Comprehensive Analysis of Raw Foodstuffs Using Dynamic Headspace Sampling with Thermal Desorption-GC-MS Analysis
The Application Notebook
Herbs are widely used in many food products, but substantial variations in aroma can result from differences in growing conditions or preparation of the plant material, which can affect product quality.
Caroline Widdowson, Hannah Calder, and David Barden, Markes International
Herbs are widely used in many food products, but substantial variations in aroma can result from differences in growing conditions or preparation of the plant material, which can affect product quality.
In this application note we show the wide range of aroma chemicals that can be detected in the headspace of basil leaves using a micro-chamber sampling device with analysis by thermal desorption (TD) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).
Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor
Of the numerous TD-compatible sampling instruments, the MicroâChamber/Thermal Extractor™ (µ-CTE™) from Markes International is one of the most versatile. It is a compact, standâalone unit comprising cylindrical chambers suitable for sampling chemical emissions from larger samples, or from materials that are not entirely homogeneous.
Operation is simple - materials are placed in one of the chambers, and the headspace vapours are dynamically extracted onto a 3½âinch × ¼-inch sorbent-packed TD tube by a flow of heated air or gas. This tube is then placed into the thermal desorber and analyzed as described below. Sampling times are short (typically < 60 min), and the instrument can analyze up to four or six samples at once, depending on the model chosen.
Thermal Desorption
Thermal desorption (TD) uses heat and a flow of inert gas to desorb volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds (VOCs and SVOCs) from sorbents or sample materials. Extracted vapours are swept onto an electrically-cooled focusing trap, which is then rapidly heated to inject them into a gas chromatograph (GC).
TD offers many advantages over conventional solvent-based sample preparation methods such as liquid extraction. These include wider analyte range (from acetylene to n-C44 and reactive species on one platform), quantitative re-collection of split flows for repeat analysis and simple method validation, and enhanced sensitivity.
In this study, the TD-100™ automated cryogen-free thermal desorber from Markes International was employed, which has capacity for 100 industry-standard tubes.
Analysis of Fresh Basil Leaves
Figure 1 shows the results obtained by dynamic headspace sampling of fresh basil leaves with analysis by TD-GC-MS. As well as the rapidity with which the entire vapour profile can be collected using the MicroâChamber/Thermal Extractor, the inertness and adjustable flowâpath temperature of Markes’ TD systems ensure reliable analysis of a wide range of analytes, including reactive or difficult-to-analyze species such as sulphur species and certain monoterpenoids.
Figure 1: Dynamic headspace sampling of fresh basil leaves, with analysis by TD-GC-MS. The inset highlights some of the lower-level compounds identified.
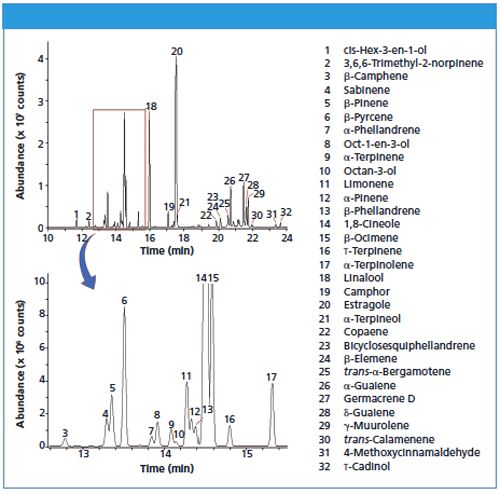
The information obtained in this case illustrates the power of TD and associated sampling techniques to provide quick yet comprehensive analyses of foodstuffs, for improved understanding of aroma profiles and product quality.
Typical Analytical Conditions
Sample: 5 g pre-packaged fresh basil leaves.
Dynamic headspace (Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor): Flow rate: 50 mL/min for 20 min. Chamber temperature: 40 °C.
TD (TD-100): Tube (Tenax TA): Desorbed at 280 °C (10 min). Trap (Tenax TA): Analytes trapped at 20 °C, desorbed at 290 °C (3 min). Split ratio: Inlet 2:1, Outlet: 16:1.
Analysis: Single-quadrupole GC-MS operated in full-scan mode (m/z 45-600).

Analytical Challenges in Measuring Migration from Food Contact Materials
November 2nd 2015Food contact materials contain low molecular weight additives and processing aids which can migrate into foods leading to trace levels of contamination. Food safety is ensured through regulations, comprising compositional controls and migration limits, which present a significant analytical challenge to the food industry to ensure compliance and demonstrate due diligence. Of the various analytical approaches, LC-MS/MS has proved to be an essential tool in monitoring migration of target compounds into foods, and more sophisticated approaches such as LC-high resolution MS (Orbitrap) are being increasingly used for untargeted analysis to monitor non-intentionally added substances. This podcast will provide an overview to this area, illustrated with various applications showing current approaches being employed.









