Speeding Up Gradients
LCGC North America
Guest author Stefan Brand and John Dolan take a look at how to speed up gradient separations while avoiding common errors.
Currently there is considerable interest in speeding up liquid chromatography (LC) separations through the use of smaller particles, changes in column dimensions, and higher flow rates. Some of these gains are made possible through the use of sub-3-μm packing particles and the availability of ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) instruments capable of pressures > 400 bar (>6000 psi). For isocratic methods, the separation time can be reduced with nearly any LC instrument simply by increasing the flow rate. However, a change in flow rate without some additional change can produce surprising changes in the chromatogram in gradient methods. This month's "LC Troubleshooting" takes a look at how to speed up gradient separations while avoiding some common errors that result in selectivity changes.
The Simplest Way?
Based upon our experience with isocratic separation, it might seem that the simplest way to speed up a gradient run is to do the same thing that we do with an isocratic one — just increase the flow rate. Take, for example, the partial chromatogram shown in Figure 1a. Here, the peaks come out in the 7-min region of a 10-min gradient run at 1 mL/min. This run has well-spaced peaks and is a good candidate for increased throughput. So we increase the flow rate from 1 mL/min for the run of Figure 1a to 3 mL/min and get the results shown in Figure 1b. This looks pretty good. Yes, we've lost some resolution between the last two peaks, but perhaps we can live with it. However, as we continue to work with the method, we realize that the peak order of the last two peaks has reversed between Figure 1a and 1b. What has happened? We're used to some change in column efficiency with flow changes in isocratic separations, but we don't expect peak spacing to change, especially not peak reversals. Is this just one more mystery of gradient elution that causes you to swear off using the technique?
What's Really Happening
The results of Figure 1b are not at all surprising if you consider the behavior of solutes in gradient separations. In isocratic runs, we calculate the selectivity, or relative peak spacing α as

where k1 and k2 are the retention factors for the two peaks of interest, calculated as

Here, tR is the retention time and t0 is the column dead time (retention time of the solvent front). Note that if we change the flow rate, both tR and t0 change in proportion to the flow change, so k remains constant with flow rate changes. If k is constant, then α will be constant . . . for an isocratic separation — gradient separations don't follow the same rules.
For gradients, the equivalent of the isocratic retention factor k is the gradient retention factor k*:
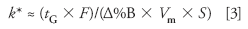
where tG is the gradient time, F is the flow rate, Δ%B is the gradient range, Vm is the column volume, and S is a constant (a value of 5 is a good value for making estimates with compounds <1000 Da). From equation 3, it is easy to see that a change in the flow rate will result in a proportional change in k*. When k* is changed (or k in isocratic separation), it is common to see changes in relative peak spacing α. So we should not be surprised to see that there is a change in selectivity when a change only in flow rate is made under gradient conditions. This is a problem that can be overcome easily by making some compensating change in the gradient conditions to keep k* constant. For example, when the flow is increased, we could decrease the gradient time. Or when the gradient range Δ%B is reduced, we could reduce the gradient time. Or if the column length and diameter are changed, we can make another change to compensate. The key is to make compensating adjustments so that k* remains constant.
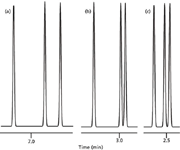
Figure 1: Simulated chromatograms of what can go wrong when changing the flow rate of a gradient separation. (a) 10-min gradient at 1 mL/min, (b) 10-min gradient at 3 mL/min, (c) 3.33-min gradient at 3 mL/min.
If gradient conditions are changed such that k* is kept constant, the same separation (in terms of relative peak spacing) should be observed. The most common gradient change is to change the flow rate or gradient time, and these changes are easily adjusted for by changing the other factor. Another way to think of this is that the gradient volume (tG × F) must be constant. The effect of this is illustrated in Figure 1c, where the flow rate was changed from 1.0 (Figure 1a) to 3.0 mL/min, and the gradient time was simultaneously reduced by 1.0/3.0 to 3.33 min. The two gradient volumes are the same: (1.0 mL/min × 10 min) = (3.0 mL/min × 3.33 min) = 10 mL. Now the same sample peak order and relative retention are observed in both runs.
A UHPLC Example
The example of Figure 1 is based upon simulated chromatograms obtained from DryLab software (Molnar Institute, Berlin). Does this predicted behavior really happen with real samples? The examples of Figure 2 show that it indeed does. In each chromatogram progressing from Figure 2a to 2f, the flow rate was increased by 1.4-fold, with an appropriate adjustment of the gradient conditions. A quick glance at Figure 2 shows that the retention time of the last peak drops from ≈6 min in Figure 2a to ≈2 min in Figure 2f as the flow rate is changed threefold from 0.35 mL/min to 1.05 mL/min. Let's take a look at the process in a little more detail.
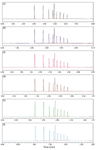
Figure 2: Chromatograms for flow-adjusted gradient runs summarized in Table II. Data courtesy of Dionex.
The original gradient was run on a 100 mm × 2.1 mm Acclaim C18 column packed with 120-Å pore, 2.2-μm particles (Dionex Corp., Sunnyvale, California). The A-solvent was water and the B-solvent was acetonitrile, with an initial flow rate of 0.35 mL/min. The gradient conditions are summarized in Table I. There is an initial 0.2-min hold, followed by a 4.2-min gradient of 10–95% B, a 2.0-min hold, and return to initial the conditions for re-equilibration. Whenever the flow rate is changed to speed a gradient, all the "working" gradient steps need to be scaled accordingly, so that the gradient volume is kept constant. By "working," we mean the portion of the gradient responsible for sample elution (the first two segments in the present example) The reequilibration steps do not need to be scaled, but it is convenient to do so, and when increasing the flow rate, as in this case, this further reduces the run time.
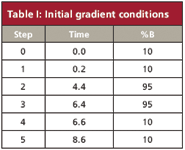
Table I: Initial gradient conditions
To obtain the different gradients of Figure 2, the gradient conditions were adjusted as shown in Table II. For example, when the flow was changed from 0.35 to 0.49 mL/min, a 1.4-fold change, the isocratic segment at the beginning of the run was reduced 0.200/1.4 = 0.143 min. Each of the steps was adjusted in this way. As a check on this, compare the gradient segment of the run shown in Figure 2f with that of Figure 2a. The gradient volume for Figure 2f is (1.467 – 0.067 min) × 1.05 mL/min = 1.47 mL, which is equal to the volume for Figure 2a of (4.400 – 0.200 min) × 0.35 mL/min = 1.47 mL. So it looks like the scaling worked correctly. Do the results confirm that we've scaled properly?
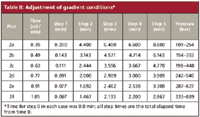
Table II: Adjustment of gradient conditions*
Table III shows the retention times of each peak in each run, normalized to the retention of the first peak. If the selectivity was exactly the same between runs, the relative retention should be the same. At the bottom of Table III is a calculation of the percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) for the runs shown in Figure 2. You can see that the %RSD is less than 1% in all cases, an excellent match. A close examination of the data, however, shows that the variation does not seem to be completely random. In fact, the highest-flow runs, Figures 2e and 2f, are the only runs that would be considered at all different from the others. We already checked the scaling, and the calculations look OK. What else could be happening to influence the retention times of these runs? One possible factor could be the column temperature. As the flow rate is increased, especially with the smaller-particle columns, frictional heating of the mobile phase takes place. An increase in the column temperature would be expected to lower retention times, and this is consistent with the results, although no effort was made to confirm a temperature change experimentally. Even with this taken into account, the relative retention agreement between runs is impressive.
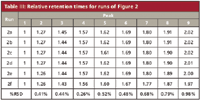
Table III: Relative retention times for runs of Figure 2
A final observation based upon the runs of Figure 2 and the related data of Table II is the system pressure. Because the viscosity of water is greater than that of acetonitrile, the pressure under the starting conditions (10% acetonitrile) will be higher than at the final conditions (95% acetonitrile) — this is reflected in the observed pressure range listed in the right-hand column of Table II for each flow rate. The pressure should increase in direct proportion to the flow rate, and this is observed for the acetonitrile-rich mobile phase (333/109 bar = 1.05/0.35 mL/min = threefold). A similar, but slightly smaller increase is observed for the water-rich mobile phase (689/254 bar = 2.7-fold); the reason for this was not investigated.
The maximum flow rate of 1.05 mL/min with the 2.1-mm i.d. column gives the same linear velocity as ≈5 mL/min with a 4.6-mm i.d. column, which means that the two flow rates are equivalent. The combination of high relative flow rate and sub-3-μm particles generates pressures beyond the capacity of traditional LC equipment, with pressure limits of 400 bar (6000 psi). Only for the runs with flow rates of <0.5 mL/min (equivalent to ≈2.5 mL/min with 4.6-mm i.d. columns) could conventional LC equipment have been used. Therefore, these experiments were run on a UHPLC capable of pressures in excess of 400 bar. With this added pressure capability, it was simple to increase the flow rate while keeping the gradient volume constant so that the method run time could be reduced from 8.6 to 2.9 min while maintaining the same selectivity. A benefit of the 2.2-μm particles used for this separation is that their performance does not change much with flow rate, so the same resolution was obtained at the higher flow rate as was seen under the initial conditions.
Conclusions
Scaling of gradient runs for changes in flow rate, column size, and other gradient conditions can be performed successfully if the conditions are adjusted so that the gradient retention factor k* is kept constant. The relationship shown in equation 3 is a useful tool to guide the adjustment of gradient conditions. In the example separation of Figure 2, the gradient volume of each gradient segment was kept constant by making the adjustments summarized in Table II. When proper adjustments were made, an equivalent separation was possible over a threefold change in flow rate.

Stefan BrandStefan Brand is a Technical Sales Representative with Dionex in Olten, Switzerland.

John W. Dolan John W. Dolan "LC Troubleshooting" Editor John Dolan has been writing "LC Troubleshooting" for LCGC for over 25 years. One of the industry's most respected professionals, John is currently the Vice President of and a principal instructor for LC Resources, Walnut Creek, California. He is also a member of LCGC's editorial advisory board. Direct correspondence about this column to "LC Troubleshooting," LCGC, Woodbridge Corporate Plaza, 485 Route 1 South, Building F, First Floor, Iselin, NJ 08830, e-mail John.Dolan@LCResources.com
For an ongoing discussion of LC troubleshooting with John Dolan and other chromatographers, visit the Chromatography Forum discussion group at http://www.chromforum.org.

New Method Explored for the Detection of CECs in Crops Irrigated with Contaminated Water
April 30th 2025This new study presents a validated QuEChERS–LC-MS/MS method for detecting eight persistent, mobile, and toxic substances in escarole, tomatoes, and tomato leaves irrigated with contaminated water.
University of Tasmania Researchers Explore Haloacetic Acid Determiniation in Water with capLC–MS
April 29th 2025Haloacetic acid detection has become important when analyzing drinking and swimming pool water. University of Tasmania researchers have begun applying capillary liquid chromatography as a means of detecting these substances.
Prioritizing Non-Target Screening in LC–HRMS Environmental Sample Analysis
April 28th 2025When analyzing samples using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry, there are various ways the processes can be improved. Researchers created new methods for prioritizing these strategies.

.png&w=3840&q=75)

.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)



.png&w=3840&q=75)













