Extraction of Antioxidants from High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) By Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
The Application Notebook
Plastics and other polymers are used in a wide spectrum of applications from industrial usage to packaging, including the packaging of food and pharmaceutical products.
Plastics and other polymers are used in a wide spectrum of applications from industrial usage to packaging, including the packaging of food and pharmaceutical products. To enhance functionality, chemical additives are often added to polymers. These additives enable polymers to be more durable, pliable and make them less subject to degradation. To ensure that the specified amounts of an additive or combination of additives are incorporated into a polymer. After the extrusion process, a rapid and accurate analytical method is required to measure additives and other process by products.
This application note demonstrates the use of pressurized liquid extraction using the FMS PLE system to extract polymer additives for quatitative analysis by HPLC. Four specific additives of known concentrations were extracted from high density polyethylene (HDPE) and the recoveries measured.
Instrumentation and Consumables
FMS, Inc. Pressurized Liquid Extraction System
- Thermo Certified GC–MS auto sampler vials
- FMS 5 mL Stainless Steel PLE Cartridge
- FMS Universal Stainless Steel PLE End Caps
Reagents
- Fisher Optima* 2-Propanol
- Fisher Optima* Cyclohexane
Sample Preparation and PLE procedure
Sample Prep
1. A sample of high density polyethylene was milled to a fine particle size to increase surface area.
2. Duplicate samples of 2 g each were weighed out and transferred to FMS 5 mL extraction cells and sealed with stainless steel reusable end caps.
3. Samples were loaded on FMS PLE system.
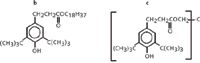
Figure 1: Molecular formulas of two hindered phenols extracted: b) Irganox® 1076 and c) Irganox® 1010.
Pressurized Liquid Extraction
Solvents Mix: 2-Propanol/Cyclohexane (95:5)
Solvent pump rate: 35 mL/min
Pre-heat temperature: 100 °C
Extraction temperature: 120 °C
Extraction time: 20 min
Cycles: 3
Total time: 1.5 h
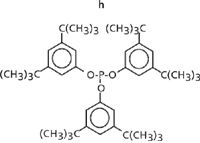
Figure 2: Molecular formula for aromatic phosphite extracted, h) Irgafos® 168.
Results
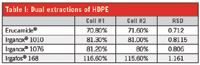
Table I: Dual extractions of HDPE
Conclusions
Analysis of the four antioxidant additives in the HDPE samples demonstrates the FMS PLE system's ability to generate excellent recoveries for all four compounds (70–130%). The low relative RPDs also demonstrate the ability to generate consistent, reproducible extraction efficiencies between runs.
The advantages of pressurized liquid extraction over traditional Soxhlet extractions are faster analyses (1.5 h versus 15 h) and reduced solvent volume (up to 200 mL). This pressurized liquid extraction technique using the FMS PLE extraction system is an ideal method for extracting antioxidant additives from HDPE.
FMS, Inc.
580 Pleasant Street, Watertown, MA 02472
tel. (617) 393-2396, fax: (617) 393-0194
Website: http://fmsenvironmental.com, Email: onlineinfo@fms-inc.com
















