Direct Determination of Mannose-6-Phosphate Content of Glycoproteins
D-Mannose-6-phosphate (M-6-P) is a terminal monosaccharide of some asparagine-linked (N-linked) oligosaccharides and is also part of an important intermediate in N-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Some lysosomal glycoproteins require M-6-P terminated oligosaccharides for proper targeting and function. Lack of M-6-P or genetic defects in its synthesis or subsequent processing can result in a variety of diseases.
Terri T. Christison, Brian M. De Borba, and Jeffrey S. Rohrer, Dionex Corporation
D-Mannose-6-phosphate (M-6-P) is a terminal monosaccharide of some asparagine-linked (N-linked) oligosaccharides and is also part of an important intermediate in N-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis. Some lysosomal glycoproteins require M-6-P terminated oligosaccharides for proper targeting and function. Lack of M-6-P or genetic defects in its synthesis or subsequent processing can result in a variety of diseases.
High performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAE-PAD) is a well-established technique for determining a large variety of carbohydrates, including M-6-P (1). The HPAE-PAD method described here accurately determines M-6-P added to an acid-hydrolyzed protein.
Experimental
A Dionex® ICS-3000 Ion Chromatography system with a CarboPac® PA200 (3 × 250 mm) analytical column was used. M-6-P was separated from the components of acid hydrolyzed bovine serum albumin (BSA) with 100 mM sodium hydroxide and 100 mM sodium acetate at 30 °C, a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min, and detected by PAD as described in reference (2).
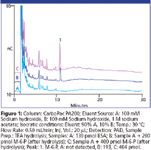
Figure 1
Results
HPAE-PAD is a selective, sensitive, and accurate method for determining the M-6-P content of a glycoprotein without derivatization (1). Here, we demonstrate an updated HPAE-PAD method for M-6-P determinations using a newer column and improved electrochemical conditions. Because a M-6-P-containing glycoprotein was not commercially available, we hydrolyzed BSA in 6.75 M trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) for 1.5 h at 100 °C (1), and added M-6-P after hydrolysis. Figure 1 shows that M-6-P is well resolved from the components of the hydrolyzed BSA and accurately determined (101 and 104% recoveries). To confirm the M-6-P peak, we treated the two samples with alkaline phosphatase, re-assayed the samples, and assayed the samples for mannose with another HPAE-PAD method (2). The M-6-P peak in each sample disappeared (not shown) and mannose was recovered (96.5 and 96.8%) (Figure 2). Therefore, HPAE-PAD can accurately determine M-6-P in an acid hydrolyzed glycoprotein sample and confirm M-6-P presence by both substrate disappearance and product appearance.
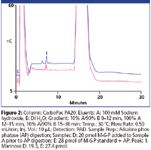
Figure 2
References
(1) Zhou, Q., Kyazike, J., Edmunds, T., Higgins, E. Anal. Biochem., 2002, 306, 163–170.
(2) Dionex Corporation. Application Note 202, LPN 2076. Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2008.

Dionex Corporation
1228 Titan Way, P.O. Box 3603, Sunnyvale, CA 94088-3603
tel. (408)737-0700, fax (408)730-9403
Website: www.dionex.com

Automated Sample Preparation (ISO 20122) for MOSH/MOAH in Seasoning Oils
May 6th 2025This work presents an Automated Sample Preparation procedure for MOSH/MOAH analysis of Seasoning Oils. We compare results from a manual epoxidation procedure compliant with DIN 16995 with results based on fully automated sample preparation (epoxidation and saponification) compliant with ISO 20122. In both cases, online clean-up via activated aluminum oxide (AlOx) are used to remove interfering n-alkanes from the MOSH fraction during the HPLC run. Automated data evaluation using a dedicated software (GERSTEL ChroMOH) is presented.
Free Poster: NDSRI Risk Assessment and Trace-Level Analysis of N-Nitrosamines
April 25th 2025With increasing concern over genotoxic nitrosamine contaminants, regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have introduced strict guidelines following several high-profile drug recalls. This poster showcases a case study where LGC and Waters developed a UPLC/MS/MS method for quantifying trace levels of N-nitroso-sertraline in sertraline using Waters mass spectrometry and LGC reference standards.
New TRC Facility Accelerates Innovation and Delivery
April 25th 2025We’ve expanded our capabilities with a state-of-the-art, 200,000 sq ft TRC facility in Toronto, completed in 2024 and staffed by over 100 PhD- and MSc-level scientists. This investment enables the development of more innovative compounds, a broader catalogue and custom offering, and streamlined operations for faster delivery. • Our extensive range of over 100,000 high-quality research chemicals—including APIs, metabolites, and impurities in both native and stable isotope-labelled forms—provides essential tools for uncovering molecular disease mechanisms and exploring new opportunities for therapeutic intervention.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)














