Extraction of Acrylamide from Fried Potato Chips (Crisps) Using ISOLUTE® SLE+ Prior to LC–MS–MS Analysis
The Application Notebook
Biotage GB Ltd
Acrylamide has been found to occur in many cooked carbohydrate-rich foods and is of concern as a possible carcinogen. The supported liquid extraction (SLE) method described in this application note achieves high recoveries of acrylamide in fried potato chips (crisps). The method is sensitive enough to potentially measure levels as low as 10 ppb in a popular brand and flavour and has also been tested in flavoured varieties that were both machine and hand fried.
Extraction Procedure
Format: ISOLUTE® SLE+ 1 mL Sample Volume Columns, part number 820-0140-C
Sample pre-treatment: Add 10 mL water to 1 g crushed sample (previously spiked with 13C3 acrylamide internal standard), and mix for 1 h. Centrifuge and remove a 0.65 mL aliquot of the aqueous layer, taking care not to include any of the thin upper oil layer.
Sample loading: Load the pre-treated sample (0.65 mL) onto the ISOLUTE SLE+ column. Apply a pulse of vacuum or positive pressure to initiate flow. Allow the sample to absorb for 5 min.
Analyte elution: Elute with ethyl acetate–tetrahydrofuran, (1:1, v/v, 2 × 2.5 mL) and allow to flow under gravity into tubes containing 2 µL ethylene glycol. Apply vacuum or positive pressure to elute any remaining extraction solvent.
Post elution: Dry the volatile constituents of the eluate in a stream of air or nitrogen. Reconstitute in water (200 µL).
HPLC Conditions
Instrument: Waters Acquity
Column: Phenomenex Hydro 4 µm 50 mm × 2 mm C18 column with a C18 guard cartridge and on-line filter
Mobile phase A: 0.1% formic acid in water
Mobile phase B: 0.1% formic acid in methanol
Flow rate: 0.3 mL min-1
Injection volume: 10 µL
Gradient: Initial 100% A, hold for 0.6 min; Linear ramp to 100% B over 0.25 min (0.85 min), hold 1.65 min (2.5 min); Linear ramp to 100% A in 0.01 min (2.51 min), hold 2.49 min (5 min)
Column temperature: 40 °C
Sample temperature: 20 °C
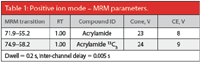
Table 1: Positive ion mode â MRM parameters.
MS Conditions
Ions were selected on the basis of achieving maximum sensitivity using multiple reaction monitoring.
Instrument: Waters Quattro Premier
Ionization mode: ES+
Desolvation temperature: 450 °C
Source temperature: 120 °C

Figure 1: Chromatogram of untreated potato chip (crisp) extract showing level of incurred acrylamide.
Results and Conclusion
A method has been developed which measures acrylamide from a challenging matrix at highly sensitive levels. Despite acrylamide being a relatively polar molecule, excellent separation was demonstrated between this and matrix interferences on the ISOLUTE SLE+ material. The method delivers good recovery (90%), low %RSD (<10%), and is significantly easier, quicker, and more cost-effective to perform than SPE-based procedures, making it ideal for routine analysis of fried and baked foods.

Biotage AB
Vimpelgatan 5, Uppsala, Sweden
Tel: +46 18 56 59 00 fax: +46 18 59 19 22
E-mail: info@biotage.com
Website: www.biotage.com

New Study Reviews Chromatography Methods for Flavonoid Analysis
April 21st 2025Flavonoids are widely used metabolites that carry out various functions in different industries, such as food and cosmetics. Detecting, separating, and quantifying them in fruit species can be a complicated process.
Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.








