substance peak identification difficult. Furthermore they led to an elevated baseline (or a bump) that made peak integration more difficult.
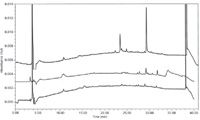
Figure 2: Overlay of chromatograms of acetonitrile blanks injected on different days, showing the inconsistent nature of the number and size of ghost peaks.
To isolate the source of the ghost peaks, we eliminated one potential source at a time until we found the root cause.
LC System Mechanical Sources
Systematic experiments were performed to rule out mechanical sources within the LC system by cleaning the LC system components that may potentially cause ghost peaks. Generally, these experiments are described in the LC system manufacturer's troubleshooting guidelines (3). In our investigation, we took the following steps:
1. Clean the LC system by flushing with 25:25:25:25 water–isopropanol–acetonitrile–methanol at flow-rate of 1 mL/min for 1–2 h (without the column attached). This procedure helps flush away any containments over a wide polarity range.
2. Change to a new in-line filter or guard column (or both), if applicable. This will ensure that the LC system is free from any potential contaminants deposited on the in-line filter or guard column.
3. Clean and purge the injector needle (to rule out a dirty injector or air peak). Typically, a needle wash solution mixture of equal volumes of water and organic solvent (acetonitrile, methanol, or isopropanol) was used to clean the needle or needle seat manually or automatically, depending on the LC system used. The cleanliness of the injector needle can be checked by running a blank gradient run (with or without an actual injection). For Waters's LC systems, a "condition column" function performs a no-injection gradient.
4. Clean and wash the UV detector cell. This can be done by following the detector manual instructions. Be careful not to exceed the UV cell's pressure limit.
5. Check the intensity of the UV lamp (to rule out a failing lamp).
After ensuring that the LC system modules were clean, blank acetonitrile was injected into the cleaned system using our gradient method. Ghost peaks were still observed with freshly prepared mobile phases, indicating that the causes of the ghost peaks were not a result of mechanical sources from the LC system.
Contamination from Glassware and Filtration of Reagents
To rule out any contamination from glassware, we tested several mobile phase bottles by rinsing them and by testing the mobile phase either with or without sonication. Initially, a blank injection was performed by using the mobile phase contained in a bottle (without sonication). Subsequently, the same bottle containing the mobile phase was placed in a water-bath sonicator. After 30 min of sonication at ambient temperature, a second blank injection using the sonicated mobile phase was performed, and the results from the two runs were compared.
From the sonication we expected to extract any additional amounts of the source contaminant from dirty glassware (the bottle) into the mobile phases. This study was repeated several times with different preparations of mobile phases. No significant changes were observed in sonicated and unsonicated mobile phases, which indicated that the mobile phase glassware was not the source of ghost peaks.
A blank injection was also performed using a freshly prepared mobile phase A (ammonium acetate buffer) that was passed through a 0.45-µm nylon filter to evaluate whether filtration introduced any contaminants. As a control, the acetonitrile blank was injected using unfiltered mobile phase A. Filtration of buffered mobile phases reduced the areas of ghost peaks slightly, and that suggested that mobile phase reagents could be the source of ghost peaks.
Contamination from Mobile Phase A Reagents and Solvents
The effect of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-grade water on ghost peaks was evaluated using water purified by a Milli-Q system (Millipore Corp., Billerica, Massachusetts) and commercially available HPLC-grade bottled water in preparing mobile phase A (ammonium acetate buffer). We did not see any significant differences between the two blank injections when comparing sources of water in the mobile phase. This led us to suspect that the ghost peaks could be arising from the organic reagents or additives in the mobile phases.
First, we evaluated the glacial acetic acid that we used in preparing ammonium acetate buffer. Five HPLC-grade acetic acid brands were evaluated while keeping the ammonium hydroxide and acetonitrile (mobile phase B) brands unchanged. Figure 3 demonstrates that some of the ghost peaks (at 23-, 25-, and 30-min retention times) resulted from impurities in a specific acetic acid brand (brand 1) used to prepare the mobile phase A. Another ghost peak at 15 min showed up primarily in brand 2 and to a minor extent in brand 3.
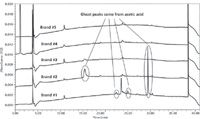
Figure 3: Comparison of blank chromatograms comparing acetic acid brands when all factors except the source of acetic acid were held constant.
The next step was to use the glacial acetic acid (brand 5; the cleanest) that gave no ghost peaks, and to compare sources of the next reagent used in preparing mobile phase A. Acetonitrile blanks were injected while changing the brands of ammonium hydroxide. Interestingly, another ghost peak at a retention time of about 11 min resulted from one source of ammonium hydroxide, as shown in Figure 4. At this point, we had successfully pinpointed the source of five ghost peaks (at about 11, 15, 23, 25, and 30 min) that came from the particular brands of acetic acid and ammonium hydroxide used to prepare the mobile phase A buffer when the problem originally appeared. This can be seen by comparing the chromatograms generated with acetic acid brand 1 (Figure 3) and ammonium hydroxide brand A (Figure 4) with the blank runs of Figures 1 and 2.

Figure 4: Blank chromatograms from two sources of ammonium hydroxide; all other factors were held constant.
Contaminant from Mobile Phase B (Organic Solvent)
By a process of elimination, the remaining unidentified ghost peak that was eluted at 24 min (Figure 1) was suspected to come from mobile phase B (acetonitrile). To prove that this peak was not coming from mobile phase A, a blank was injected using Milli-Q water instead of ammonium acetate buffer (as mobile phase A) and acetonitrile (as mobile phase B), as shown in Figure 5. Then two HPLCgrade brands (X and Y) of acetonitrile were compared, as shown in Figure 6. Based on these overlay chromatograms, we are certain that acetonitrile brand X (our original source) contributed to the ghost peak that was eluted at 24 min. Lastly, by choosing the selected ammonium hydroxide, acetic acid, and acetonitrile brands with no ghost peak contributions, a blank sample was injected to produce a clean baseline (Figure 7). The tiny peak at 30 min did not interfere with impurities that had been identified in our samples, so this was acceptable.
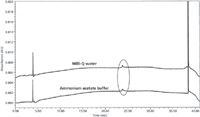
Figure 5: The effect of elimination of ammonium acetate in mobile phase A.
Conclusions
We successfully isolated the source of all major ghost peaks in our LC method by using a systematic elimination approach. In our case, the ghost peaks were coming from both mobile phases. After ensuring that all the mechanical aspects of the LC system are functioning properly, it is appropriate to shift the investigation directly to the mobile phases. We recommend evaluating different brands of HPLC-grade reagents, because some can contain impurities that can cause ghost peaks in specific LC methods.
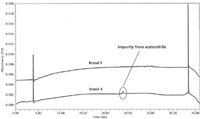
Figure 6: Comparison of blank chromatograms obtained from two different sources of acetonitrile; all other factors were held constant.
As preventive action, we suggest specifying the vendors and part numbers of solvents and reagents used in preparing mobile phases in the analytical procedure. This information is very useful during method development and especially in method transfer so that ghost peak problems can be prevented. However, if the method specifies an "equivalent" brand of reagent, it is not always necessary that the replacement reagent be of optimal grade or expensive. In such a situation, one needs to evaluate the most suitable reagents for the assay because each contaminant arising from reagent impurities may have a different UV absorption and may only be a problem under specific conditions and not others.
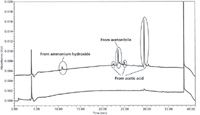
Figure 7: Successful elimination of interferences (top chromatogram) after selecting uncontaminated reagents (bottom chromatogram).
Sometimes the cause of ghost peaks remains unresolved and the peaks are impossible to eliminate. In such cases, three possibilities exist:
1. For a ghost peak that is consistently present and is eluted at a specific retention time, but does not overlap with any peak of interest, the contribution of the ghost peak's area (obtained from blank injections) can be ignored.
2. For a ghost peak that is inconsistently present, but is eluted at a specific retention time and does not overlap with any peak of interest, the identified contaminant can be used as a retention time marker in system suitability testing and excluded from reporting as an impurity. This approach may only be used after identifying the source of the contaminant. For example, a common contaminant may come from widely used plasticizers that may easily (but inconsistently) leach and extract out from a variety of products into the blanks and sample solutions.
3. For a ghost peak that is consistently present and is coeluted with a peak of interest, the ghost peak's average area response in blank injections bracketing the sample injections can be subtracted from the sample chromatograms to obtain the net peak area, but only if the overlapping ghost peak has consistent area response throughout the entire LC analysis batch. This approach can be used provided that the ghost peak is present in all blank injections and is not sample-related. It should be noted that such background subtraction is much less desirable than eliminating the interfering ghost peak by isolating its source or moving it out of the way in the chromatogram.
In any case, the outcome of the ghost peak investigation should be well documented and reflected in the test procedure if necessary.
References
(1) S. Williams, J. Chromatogr. A 1052(1–2), 1–11 (2004).
(2) J.W. Dolan and L.R. Snyder, Troubleshooting LC Systems (Humana Press, Clifton, New Jersey, 1989).
(3) HPLC Troubleshooting Guide, American Laboratory and Waters Corporation, 720000181EN, 08/02.
Silvia Sadikin is a formulation development scientist at SuperGen in Pleasanton, California, working with early LC method development, preclinical and clinical preformulation, and formulation development. Dee Dee Zhang is an analytical scientist at SuperGen working with R&D formulation and analytical personnel on R&D and clinical stability studies. Roger Inloes is the director of analytical development at SuperGen and is responsible for the release and stability testing of drug substances and drug products. Sanjeev Redkar is the vice president of manufacturing and preclinical development at SuperGen.
John W. Dolan

John W. Dolan
"LC Troubleshooting" Editor John Dolan has been writing "LC Troubleshooting" for LCGC for more than 25 years. One of the industry's most respected professionals, John is currently the Vice President of and a principal instructor for LC Resources, Walnut Creek, California. He is also a member of LCGC's editorial advisory board. Direct correspondence about this column via e-mail to John.Dolan@LCResources.com.

Common Challenges in Nitrosamine Analysis: An LCGC International Peer Exchange
April 15th 2025A recent roundtable discussion featuring Aloka Srinivasan of Raaha, Mayank Bhanti of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), and Amber Burch of Purisys discussed the challenges surrounding nitrosamine analysis in pharmaceuticals.
Extracting Estrogenic Hormones Using Rotating Disk and Modified Clays
April 14th 2025University of Caldas and University of Chile researchers extracted estrogenic hormones from wastewater samples using rotating disk sorption extraction. After extraction, the concentrated analytes were measured using liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection (HPLC-PDA).













