Determination of Phthalates leached from Toys into Artificial Saliva
Application Note
Phthalates are plasticizers that are added to plastics to make them softer and more flexible. Plastics that contain phthalates are commonly used in the manufacturing of toys. Since phthalates are not permanently bonded to plastics, they can be released from toys through touching, licking, and chewing. For the sake of child safety, it is important to qualitatively and quantitatively ascertain the leachability of phthalates from plastic toys into saliva. This application note artificially reproduces children licking and chewing toys, followed by a simple extraction to determine phthalate levels leached from toys into artificial saliva.

Preparation of Artificial Saliva (AS)
AS was prepared by mixing 0.18 g xanthan gum, 1.2 g potassium chloride, 0.85 g sodium chloride, 0.05 g magnesium chloride, 0.13 g calcium chloride, and 0.13 g di-potassium hydrogen orthophosphate with 1 L of reagent water (1), and stirred for 4 h.
Procedure
a) Cut plastic toys into small pieces.
b) Weigh 1 to 2 g of toy samples to a 50 mL centrifuge tube (ECPAHFR50CT).
c) Add 10 mL of AS and two stir bars to the 50 mL tube.
d) Shake for 1 h using a horizontal shaker to mimic children licking and chewing toys.
e) Transfer the AS to a new 50 mL tube, add 10 mL of ethyl acetate and shake for 1 min.
f) Add salts in the Mylar pouch (ECQUUS2-MP) and shake vigorously for 1 min.
g) Centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 5 min.
h) Transfer 1 mL of the supernatant into a 2 mL auto-sampler vial.
i) Add 10 µL of 50 ppm triphenyl phosphate (TPP) as internal standard.
j) The sample is ready for GC–MS analysis.
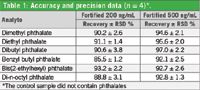
Table 1: Accuracy and precision data (n = 4)*.
GC–MS parameters are available upon request.
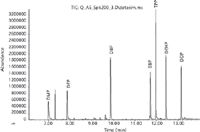
Figure 1: Chromatogram of AS fortified with 200 ng/mL phthalates.
Results
Matrix matched calibration curves were constructed by analysing matrix matched standards (0–1000 ng/mL). The responses were linear with correlation coefficient higher than 0.9973. The limit of quantification of this method was 25 ng/mL.
Application to Real Samples
This newly developed method was successfully applied to real toy samples. Diethyl phthalate was found leaching from toy samples into artificial saliva at a concentration of 285 ng/g (RSD = 5.9%, n = 3).
Conclusion
A procedure artificially reproducing the licking and chewing of toys by children is performed using artificial saliva. Phthalates leached from toys are extracted with ethyl acetate and determined by GC–MS. This procedure is simple, fast, and reliable for the determination of phthalates leached from toys into artificial saliva.
Reference
A. Preetha and R. Banerjee, "Comparison of Artificial Saliva Substitutes," Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 18(2), 178–186 (2005).

UCT, LLC
2731 Bartram Road, Bristol, Pennsylvania 19007, USA
Tel. (800) 385-3153

A Novel LC–QTOF-MS DIA Method for Pesticide Quantification and Screening in Agricultural Waters
May 8th 2025Scientists from the University of Santiago de Compostela developed a liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC–QTOF-MS) operated in data-independent acquisition (DIA) mode for pesticide quantification in agriculturally impacted waters.
Investigating 3D-Printable Stationary Phases in Liquid Chromatography
May 7th 20253D printing technology has potential in chromatography, but a major challenge is developing materials with both high porosity and robust mechanical properties. Recently, scientists compared the separation performances of eight different 3D printable stationary phases.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)









