Flavour/Fragrance Profiling of Food: A Kinetic Study Using Micro-chamber Sampling with TD-GC–MS
Markes Application Note
Introduction
The decomposition rate and therefore shelf life of food products is of huge interest to the food industry. As food decomposes, the emission profile changes such that desirable flavour compounds diminish while malodours and/or toxic compounds are emitted. Monitoring changes in the chemical profile over time using conventional GC–MS methods can present a challenge in terms of what sampling method to use, the need to perform several analyses and the presence of interference, often water.
The Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor (μ-CTE) from Markes International is a novel device that provides a single, efficient dynamic headspace sampling method for emissions analysis. Minimal sample preparation is required; whole samples including foods, drinks, ingredients, packaging, etc. may be placed directly into the individual chambers and held under controlled conditions for a prolonged period.1,2 During this time, headspace vapours can be extracted onto thermal desorption (TD) sorbent tubes at chosen intervals. TD is a GC-specific sample concentration technique used to significantly increase the sensitivity of organic analysis. TD conditions may be optimised to analyse all headspace vapours or just the key olfactory compounds whilst interferences (such as water, ethanol etc.) are purged to vent.
To demonstrate the efficiency of the sampling method for food decomposition studies, a bacon sample was incubated in the μ-CTE and the emissions sampled over a period of 10 days.
Experimental
~8 g of a premium brand, dry-cured bacon was placed into a chamber of the μ-CTE and held at 30 °C with a constant (5 mL/min) flow of dry air. A sorbent tube containing Tenax TA (Buchem BV, Apeldoorn, The Netherlands) and Carbopack X (Sigma-Aldrich Co., St Louis, Missouri, USA) was attached to the chamber and vapours (900 mL) were sampled at 0, 1, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9 and 10 days, followed by TD-GC–MS analysis. The TD-100 autosampler (Markes International) was used to simplify analysis of multiple sorbent tubes. The conditions used were as follows:
TD
Focusing trap: General purpose (U-T11GPC-2; Markes International)
Trap low: 25 °C
Trap high: 320 °C
Trap hold: 5 min
GC–MS
Column: VF-624 ms, 60 m, 0.32 mm, 1.8 μm
Constant pressure: 10.26 psi
Temp programme: 40 °C hold 2 min, 10 °C/min to 230 °C hold 15 min
Mass scan range: m/z 35–200
MS source temp: 230 °C
MS quad temp: 150 °C
Results and discussion
Figure 1 shows the emission profiles of the sample at days 0, 1 and 10 (others have been omitted for simplicity), and Table 1 lists some notable compounds identified.
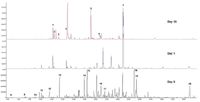
Figure 1: Overlaid chromatograms for bacon sample emissions at day 0 (black), day 1 (blue) and day 10 (red).
At day 0, it is clear from the complexity that this bacon releases many olfactory compounds (e.g., 4-hexen-3-one and hexenal) to the atmosphere. At days 1 and 10, the odour profile has changed significantly, indicating that many complex reactions have occurred.
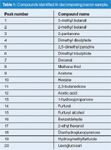
Table 1: Compounds identified in decomposing bacon sample.
This straightforward method provided comprehensive chemical information over the degradation process, therefore a detailed analysis of several nominated compounds over the 10 days was then carried out (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Individual compound concentration profiles over 10 days.
- Levoglucosan is a sugar that was found to decrease rapidly over time, possibly via enzyme consumption. The level of levoglucosan became undetectable within five days.
- Methane thiol is a breakdown product of many organic compounds and has a characteristic off-odour. The level increased over the 10 days but generally very low levels were observed.
- Acetone is a common breakdown product of organic matter and its level increased sharply at day 2, then gradually decreased until undetectable at day 8.
- 2,3-butanedione is a natural by-product of many enzymatic reactions but can be harmful if high levels are ingested. The concentration of 2,3-butanedione follows a similar trend to that observed with acetone; a rise and fall over a period of about eight days.
- 3-methyl butanal is a compound released by the reaction of 3-methyl butanol with the enzyme 3-methyl butanal reductase. A sharp rise by day 2 was seen, followed by a gradual decrease.
Conclusion
This application highlights the novel use of the Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor (μ-CTE) and TD-GC–MS analysis for food degradation studies. Such analysis permits complete characterisation of the emission profiles of a food sample over a long period of time, allowing observation of the chemical changes occurring at various stages. Of note, the use of low temperatures during analysis allowed recovery of thermally labile components such as methyl thiol in the same analysis as important sugars such as levoglucosan. Minimal sample preparation is required and the individual chambers can be held at a defined temperature over weeks if necessary to ensure consistency of data.
References
1. Markes International TDTS note 67. Introducing the Micro-Chamber/Thermal-Extractor (μ-CTE) for rapid screening of chemicals released (emitted) by products and materials.
2. Markes International TDTS note 69. The Micro-Chamber/Thermal-Extractor - The innovative, rapid and cost-effective approach for testing VOC emissions from materials.

Markes International Ltd
Gwaun Elai Medi Science Campus, Llantrisant CF72 8XL, UK
tel. +44 1443 230935 fax +44 1443 231531
E-mail: lkelly@markes.com
Website: www.markes.com

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.













