Advanced Analytical SEC Measurements of Anthrolysin Molecular Weight and Structure
The Application Notebook
Malvern Instruments
Anthrolysin (ALO) is a pore-forming cholesterol-dependent cytolysin (CDC) secreted by Bacillus antracis. Research suggests that ALO plays a role in the pathogenesis of Anthrax. An SEC experiment was performed using a Superdex 200 (GE Healthcare) with a buffer containing 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.3. The Viscotek TDA with UV, RI, light scattering, and viscometer detectors was used to determine the molecular weight (MW) and intrinsic viscosity (IV) of ALO in solution with the results shown in Figure 1.
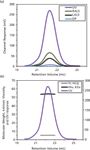
Figure 1: (a): Chromatograms of ALO from the Viscotek TDAmax. Data lines show UV (purple), RALS (green), LALS (black), and DP (blue). (b): Molecular weight (Mw) and intrinsic viscosity (IV) patterns of ALO. Data lines show molecular weight (black), UV (purple), and IV (grey).
Results and Discussion
The absolute MW was calculated to be 53.6 kDa indicating that ALO exists as a monomer when in solution. A retention volume of 22.2 mL was recorded for the peak and if a traditional column calibration method had been used this would have corresponded to a MW of only 15–20 kDa. This means that without the advanced detectors used in this work, the underestimation of protein MW frequently goes unnoticed.
In addition to measuring the absolute MW of ALO, the addition of the viscometer detector allowed the IV to be measured. The IV is inversely proportional to the molecular density of a protein so any changes in structure, shape, or hydration (that is, flexibility) will lead to changes in the volume of that protein and consequently the density and IV. For ALO (53.6 kDa) the IV was measured as 0.51 dL/g. As a comparison the monomer of a BSA (66.5 kDa) has an IV of approximately 0.4 dL/g, indicating that BSA has a more compact structure than ALO. This is paradoxical when considered with its late elution from the column but may indicate column interaction at some level.
This application note shows that the use of multi-detection TDA–SEC is essential to obtain accurate and insightful data from SEC experiments.
Work performed in conjunction with the Institut Pasteur, Paris, France.
References
(1) R.W. Bourdeau, E. Malito, A. Chenal, B.L. Bishop, M.W. Musch, M.L. Villereal, E.B. Chang, E.M. Mosser, R.F. Rest, and W.J. Tang, J. Biol. Chem. 284, 14645–14656, (2009).
(2) A. Chenal, C. Vendrely, H. Vitrac, J.C. Karst, A. Gonneaud, C.E. Blanchet, S. Pichard, E. Garcia, B. Salin, P. Catty, D. Gillet, N. Hussy, C. Marquette, C. Almunia, and V. Forge, J. Mol. Biol. 415, 584–599 (2012).
(3) J.C. Karst, A.C. Sotomayor-Pérez, D. Ladant, and A. Chenal, Methods Mol. Biol. 896, 163–77 (2012).

Malvern Instruments Ltd.
Enigma Business Park, Groveland Road, Malvern, UK
Tel: +44 (0) 1684 892456 E-mail: salesinfo@malvern.com
Website: www.malvern.com

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)

















